IOM417 Fundamentals of Project Management Assignment002 Coursework 2023/2024
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
IOM417
2023/2024
Assignment002 Coursework
Fundamentals of Project Management
Section A Project Management Exercises (50 marks)
Section A consists of Project Management key concepts and skills, Computational exercises are assigned to help you understand these concepts and practice the skills.
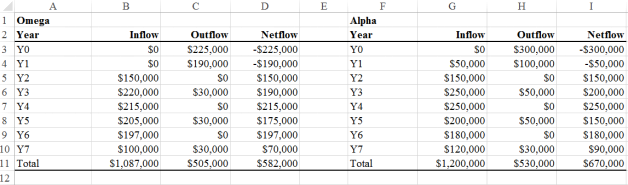
1. You work for the 3T company, which expects to earn at least 18 percent on its investments. You have to choose between two similar projects. The following chart shows the cash information for each project. Which of the two projects would you fund if the decision is based only on financial returns? (5) Why? (7)
Table 1. Project Omega and Alpha cash flow table.
2. You are creating a customer database for the Lehigh Valley Iron Pigs minor league baseball team. Draw a project network, given the following information. Complete the forward and backward pass, compute activity slack, and identify the critical path (12). How long will this project take? (2) How sensitive is the network schedule? (2) Calculate the total slack for all non-critical activities. (2)
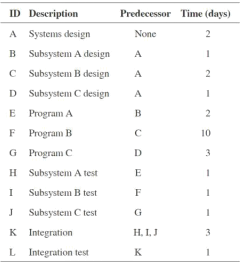
Table 2. Customer database project task list and its interdependency.
3. Given the information provided for the development of a catalog product return process for periods 1 through 5, using the ES and EF as the dates for scheduling and assigning the PV values (using the rules 1, 2, 3, illustrated in Figure 2) to each task, developing a baseline for the project. Compute the SV, CV, SPI, and CPI for each period (15). Computing all the indexes at the different ending periods, explain to the project sponsor your assessment of the project at the end of period 5, and propose the future expected status of the project at the completion (5).
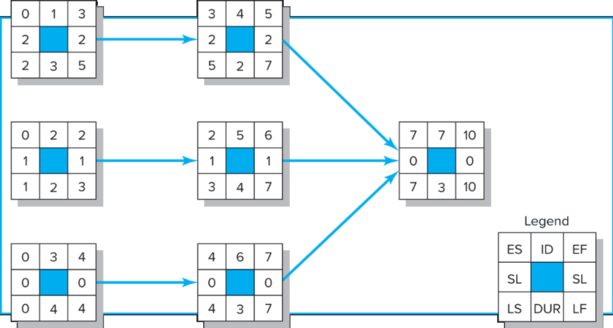
Figure 1. Network diagram of product return process development project.
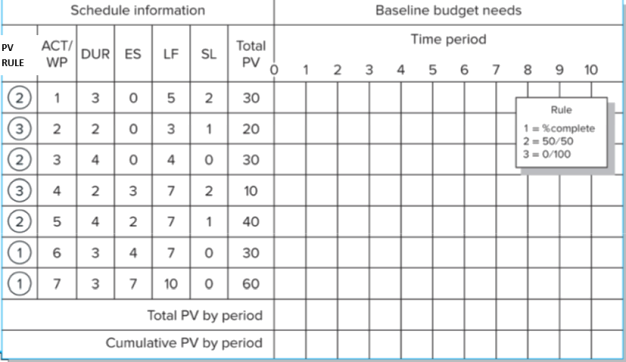
Figure 2. Cost and schedule baseline of product return process development project.
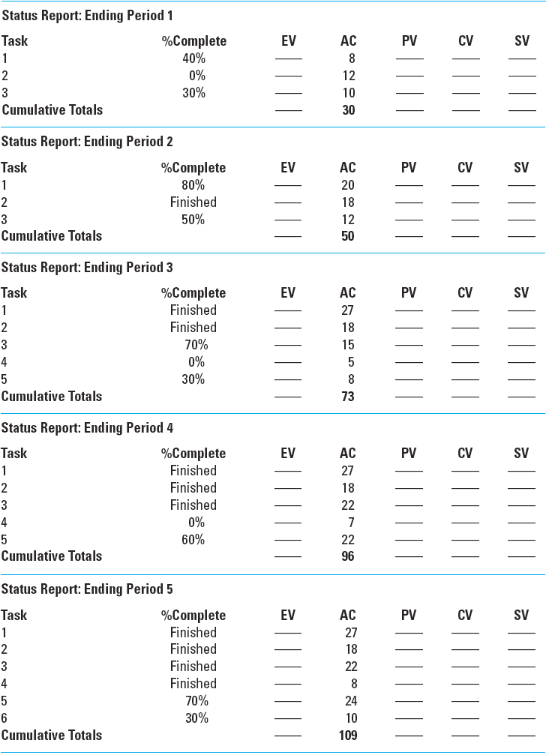
Figure 3. Index report at the various ending periods.

Figure 4. Summary of the key indexes of the status at various ending periods.
Section B: Case-based Project Management Practice (50 marks)
Section B consists of Project Management case analysis or exercises and may require you to produce appropriate charts, figures, and Project management software output. Each question has detailed instructions for you and you must answer all questions.
Read the Cerberus Corporation case and answer the question at the end.
Cerberus is a successful producer of specialty chemicals. It operates nine large campus sites in the United States, with many different business units on each site. These business units operate independently, with direct reporting to corporate headquarters. Site functions such as safety, environmental, and facilities management report to a host organization—typically the business unit that is the largest user of their services.
SUSAN STEELE
Susan Steele has worked in the Facilities group at the Cerberus Richmond site for the last two years. The Facilities Manager, Tom Stern, reports to the General Manager of the largest business unit on-site, the highly profitable Adhesives, and Sealants Division. Susan started with Cerberus when she graduated with her business degree from Awsum University. She was excited about her new assignment—leading a project for
the first time. She remembered Tom saying, “We’ve got office furniture dating back to the 80s. There are those ugly green-top desks that look like they came from military surplus! I’m especially concerned about computer workstation ergonomics—it’s a major issue that we absolutely must fix! I want you to lead a project to transition our office furniture to the new corporate standard.”
Susan assembled her project team: Jeff, the site safety/ergonomics engineer; Gretchen, the space planner; Cindy, the move coordinator; and Kari, the accounting liaison for Facilities. At their first meeting, everyone agreed that ergonomics was the most urgent concern. All five business units responded to a workstation survey that identified injury-causing ergonomics. The team was developing a plan to replace old desks with new, ergo-adjustable furniture by the end of the year. Susan asked Kari about the budget, and Kari responded, “Facilities should not pay for this. We want the individual business units to pay so that the costs will show where they are incurred.”
Gretchen spoke up: “You know; we’ve got lots of department moves going on constantly. Everybody is always jockeying for space and location as their business needs change. Besides the ergonomics, could we say that only corporate standard furniture gets moved? That would force changing some of the stuff that’s just plain ugly.” Everyone agreed that this was a great idea.
Susan presented the project plan to Tom and got the green light to proceed.
JON WOOD
Jon Wood is a planning manager, with 22 years of experience at Cerberus. His business unit, the Photographic Chemicals Division (PCD), is losing money. Digital photography is continuing to reduce the size of the market, and PCD is having trouble matching the competition’s relentless price-cutting. Jon recently transferred to Richmond from corporate headquarters, where he ran the economic forecasting group. He is considered a
new broom and he is determined to sweep clean.
One of Jon’s early actions was to negotiate with his general manager for a department move. Money was tight, and the site facilities function charged an arm and a leg for moves (covering all their fixed overhead, the operations people groused). However, Jon felt it was important to move from Building 4, where they were next to Production, to Building 6, where they could be close to Marketing, Forecasting, and Accounting. His General Manager agreed, and there was lots of excitement in his team about their upcoming move. Jon assigned one of his planners, Richard, to work with the Facilities team on the layout and move plan for the group. Things seemed to be going fine—Jon saw Richard sitting down with the move coordinator, and they seemed to be on track.
The day before the move, Jon hung up the phone from a particularly tense teleconference with a Canadian subcontractor. Production was not going well, and product availability would be tight for the rest of the quarter. Clustered around his desk were Richard, Cindy, and a person he hadn’t met yet, Susan. After hurried introductions, Susan told Jon that his filing cabinets could not be moved. The cabinets are large lateral files, five feet wide and two feet deep, a combination of both filing cabinets and bookshelves. Jon brought them with him from Corporate because he thought they looked nice with their dark grey steel sides and wood veneer tops. Susan told him that he would have to replace them with new corporate standard cabinets, virtually the same size. Jon said, “You mean you want me to throw away perfectly good filing cabinets and spend another $2,000 on new ones, just so they match? I won’t do it!” Susan replied, “Then I won’t authorize the movement of the old cabinets.” Jon said, “You’re joking—these cabinets are grey, the new ones are grey—the only difference is the wood top! You’d throw away $2,000 for nothing?”
Susan replied stiffly, “I’m sorry, that’s the policy.”
Jon said, “I don’t care what the policy is. If I have to move them myself, those cabinets are not going to the dump? My division is losing money and I’m not going to throw money away. If you don’t like it, you’re going to have to get your general manager to convince my general manager to make me do it. Now would you please leave so I can get some work done”.
1. If you were Susan, what would you do and why? (15)
2. What, if anything, could Susan have done differently to avoid this problem? (15)
3. What could the management of Cerberus do to more effectively manage situations like this? (20)
2023-12-23