PHAS0011 ICA -MOCK
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
PHAS0011 ICA -MOCK
This open-book ICA includes 3 questions, totalling 60 marks:
Modern Physics (24 marks)
Astrophysics (24 marks)
Medical Physics (12 marks)
The exam duration is 1 hour
The numbers in square brackets in the right-hand margin indicate a provisional allocation of maximum possible marks for different parts of each question
Please attempt all questions
The following maybe assumed if required
Electron mass = 9.11 10-31 kg
Proton mass = 1.0078 amu
Helium mass = 4.0025 amu
1 amu = 931.5 MeV = 1.66 10-27 kg
1 eV = 1.6 10- 19 J
Mass of the Sun M。 =2.0 1030 kg
Radius of the Sun !。 = 6.96 108 m
Solar luminosity L。= 3.8 1026 W
1 parsec pc = 3.1 1016 m
1 year yr = 3.16 107 s
Planck’s constant h = 6.63 10-34 m2 kg s- 1
Speed of light c = 3.0 108 m s- 1
Gravitational constant G = 6.67 10- 11 m3 kg- 1 s-2
1. (a) The speed of an electron is measured to be 5 km/sec to an accuracy of 0.003 %. Find the minimum uncertainty in determining the position of the electron. [3]
The average lifetime of a muon is about 2 micro-second. Estimate the minimum uncertainty in the rest energy of the muon. [3]
(b) Consider a blackbody radiation curve and explain qualitatively why the peak wavelength of the light that it emits is retaliated to the temperature T by 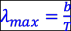 , where b = 3.0 x 10-3 m K, and explain briefly why the power radiated is proportional to T4 . [2]
, where b = 3.0 x 10-3 m K, and explain briefly why the power radiated is proportional to T4 . [2]
Find the peak wavelength of the blackbody radiation emitted by the tungsten filament of a lightbulb, which operates at 2000K. [2]
Consider four types of electromagnetic radiation: yellow light from a sodium street
lamp, radio waves from anAM radio station, radio waves from an FM radio station and microwaves from an antenna of a communications system. Rank these types of waves in terms of photon energy from highest to lowest. [2]
(c) Explain qualitatively why the energy levels of an electron of mass m confined between two impenetrable walls separated by L are:
If L = 0.2 nm what are the energy levels for n= 1 and 5? [2]
(d) The ground-state wave-function for the Hydrogen atom is given by
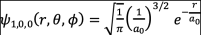 .
.
Find at what radius r the probability density has a maximum. [4]
Comment on the meaning of a0. [2]
For the above ground-state wave-function for the Hydrogen atom, write down
an expression (without solving it) for the probability that the electron will be found outside the Bohr radius. Would you expect the probability to be larger or smaller than 50%? [2]
Astrophysics
2. (a) Show how observations can be used to derive two physical properties of a star that then enable us to estimate its radius. How does knowing the radius assist in classifying a star’s location on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? [6]
(b) The lowest energy states of the hydrogen atom corresponding to principal quantum numbers n = 2, 3, 4 are, respectively, 10.2eV, 12.1eV and 12.8eV.
What is the wavelength (in nm) of a photon that would excite the electron from the ground state to n=4. If there was a subsequent decay back to n=2 and then the ground state what would be the wavelengths of the two resulting photons? How would these transitions differ as seen in the spectrum of a gas cloud? [6]
(c) Describe clearly the physical principles behind two independent observations
which indicate the presence of dark matter in the universe. Although its presence is not detected in radiation, what further measurements indicate it is non-baryonic in nature? [8]
(d) During a total solar eclipse in 1919, Einstein’s prediction of gravitational lensing was verified by Eddington who measured the deflection of starlight near the solar limb. Calculate the size of this deflection in arcseconds. [4]
Medical Physics
|
3. |
a) |
A technique known as Capsule Endoscopy involves a patient swallowing a 15-mm long capsule containing a miniature camera, which transmits images of the inside of the gastrointestinal tract to an external receiver as the capsule passes through the patient. Suppose that during a test of a new capsule it becomes necessary to verify the location of the capsule inside the body of a patient at 10-minute intervals. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using each of the following imaging techniques for this purpose: i) ultrasound ii) x-ray radiography iii) x-ray computed tomography iv) magnetic resonance imaging. [8] |
b) If a beam of x-rays passing through a 5 cm thickness of bone is attenuated by 12 decibels, calculate the percentage of incident x-rays that are transmitted across the bone and the linear attenuation coefficient of bone in units of cm- 1 . [4]
2023-12-23
Modern Physics/Astrophysics/Medical Physics