Econ 513, Fall 2019, midterm
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Econ 513, Fall 2019, midterm
Be concise. You can cite results from the lecture notes with proper attribution, e.g. ’In lecture 5, p. 2 it is shown that the OLS estimator  is an unbiased esti-mator of
is an unbiased esti-mator of  if Assumption 1 of the CLR model on p. 2 of lecture 4
if Assumption 1 of the CLR model on p. 2 of lecture 4  holds.’ All subquestions are 10 points.
holds.’ All subquestions are 10 points.
Problem 1 Answer the questions by yes or no. Give a concise argument to support your answer. An argument is necessary to receive credit.
a. A university hires a consultant to study time to graduation of its students. The consultant proposes to use a linear regression model to predict the time to graduation. The university collects a lot of data about its stu-dents and these variables are used in the regression model. However there are variables like motivation that are unobservable. A colleague tells the consultant not to worry because unobserved variables do not appear in the regression model and what we cannot observe does not have an effect on the regression analysis. Correct?
b. Because the goal is prediction of time to graduation we do not have to worry about correlation between the independent variables and the ran-dom error. Correct?
c. Two variables that help to predict time to graduation are hours of manda-tory supervised study and number of visits to the library. Both have a negative effect on time to graduation. The university considers to im-plement one of two policies directed at students whose predicted time to graduation is long. Policy 1 increases hours of supervised study and policy 2 is a program of organized visits to the library. Is correlation between the random error and hours of supervised study, visits to the library (data are before the implementation of the policies) now a concern?
d. The university decides to do an experiment where for a group of students hours of supervised study are determined randomly (as by a lottery) and for another group of students the number of organized visits to the li-brary is determined randomly. The time to graduation is recorded and simple regressions with only hours of supervised learning for one group and number of visits to the library for the other as independent variable are estimated. Are the estimates the causal effects of supervised study and library visits, respectively? Hint: compare to regression in the lottery data in the lecture notes if all winners had responded to the survey.
e. The consultant finds that the experimental estimate of the regression co-efficient is close to 0 for number of visits to the library, but close to the regression coefficient of the predictive regression for hours of supervised study. Is the error term correlated with number of visits to the library in the predictive regression?
f. Same question for hours of supervised study.
Problem 2 In a multiple linear regression model with an intercept and 18 inde-pendent variables and 500 observations, we estimate a regression coefficient on the 12-th independent variable by 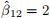 with standard error equal to 1.
with standard error equal to 1.
a. What assumptions do you have to make to compute a confidence interval with coverage probability exactly equal to .95.
b. Compute the interval.
c. What assumptions do you have to make to compute a confidence inter-val with coverage probability equal to .95.in a large sample (number of observations large).
d. Compute the large sample confidence interval.
e. Test
against
with 5% significance level (use attached table with critical values ).
f. Does it make a difference if the random errors do not have a normal distribution?
g. Also test
against
with 5% significance level.
2021-09-22