Economics 1021A Intro Microeconomics ASSIGNMENT #2 Fall 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ASSIGNMENT #2
Intro Microeconomics
Economics 1021A
Fall 2023
QUESTION 1 (40 MARKS)
There are four multiple-choice questions below, each containing errors. Your task is to identify and list these errors, paying close attention to discrepancies or inconsistencies in the question stems and answer choices. E.g., is more than one answer correct? Are some answer choices irrelevant? Does any of the text in the question stem misalign with microeconomic principles? Each question is worth 10 marks, totalling 40 marks for the assignment.
1. In a perfectly competitive market, where firms can set prices due to differentiated products, how does a firm calculate its profit maximization point?"
Answer Choices:
A) By producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B) Through setting the price higher than the market equilibrium price.
C) By equating average total cost with average revenue.
D) In perfect competition, firms maximize profit at the point where price equals average revenue.
(5marks) List and explain errors below:
Explanation of Errors:
a) Error(s) in Question Stem:
b) Issues with Answer Choices:
2. Refer to the accompanying diagram that shows the demand curve and costs for a perfectly competitive firm. Which one of the following statements is correct regarding the firm's economic profit or loss?

a) The economic profit is $15.
b) The profit corresponds to the area formed by the price at $35, point A, point D, and the price at $30.
c) The firm will have an economic loss obtained by multiplying the difference between the price and marginal cost at the output level of 6 units.
d) Economic profit is obtained by subtracting total revenue (TR) from the total cost (TC) curve in the diagram at Q = 3.
(5marks) List and explain errors below:
Explanation of Errors:
c) Error(s) in Question Stem:
d) Issues with Answer Choices:
3. In a monopolistically competitive market, where firms have significant control over prices similar to a monopoly, how does this market structure compare to a perfect competition in terms of product differentiation and market entry?
a) In monopolistic competition, firms often engage in international trade agreements to enhance competitiveness.
b) In perfect competition, firms face significant barriers to entry, unlike in monopolistic competition.
c) Monopolistic competition is characterized by many firms selling identical products.
d) In perfect competition, firms are price takers, while in monopolistic competition, firms have some control over their pricing.
(5marks) List and explain errors below:
Explanation of Errors:
e) Error(s) in Question Stem:
f) Issues with Answer Choices:
4. In economic theory, a lighthouse is typically used as an example of a public good due to its non-rivalrous and non-excludable nature. However, in a small coastal town, the local government claims to have developed technology that limits the lighthouse's light beam to only illuminate the paths of ships that have paid a subscription fee. With this change, how does the technology ensure that the light from the lighthouse remains a perfect example of a non-excludable good?
a) The technology increases the efficiency of the lighthouse, thus reducing operational costs.
b) A subscription fee turns the lighthouse into a private good, enhancing its value for paying customers.
c) Subscription fees ensure the lighthouse's operation, categorizing it as a private good.
d) National defense, like lighthouses, is a classic example of a non-rivalrous and non-excludable public good.
(5marks) List and explain errors below:
Explanation of Errors:
g) Error(s) in Question Stem:
h) Issues with Answer Choices:
QUESTION 2 (15 MARKS)
Refer to the graph below, which details an industry composed of numerous firms, all sharing an identical cost structure. The "typical individual firm" in panel A illustrates this common cost structure. The market price is established at P1.
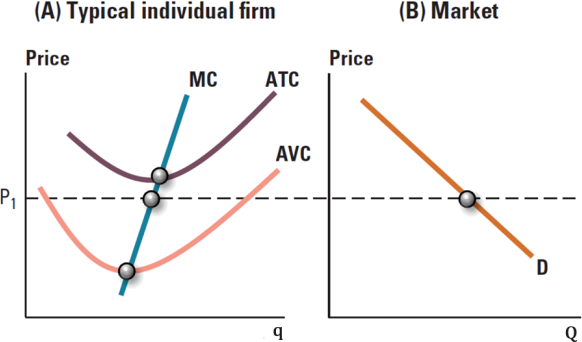
Your analysis should unravel how individual firms' production decisions aggregate to form the market supply curve. Using the provided graph as a foundation, you are to:
a) (2 marks) Identify the output quantity for the typical individual firm when the market price is P1, denoting this quantity as q1.
b) (6 marks) Based on the individual firm's cost curves, plot the short-run supply curve of the market in panel B. Make sure to indicate the correct position and slope.
c) (2marks) Indicate the equilibrium quantity for the entire market at the price P1, labeling it as Q1.
QUESTION 3 (20 MARKS)
There are two tables below related to the strawberry industry. The first table details the cost structure of a single perfectly competitive firm, representative of one hundred identical firms within the industry. The second table outlines the market demand and market supply schedules for the industry as a whole.

a) (5 marks) Plot the data above in the appropriately grids below. Label the market equilibrium price and quantity for strawberries and the demand curve for the individual firm.
b) (2 marks) Identify the profit-maximizing quantity (q*) for an individual strawberry farm, assuming it is a price taker in the market.
c) (5 marks) Calculate the profit or loss for the individual farm at the market equilibrium price and identify it on the farm's cost curves graph. Show your work
Profit or loss = ___________________
d) (3 marks) In the long run, what is the economic profit of the competitive firm? Explain your answer.
Profit or loss = _______
e) (2 marks) What will the market equilibrium price and quantity be in the long run? Show any calculations.
QUESTION 4 (10 MARKS)
An apple grower's orchard provides nectar for a neighbor's bees, and in turn, the beekeeper's bees pollinate the apple blossoms. Using the figures provided below, explain why this scenario of reciprocal positive externalities might result in an underinvestment in both the apple orchard and beekeeping. Please note that the "P" in MPC (Marginal Private Cost) and MPB (Marginal Private Benefit) represents the private costs and benefits that exclude any externalities, whether positive or negative.

QUESTION 5 (20 MARKS)
Suppose you just graduated from King’s and in your first job is an operations supervisor at Hettinger Inc., a company that makes fidget spinners. widgets. You manager has just asked you to do a cost and production report. Your assistant is usually responsible for this but did not finish it before leaving on vacation yesterday. All you have is the following incomplete table of production and costs and are not able to contact him. Fortunately, you have the following information on the cost of labour and capital that will help you complete the table and make recommendations to your manager.
• Labour cost per unit: $10
• Capital cost per unit: $50
• Also note that the fidget spinner industry can be assumed to have a market structure similar to that of perfect competition.
a) (11 marks) Fill in the missing information in the table using your knowledge of producer theory.

b) (5 marks) Suppose the market price of fidget spinners is $1. Using your answers to the part a), what level of production (Q*) would you recommend in the short run to your manager? Show your work to justify your answer below:
Q* = _____.
c) (4 marks) Suppose that you expect the market price of fidget spinners to remain around $1 for the foreseeable future. Given the cost and production data above, should you be concerned about your long-run job prospects at Hettinger Inc.? Clearly explain your answer below:
QUESTION 6 (15 MARKS)
Consider the table below for a monopolistically competitive firm offering a car wash service in a large urban city:
a) (5 marks) Complete the missing values in the table.

b) (5 marks) Plot the demand, marginal revenue, marginal costs, and average costs curves in the space below:

c) (3 marks) What is the profit maximizing number of washes (per month)? What is the profit maximizing price? Explain briefly how you got your answer.
Q* = _______.
P* = _______.
d) (2 marks) List three ways this firm can differentiate its product from other car washes:
1.
2.
3.
QUESTION 7 (10 MARKS)
The diagram shown below depicts a monopolistically competitive firm when the industry is in its long-run equilibrium:
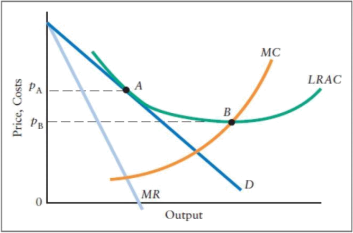
a) (4 marks) Explain why free entry and exit implies that the long-run equilibrium is at point A.
b) (3 marks) What is the significance of point B and price pB?
c) (3 marks) Explain why long-run equilibrium in monopolistic competition can be considered tobe less efficient than in perfect competition. Explain why that may not be the case.
2023-12-02