Homework Seven
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Homework Seven
Q1 (40 points) An economy has two kinds of consumers and goods. Type A consumers have utility function 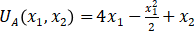 and Type B consumers have utility function
and Type B consumers have utility function 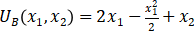 . Consumers can only consume nonnegative quantities. The price of good 2 is 1 and all consumers have incomes of 100. There are N type A consumers and N type B consumers.
. Consumers can only consume nonnegative quantities. The price of good 2 is 1 and all consumers have incomes of 100. There are N type A consumers and N type B consumers.
(a) Suppose that a monopolist can produce good 1 at a constant unit cost of c per unit and cannot engage in any kind of price discrimination. Find its optimal choice of price and quantity. For what values of c will it be true that it chooses to sell to both types of consumers?
(b) Suppose that the monopolist uses a “two-part tariff” where a consumer must pay a lump sum k in order to be able to buy anything at all. A person who has paid the lump k can buy as much as he likes at a price p<4. What is the highest amount k that a type A is willing to pay for the privilege of buying at price p? If a type A does pay the lump sum to buy at price p, how many units will he demand? Describe the function that determines demand for good 1 by type A consumers as a function of p and k. What is the demand function for good 1 by type B consumers? Now describe the function that determines total good 1 by all consumers as a function of p and k.
(c) If the economy consisted only of N type A consumers and no type B consumers, what would be the profit maximizing choices of p and k?
(d) If c<1, find the values of p and k that maximize the monopolist’s profits subject top the constraint that both types of consumers buy from it.
Q2 (40 points) Consider an industry with 3 firms, each having marginal costs equal to 0. The inverse demand curve facing this industry is: P(Q) = 60 – Q
Where Q = q1 + q2 + q3 is the total output.
(a) If each firm behaves as a Cournot competitor, what is firm 1’s best response function – optimal choice given other firms outputs?
(b) Calculate the Cournot equilibrium
(c) Firm 2 and 3 decided to merge and form a single firm with marginal costs still equal to 0. Calculate new industry equilibrium. Is firm 1 is worse of or better of as a result? Was it a good idea for firms 2 and 3 to merge? Would it be a good idea for all three firms to organize the cartel?
(d) Suppose firm 1 can commit to a certain level of output in advance. If the choice of firm 1 is q3, what would be the optimal choices of firms 2 and 3?
2023-11-27
Intermediate microeconomics