Macroeconomic Theory (AS.440.602) Final Exam Example
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Question 1
The following questions should be answered based on the relevant materials that we studied in the first part of the semester. In all questions, assume that net taxes (T) are not a function of output (Y).
a. Based on the AD-AS model, what happens to the price level if government spending declines and oil prices increase at the same time? Your answer should be backed by accurate graphs.
b. Show how does an increase in unemployment benefits affect the natural rate of unemployment. Your answer should be backed by accurate graphs.
c. Show that I=S in equilibrium (with S being total/national saving).
d. Explain why the Phillips Curve has changed since the early 1970s.
e. If the government increases both spending (G) and net taxes (T) by x, by how much will output (Y) increase? Show your work.
Question 2
The representative agent lives for infinite periods (0, 1, 2, …) and receives exogenous incomes of
y0 , y1 , y2 ,..., respectively. The lifetime present discounted value of utility is given by:
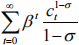
with β(< 1) being the discount factor. The agent is allowed to save or borrow at the real interest rate r , but she cannot die with debtor wealth. Assume also that the initial wealth is zero.
The period budget constraint is given by:
ct + st = yt + (1+ r)st−1
a. Solve the optimization problem of the agent using the period by period budget constraints and find the Euler equation.
b. Find the growth rate of consumption between time t and time t+1 using the parameters of the problem. How does β affect the growth rate of consumption?
c. Can the agent be engaged in consumption smoothing if β(1+ r) ≠ 1? If yes, what is the condition for that to happen?
d. Assuming consumption smoothing, show the present discounted value of optimal lifetime utility?
e. Assume now that the agent would like to smooth saving by letting s be constant over her lifetime. Does that imply consumption smoothing? If yes, explain why. If not, what condition is needed for consumption smoothing to materialize?
Question 3
In each period t, the representative household purchases consumption ct , supplies labor lt and holds physical capital kt . The problem of the household is then to maximize:
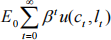 (1)
(1)
subject to:
ct + kt+1 = (1−τt )wt lt + (1−δ + rt)kt (2)
where E0 is the expectation operator, β <1is the subjective discount factor and u(ct , lt ) is the period utility function from consumption and labor. Furthermore, wt is the real wage, rt is the price of capital,δ denotes the depreciation rate of capital andτt is the labor-income tax rate.
The representative firm hires labor and rents capital from households to produce goods using the following production function
yt = ztf (kt , lt ) , (3)
with yt and zt being output and total factor productivity (which the firm takes as given), respectively. The problem of the firm is to maximize:
 (4)
(4)
Please answer the following parts:
a) Derive the consumption Euler equation, labor supply condition and capital supply condition from the households’ problem.
b) Derive the labor demand and capital demand conditions from the firm’s problem.
c) Combine the first-order conditions of the firm and household, and write the resulting condition in terms of the model’s primitives.
d) Solve the problem of the social planner and compare the results to part c. What is necessary for the solution of the social planner to be achieved by the market?
e) Assume yt = ztkt(c)lt1−c , with c being the capital share of output. Show the corresponding labor demand and capital demand conditions.
f) Based on your answer to part e, show what wtlt/yt is equal to. Explain the intuition behind this result.
Question 4
The representative agent lives for infinite periods (0,1,2,..). Each period, the agent consumes ( ct ) and supplies labor ( lt ). The pre-tax real wage per unit of laboris wt and the agent pays a tax rate ofτt . The lifetime present discounted value of utility is given by:

with β(< 1) being the discount factor. The time t budget constraint of the agent is given by:
ct + st = (1−τt )wt lt + (1+ r)st−1
The agent is allowed to save or borrow at the real interest rate, but she cannot die with debt or wealth. Assume also that the initial wealth is zero.
a. Solve the optimization problem of the agent and show the consumption Euler equation.
b. Assumingu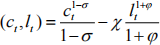 , show the consumption Euler equation.
, show the consumption Euler equation.
c. Assumingu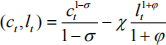 , show the labor supply condition for time t. Find the
, show the labor supply condition for time t. Find the
elasticity of labor supply with respect to the tax rate. Is it constant or varies with the tax rate itself?
d. Assumingu(ct , lt ) = ln(ct ) − Xln(lt ). What does this functional form imply about the disutility from work? Explain your answer.
2023-12-25