Study Guide for Final Exam ECO201
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Study Guide for Final Exam ECO201
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: Italy and Greece. Each can produce steel or chemicals, but at different levels of economic efficiency. The production possibilities curves for the two countries are shown in the graphs below.
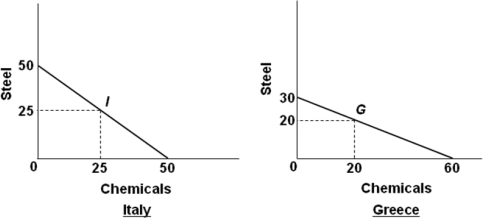
Refer to the graphs and information above. It can be deduced that:
a. Greece has a comparative advantage in chemicals
b. Greece has the absolute advantage in both products
c. Italy has a comparative advantage in chemicals
d. It is more costly in terms of resources to produce steel in Italy
2. If nations Quirk and Turk only produce aluminum or oil, the table below shows the maximum output of each nation:
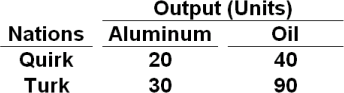
Which one of the following terms of trade is most likely to produce mutually-beneficial exchange between the two nations?
a. 0.5 unit of oil for 1 unit of aluminum
b. 0.5 unit of oil for 2 units of aluminum
c. 1 unit of oil for 0.4 unit of aluminum
d. 1 unit of oil for 4 units of aluminum
3. Sweatshirts and tee-shirts are complements in consumption and the price of a sweatshirt increases. As a result, the demand for
a. sweatshirts will increase that is, the demand curve will shift rightward.
b. tee-shirts will increase that is, the demand curve will shift rightward.
c. sweatshirts will decrease that is, the demand curve will shift leftward.
d. tee-shirts will decrease that is, the demand curve will shift leftward.
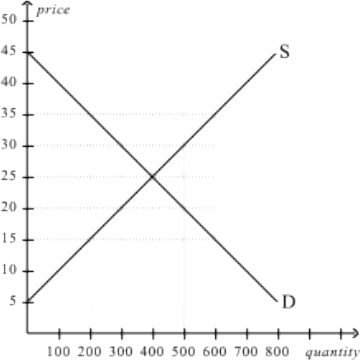
4. Refer to the graph above, at a price of $15,
a. There would be a surplus of 400 units.
b. There would be a shortage of 200 units.
c. There would be a shortage of 400 units.
d. There would be a shortage of 600 units.
5. Refer to the graph above, at a price of $35,
a. a shortage would exist and the price would tend to rise from $35 to a higher price.
b. a surplus would exist and the price would tend to rise from $35 to a higher price.
c. an excess demand would exist and the price would tend to fall from $35 to a lower price.
d. an excess supply would exist and the price would tend to fall from $35 to a lower price.
6. Suppose that, next period, demand for this good in the graph above decreased and, at the same time, supply of this good decreased. What would happen in the market for this good?
a. Equilibrium price would decrease, but the impact on equilibrium quantity would be ambiguous.
b. Equilibrium price would increase, but the impact on equilibrium quantity would be ambiguous.
c. Equilibrium quantity would decrease, but the impact on equilibrium price would be ambiguous.
d. Equilibrium quantity would increase, but the impact on equilibrium price would be ambiguous.

7. The above diagram depicts domestic demand for and supply of rice for Japan. Assume that there is $19 per unit subsidy given to domestic farmers. This subsidy induces farmers to produce more and lowers the market price to $8 per kilogram. How much is the consumer surplus, producer surplus, cost to the government and the deadweight loss under the subsidy?
a. CS = $1,350; PS = $1,822.5; Cost to the government = $2,565; DWL = $522.5.
b. CS = $870; PS = $640; Cost to the government = $1,045; DWL = $465
c. CS = $480; PS = $640; Cost to the government = $1,120; DWL = $0
d. CS = $1,350; PS = $1,822.5; Cost to the government = $3,035; DWL = $522.5
8. Now, using the same diagram above but assume there is $14 per unit tax imposed on this
market instead of subsidy; the price paid by buyers becomes $22. What is your conclusion on the relative price elasticities of supply and demand at that price?
a. Demand is more elastic than supply because consumers bear more of the tax burden.
b. Demand is less elastic than supply because consumers bear more of the tax burden.
c. Supply is more elastic than demand because producers bear more of the tax burden.
d. Supply is less elastic than demand because producers bear more of the tax burden.
9. If the quantity demanded changes by a relatively small amount for a given change in price, then demand is
a. perfectly inelastic.
b. perfectly elastic.
c. elastic.
d. inelastic.
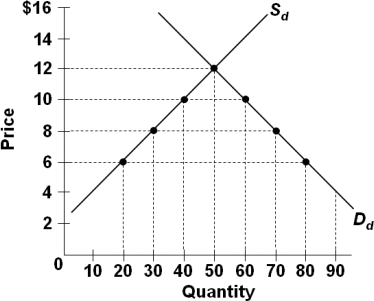
10. Refer to the graph above, where Sd and Dd are the domestic supply and demand curves for a product. The world price of the product is $6. If the economy is open to international trade but a per unit tariff of $4 is imposed, then the total revenue going to domestic producers would be:
a. $400, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $120, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80
b. $240, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $240, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80
c. $400, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $240, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80
d. 240, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $120, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $120
11. The basic difference in the economic effects of a tariff compared with a quota is that a:
a. Quota reduces domestic consumption of the product, but a tariff does not
b. Tariff allows imports to increase if demand increases, whereas a quota does not
c. Tariff raises product prices, but q quota does not
d. Quota raises product prices, but a tariff does not
12. Sheila's Sports Shop is a very popular sporting goods store, which has a yearly revenue of
$600,000. Sheila runs the business herself. Her alternative employment options are to be a college swimming coach for $50,000 per year or a construction worker for $40,000 per year. Sheila spends $230,000 purchasing goods for resale to her customers. She also has four employees, who each earn $25,000 per year. Sheila owns the building that her Sports Shop is housed in and she could have rented it out for $20,000 per year. What are Sheila's costs for own resources, and her economic profit?
a. $70,000 per year; $200,000 per year
b. $90,000 per year; $160,000 per year
c. $330,000 per year; $250,000 per year
d. $90,000 per year; $270,000 per year

13. Consider the change in the price of a book depicted in the above figure. The original budget line is BC. The new budget line is BD. As a result of this price change, the substitution effect can be represented by a movement from and income effect can be represented by a movement from .
a. point A to point E; point E to point F.
b. point A to point G; point G to point F.
c. point F to point G; point G to point A.
d. point F to point E; point E to point A.

14. The above table gives some of Tammy's total and marginal utilities from comedy videos. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Tammy's marginal utility from the third comedy video is equal to 580/3.
b. Tammy's total utility from five comedy videos is 800.
c. Tammy's marginal utility from the first comedy video is less than her marginal utility from the third comedy video.
d. None of the above answers are correct.
15. If economic profit is equal to zero, then
a. the entrepreneur's profit as measured by accountants is also equal to zero. b. the entrepreneur's profit as measured by accountants must be less than zero. c. the entrepreneur is making only a normal profit.
d. The entrepreneur's profit cannot be determined based on the information given.
This table is table is for questions 16-18

Silvio's Pizza is a small pizzeria. The firm's production function is shown in the table above.
Suppose that Silvio's costs includeonly the cost of renting ovens, which is $100 per oven per week, the labor cost, $280 per worker per week, and the opportunity cost of Silvio's entrepreneurship,
$1,000 per week.
16. Suppose Silvio's uses Plant 1 and hires 3 workers. What is the firm's average fixed cost and average variable cost?
a. AFC = $4.33; AVC = $7.00
b. AFC = $8.40; AVC = $11.00
c. AFC = $19.40; AVC = $8.40
d. AFC = $11.00; AVC = $8.40
17. Suppose Silvio's uses Plant 2. The firm's average total cost is minimized when pizzas per week are produced.
a. 180
b. 130
c. 220
d. 60
18. Suppose Silvio's uses Plant 2. What is the marginal cost of producing the 200th pizza?
a. $5.09
b. $7.00
c. $10.55
d. $4.40
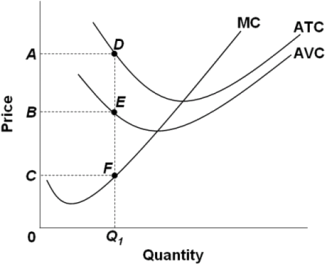
19. Refer to the diagram above, which statement is incorrect.
a. At the production of Q1, this firm can be experiencing diminishing MPL.
b. At the production of Q1, the total product curve is increasing at an increasing rate.
c. At the production greater than Q1, the marginal product of labor could be negative.
d. At the production of Q1, Marginal product of laboris not at its maximum.
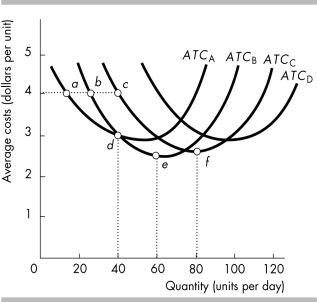
20. The average total cost curves for plants A, B,C, and D are shown in the above figure. The plant size that is the most economically efficient .
a. is plant A.
b. is plant B.
c. is plant C.
d. depends on the desired level of output.
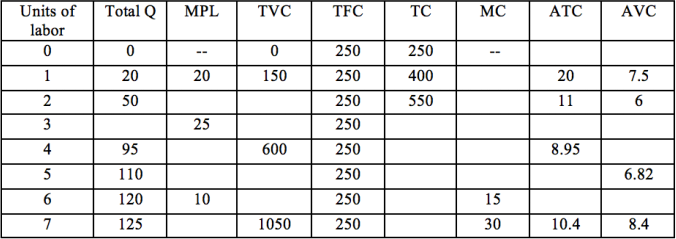
Use information in Table 1: Acme-solar Production and Costs to answer questions 21 - 24
Acme-solar produces solar-powered calculators using a technology that requires capital (which is fixed in this period) and labor. The firm hires labor in a competitive labor market at a cost of $150 per unit, and sells its calculators in a perfectly competitive market. Acme-solar’s production
function allows them using inputs efficiently and producing output options in the table above.
21. If Acme-solar hires 4 workers, its total cost will be:
a. $600
b. $850
c. $1,000
d. $1,150
22. Acme-solar’s production data suggest that:
a. The Law of Diminishing Returns is not evident.
b. The Law of Diminishing Returns is evident from the outset as production increases.
c. The Law of Diminishing Returns in initially evident as production increases, but ceases as output continues to expand
d. The Law of Diminishing Returns is not initially evident as production increases, but eventually occurs as output continues to expand.
23. If the competitive market equilibrium price for solar-powered calculator is $8,how many units of labor would you expect Acme-solar to hire this period?
a. 2 workers
b. 3 workers
c. 4 workers
d. 5 worker (or more)
24. Which of the following, ceteris paribus (keep everything else constant), would you expect to result in an increase in the number of workers hired by Acme-solar next period (as opposed to this period in question 23)?
a. A reduction is Acme’s fixed costs.
b. An increase in Acme’s fixed costs.
c. An increase in the MPL of each worker.
d. A reduction in the MPL of each worker.
2023-12-08