ACTF: polychlorinated biphenyls rate of change modelling
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ACTF: polychlorinated biphenyls rate of change modelling
Background
Historically Baltic grey seals were exposed to a chemical called polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), resulting in health effects and delayed recovery from a decade of declining population growth rates. This kind of chemical will have a large
effect on the rate of change of population. But a lot of existed models do not
consider this chemical factors when building the population model, in this paper a new model called toxicokinetic–toxicodynamic (TKTD) is constructed to help to know the population change in the grey seals better. The differential equation is
used to model the rate of change of PCB concentration. In the paper, describing the bioaccumulation, elimination, and vertical transfer of PCBs from mother to
offspring. By using the differential equation, the rate of change of PCB
concentration is obtained and this model will help to contribute a factor to the population change.
Model and Solution
There are 45 age groups (i=2,3, … ,46) and 3 time periods(j=l,d,g). The original grouped differential equations are:
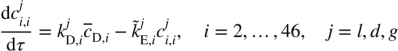
Where I index is the age group and j index is time period. cD is the mean PCB. kD and kE are two positive constant related to the sex. To simplify the differential
equation, I only focus on the first age group and the first time period and take kD and kE to be 1. Also set mean PCB to be 0.25. Here t represents time.
So the new differential equation will be:
dC/dt=0.25-C
This differential equation could not be solved by separable method. The slope
field could be plotted and the solution could be obtained from the slope field using euler method. Try to follow the slope in the slope field to get the solution C=C(t). For calculation, euler method is used in the following way: first we have the initial value (t0, C0), then for each step ti=ti- 1+delta t and Ci=Ci- 1+delta t (0.25-Ci- 1). If
the tangent line is above the curve, the euler method will get overestimate and if
the tangent line is below the curve, the euler method will get underestimate.
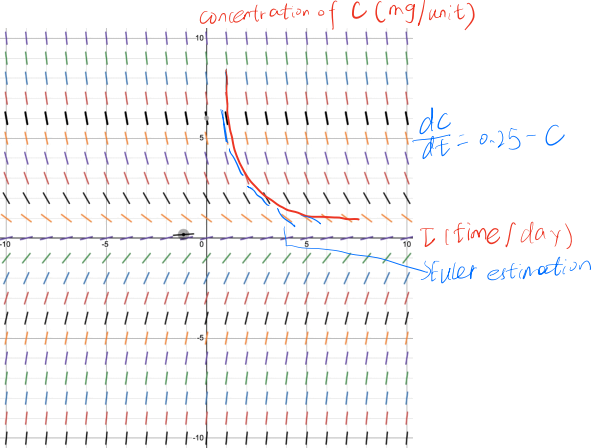
Figure 1. slope field of simplified differential equation
Conclusion and limitation
By using the system differential equation, the concentration of PCB is modelled for different time periods and different age groups. In this ACT, we focus on one time period and one age group, the differential equation is simplified and slope field is obtained using desmos. When concentration of PCB is around 0.25, the concentration of PCB will not change too much. This is the same as the paper
conclusion that concentration of PCB will keep at a constant in the long run and concentration of PCB will influence the population. However, our model is with strength as well as some limitations. Different age groups will have different
effects according to the original paper. Our Act only focus on part of them (one age group and one time period). Another limitation is that the paper use more
female seals in the experiment, so the result may have some biased. Lastly, use euler method will have some errors and this is not the accurate solution.
References
Mauritsson, K., Desforges, JP. & Harding, K.C. Maternal Transfer and Long-Term Population Effects of PCBs in Baltic Grey Seals Using a New Toxicokinetic–
Toxicodynamic Population Model. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 83, 376–394
(2022).https://doi-org.myaccess.library.utoronto.ca/10.1007/s00244-022-00962-3 (the formula is on page 5 Bioaccumulation Model part)
2023-12-07