Practical 5 - Uniaxial Compression Rock Failure
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Practical 5 - Uniaxial Compression Rock Failure
Part I:
1. The following data were obtained from a uniaxial loading test on a cylindrical specimen of basalt:
|
Axial stress (MPa) |
Axial strain |
Circumferential strain |
|
5.0 |
0.835 |
-0.234 |
|
10.0 |
1.67 |
-0.468 |
|
20.0 |
3.34 |
-0.935 |
|
30.0 |
5.03 |
- 1.41 |
NB: Strains must be multiplied by 10-4
The strains were entirely recoverable. From the data, obtain the elastic constants Young’s modulus (E) and the Poisson’s ratio (υ). From these constants calculate the bulk modulus (λ) and the shear modulus (G) using the equations:

Use these results to calculate the compressional (P) and shear (S) wave velocities for the rock, given the
density is 2930 kg/m3. What might cause the in situ velocities at a depth of about 100 m to be different from those measured in the laboratory or calculated from mechanical data such as these?
2. In atypical triaxial rock mechanics test, a cylindrical specimen is placed under a hydrostatic stress (σ1 =
σ2 = σ3) and then compressed axially until failure occurs. The following data are from such a test on sandstone:
|
Confining pressure (MPa) |
Failure stress (MPa) |
|
10.0 |
99.2 |
|
20.0 |
129.3 |
|
30.0 |
160.0 |
|
40.0 |
189.1 |
Plot these data on a Mohr diagram (on graph paper), obtain a best-fit Mohr-Coulomb failure envelope and determine the following parameters:
(a) the friction angle, φ
(b) the cohesive strength, C
(c) the coefficient of internal friction, μ .
(d) what differential stress would be required to fail a sample at 50 MPa confining pressure?
Part II: Experimental Uniaxial Compression Test on a sample of granite
We will perform a uniaxial compression test on a sample of granite in the lab. We will measure the axial strain / displacement during the experiment, as well as use a high-speed camera to record the fracture propagation. This will be a demonstration of the rock fracture process.
3. Below is some previously collected data from anunconfined compressive strength test on a 20 mm diameter sample of Ahiem dunite from Norway, including load measurements and two different strains. The sample has had strain gauges placed around the sample in order to measure the axial strain and the circumferential (radial strain) during deformation.
![]() (a) Plot stress versus axial, circumferential and volumetric strain. On your graph, annotate the elastic
(a) Plot stress versus axial, circumferential and volumetric strain. On your graph, annotate the elastic
portion of the graph and the yield point. You can plot this in excel / matlab as you wish.
(b) What are the competing processes that control the volumetric strain during the experiment?
(b) Calculate the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio for the dunite and explain your assumptions.
(c) Provide a short interpretation of the data (a few sentences of discussion only) – are cracks opening or closing, is there elasticity or not – support your observations and interpretations with the data.
Reading around the subject should help you with these interpretations.
|
Load (kN) |
Axial strain (x10-4) |
Circumferential strain (x10-4) |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1.375 |
0.596 |
-0.076 |
|
2.749 |
1.098 |
-0.170 |
|
4.910 |
1.887 |
-0.340 |
|
6.481 |
2.519 |
-0.489 |
|
8.543 |
3.236 |
-0.660 |
|
9.132 |
3.511 |
-0.732 |
|
10.114 |
3.959 |
-0.843 |
|
11.194 |
4.426 |
-0.970 |
|
11.979 |
4.700 |
- 1.049 |
|
13.157 |
5.274 |
- 1.219 |
|
13.844 |
5.668 |
- 1.330 |
|
14.336 |
5.989 |
- 1.432 |
|
16.005 |
6.600 |
- 1.657 |
|
16.593 |
7.017 |
- 1.809 |
|
17.281 |
7.342 |
- 1.945 |
|
18.459 |
7.930 |
-2.198 |
|
19.638 |
8.638 |
-2.543 |
|
20.325 |
9.500 |
-3.057 |
|
21.798 |
10.298 |
-3.560 |
|
22.976 |
11.432 |
-4.487 |
|
24.744 |
13.262 |
-6.434 |
Some useful equations and information:
To calculate volumetric strain:
εv = εaxial + 2εcircumferential
For P and S wave velocity:
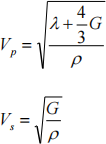
4. A granite sample was previously loaded uniaxially until failure in a similar manner to the laboratory demo, and the fracture propagation was captured with high speed camera (see below) at a frame rate of approximately 14,000 FPS.
(a) Estimate the minimum velocity of fracture propagation from these images. The sample is 25mm in diameter, and 62.5mm long. The time from the triggering of the camera is annotated on the photo.
(b) What is the angle of the fracture to σ1 ? What type of fracture is this?
2023-12-13
