MTH6154 Financial Mathematics I Coursework 2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MTH6154 Financial Mathematics I
Coursework 2
This coursework is not to be turned in. Try it yourself and ask questions during the tutorial.
Give all answers to 3 significant figures (e.g. 2.54 not 2.53782 and 0.0342% not 0.034239%).
Exercise 1. Suppose the nominal interest rate is 4% and is continuously-compounded. Compute the (i) present value, (ii) duration, (iii) effective duration, and (iv) convexity of the following cash-flow streams:
(a) An investment that pays you £1,000 at the end of year 2 and £500 at the end of year 3.
(b) A liability that requires you to pay £1,500 at the end of years 3 and 4.
Exercise 2. Calculate the internal rate of return of an investment that, for an initial £1,000, gives payments of £500 at the end of the second year and £750 at the end of the fourth year.
Exercise 3. Write down the cash-flow stream generated by a 3-year bond, with face value £200,000, semi-annual coupons at rate 6% per annum, and redeemable at par.
Exercise 4. Suppose that the 1, 2, and 3-year LIBOR rates are 3.5%, 4% and 4.7% respectively. Suppose also that the forward rates f3,5 and f4,5 are 5% and 4.9% respectively. Calculate:
(a) The spot rates s1 , s2 and s3 and the forward rate f3,4 .
(b) The spot rate s4 . [Hint: Use your answer to part (a).]
(c) The present value of a cash-flow stream consisting of two payments of ↔100 after 3 and 4 years respectively.
Exercise 5. After graduation you have two job offers, both for a fixed term of 3 years:
❼ Company A offers you a salary of £32,000 at the end of the first year, £38,000 at the end of the second year, and £44,000 at the end of your final year.
❼ Company B offers you a signing bonus of £5,500 when you start the job, and then a constant salary of £35,000 at the end of each of the three years.
By comparing the present values of the pay packages, determine which company offers the better deal if the interest rate is 15% and is compounded (i) annually, (ii) continuously.
Exercise 6. A pension fund has liabilities of ↔20 million due in 10 years’ time and ↔40 million due in 15 years’ time, and has assets consisting of £P million worth of 25-year zero-coupon bonds (i.e. an asset that pays £P million in 25 years’ time) and £Q million in the bank. Suppose the interest rate is 7% and is continuously-compounded.
(a) By calculating present values and durations, find the values of P and Q that achieve first-order immunisation.
(b) By calculating convexities, decide whether these values of P and Q also achieves Reddington immunisation.
(c) Explain briefly why the pension fund could not achieve first-order immunisation if instead of 25-year zero-coupon bonds they own 5-year zero-coupon bonds (i.e. an asset that pays a fixed sum in 5 years’ time).
Exercise 7. Suppose that a company has assets that pay ↔2 million in 1 year’stime and ↔14 million in 2 years’ time and liabilities of ↔9 million due in 3 years’ time and 4 years’ time. Assume the nominal interest rate is 7.54%.
(a) Verify that the present value of the assets and liabilities of the company are equal (to 3 significant figures).
(b) Determine the profit or loss, expressed as a present value, that the fund would make on its total assets and liabilities if the interest rate increased to 8%.
(c) Explain how you might have anticipated whether your answer in part (b) would be positive or negative without doing any calculations.
Exercise 8. Consider a cash-flow stream consisting of a series of n annual payments of £C made at the beginning of each year, starting immediately. Assume a continuously-compounded interest rate of r.
(a) Write down a closed-form expression for the present value of the cash-flow stream. [Hint: Use a formula for geometric series.]
(b) By differentiating your expression in part (a), calculate the effective duration of the cash-flow stream.
Exercise 9. An investor has one liability of £20, 000 to be paid in 3.5 years and another of £18, 000 to be paid in 6 years. The interest rate is 10% compounded annually. Show that we cannot Reddington immunise these liabilities with 4 year zero coupon bonds and 7 year zero coupon bonds by trying to construct find a portfolio of these bonds that does Reddington immunise them.
Exercise 10. Suppose that interest is paid at nominal rate r and compounded n times a year. Consider a cash-flow stream consisting of payments C1 ,..., Cm at the end of years t1 ,...,tm .
(a) Prove that the effective duration ν and the duration τ of a cash-flow stream with yearly payments are related via
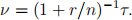
(b) Prove that the convexity is equal to
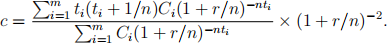
2023-11-02