Quiz 2, Physics 4002, Fall, 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Quiz 2, Physics 4002, Fall, 2023
Instructions: This is a open book and notes exam. You may use your electronic devices if you have used them to take notes for the class, but you are not allowed to browse the internet in an attempt to find a solution. Do each problem on the sheets of paper provided, with only one problem on each sheet (the problems will be separated for grading). If you have used more than one sheet of paper for a problem, staple together those sheets. Make sure your name and ID number are on every sheet, so they can be identified if they become separated.
1. (30 pts.) Consider a circular conducting loop of radius R that lies in the xy plane with its center at the origin
(a) Using Coulomb’s Law, write down the integral that gives the electric potential on the z axis.
(b) Determine the potential at a large distance from the loop as a multipole expansion, keeping at least 2 non-zero terms in the expansion. Show that it agrees with part (a) for points on the z axis with z >> L. (Hint: remember that the argument of the Legendre polynomials is the cosine of the angle between r and r,, which can be written as r.r')
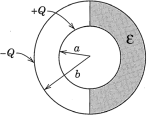
2. (30 pts.) The space between two concentric conducting spheres of radius a and b with a < b is half filled with a dielectric with permittivity ε (see figure). The inner sphere is at a potential V0 and the outer sphere
(a) Find potential and the electric field everywhere between the spheres
(b) Calculate the free surface charge density on the inner sphere, and its total charge Q
(c) Determine the capacitance of this system.
3. (40 pts.) Consider a circular current loop, oriented in the xy plane with its center at the origin. The loop has a radius R and carries a current I . (a) Write down the integral that gives the vector potential for a point on the x axis, and evaluate it in the limit that x >> R. (b) What is the magnetic moment of the current loop? Use this to evaluate the vector potential at all points in space, and show that it agrees with the result of part (a) for points on the x axis with x >> R.
Useful integrals:

Legendre Polynomials:
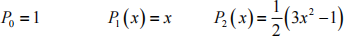
2023-12-20