PHYS5044 Fundamentals of Sensing and Measurement
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
P431M
[ PHYS5044 ]
Fundamentals of Sensing and Measurement
1 (a) Make a selection between a typical inorganic scintillator (e.g. NaI(Tl)) and a typical organic (e.g. plastic scintillator) on the basis of the following properties
- speed of response
- light output
- linearity of light with deposited energy
- detection efficiency for high energy gamma rays
- cost
(b) For a NaI(Tl) scintillation radiation detector, describe the processes which produce a signal from the scintillator
A typical chemical sensor used for the detection and specific recognition of a vapour from a potential set of different vapours (an electronic nose) consists of a conducting polymer (e.g. polypyrrole or polyaniline) film coated between two electrodes, which accurately measures resistance changes when vapours are adsorbed into the conducting polymer.
(c) Describe the principles of operation of the conducting polymer resistance measurement. Explain how this measurement method enables detection of both redox-active gases (those that accept or donate electrons) and redox-inactive gases (those that do not).
(d) Outline the selectivity, sensitivity and dynamic range that might be re-quired for a typical electronic nose sensor application and explain why an array of conducting polymer films would be necessary to achieve the specific recognition requirements
2A (a) Describe three characteristics of laser light that are particularly useful for measurement using light. Illustrate your answer with example sensing and measurement applications.
(b) Describe how, for one or more measurement techniques, the short coher-ence length of light from LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) provides an advantage over laser light.
A laser Doppler velocimeter is used to measure the vibration characteristic of a loudspeaker cone. The system employs a HeNe laser (wavelength=633nm) with a coherence length of 30cm and an acousto-optic (Bragg) cell to increase the frequency of the laser illuminating the loudspeaker by 40MHz.
(c) Sketch a diagram of a suitable interferometer for use in this experiment including the Bragg cell. For the distinct branches of the measurement system, label the frequencies of the propagating laser light, in terms of the frequency, fo, emitted by the laser, the modulation frequency, fb, of the Bragg cell and the Doppler shift, fd, imparted by reflection from the moving loudspeaker.
(d) Explain what advantages are obtained by use of a Bragg cell. What is the frequency at the output of the photodetector when the loudspeaker is stationary?
The output of the interferometer is passed through an electronic band-pass filter that transmits frequencies in the range 39.9 to 40.1MHz yielding a signal-to-noise ratio of 200.
(e) What is the range of velocities that can be recorded by the velocimeter?
(f) It is required to increase the maximum velocity that can be recorded by the velocimeter by a factor of 100. Explain quantitatively what modification is required to the system as described above and what the signal-to-noise ratio will be if it is assumed that the noise spectrum is white (power spectral density is uniform with frequency).
2B A sensor is used in a computer server room. It is observed that the signal is very noisy unless the sensor is placed inside a grounded metal box. When the signal from the sensor is connected to an oscilloscope which is located outside the box the signal is again noisy.
(a) Explain your observations
(b) How can you connect the sensor to an oscilloscope without making the noise bad?
(c) A pair of acoustic transducers are used as a distance sensor to measure the distance to an object in water as depicted below. The transducer has a frequency of 1MHz with a bandwidth B = 400kHz. If the transducers are circular, and have a diameter of 10mm calculate the power received by the receiver transducer as a function of separation for an equivalent transmitted power of 0.1nW.
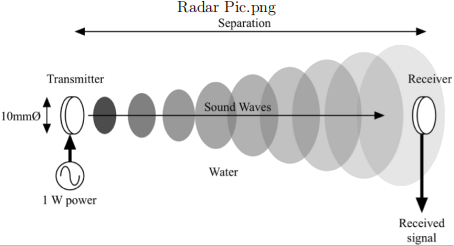
(d) If the receiver power is limited by thermal noise, how large is the maximum separation between the two transducers which can be measured?
(e) How would this distance change if the transducers were replaced by two transducers having the same diameter and a higher operating frequency of 4MHz with the same bandwidth?
2023-12-01