OPSMGT 370: Operations and Supply Chain Strategy SEMESTER ONE, 2022
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
OPSMGT 370: Operations and Supply Chain Strategy
SEMESTER ONE, 2022
1 Consider the four products below. For which ones would you recommend efficient supply chains
and for which ones would you recommend responsive supply chains? Briefly explain why? [10 marks]
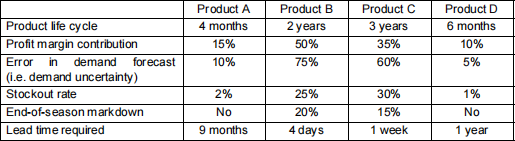
Now, assume there is uncertainty in the supply required for production of Products A and B, while
the supply for Products C and D is stable. Would this change your recommendation for Products
A and B? How? [4 marks]
2 a) What are the opportunities that drive many firms to global supply chains? What would determine
the success and failure of a given global supply chain? [6 marks]
b) Is supply chain visibility better or poorer in global supply chains? How could this influence
achieving sustainability in global supply chains? [6 marks]
Question 3 [16 marks]
MaxTooth, a New Zealand based company, produces electronic toothbrushes to sell in New Zealand. Demand is stable and is 200,000 per year. The sales price is $60. All the production happens in a local factory in New Zealand, and the unit production cost is $20.
MaxTooth is considering expanding its supply chain to outside NZ. In such a case, it will be able to sell in both Australia and New
Zealand markets . Demand in the Australia market is currently estimated to be 600,000 units per year, but it is volatile and every year, it may increase by 20% with 0.5 probability or decrease by 20% with 0.5 probability. Furthermore, MaxTooth will need to move all its
production to a bigger factory outside NZ. The unit production cost in the considered offshore factory (including transportation costs) is $30 per unit. However, the offshore factory requires a two-year contract with a fixed setup payment of $2,000,000. In addition, although it can currently produce up to 800,000 units per year, its production capacity is volatile and every year, its maximum production capacity may increase by 25% with 0.5 probability or decrease by 25% with 0.5 probability.
Given the information above, construct a decision tree and determine whether MaxTooth should expand its supply chain globally or not (show your decision tree and your calculations). Assume a 0.1 return rate for a year. [16 marks]
Question 4 [14 marks]
A sports-car manufacturer produces all parts and components of its training cars . To produce the driveshaft of the car, the manufacturer uses its flexible production line. There is a $3,500 set-up cost each time the production line is prepared for the driveshaft production. In addition, producing each driveshaft costs $600. The production line can produce driveshafts at a weekly rate of 20 driveshafts . Stocking the driveshafts at inventory adds another cost equivalent to 25% of the unit production cost.
All race driving schools/yards in the country use this brand of training car, so the manufacturer faces a fixed demand of 745 cars per year. Assume each car needs one driveshaft and assume 52 weeks in a year.
a) What is the optimal production batch size for the driveshaft? [4 marks]
b) What is the optimal production cost of the driveshaft? [4 marks]
The manufacturer has recently received an offer from a supplier whereby the manufacturer can procure the driveshafts from the
supplier rather than producing them itself. The supplier offers $400 for each driveshaft. However, the manufacturer will need to pay a
fixed transportation and processing fee ($5,000) each time the supplier delivers the ordered batch. The manufacturer also estimates that because of the proper boxing, the cost of stocking a procured driveshaft at inventory is only 12.5% of the unit procurement cost.
c) Would you recommend the manufacturer to switch to procuring the driveshafts rather than producing them? Show your calculations that support your recommendation. [6 marks]
Question 5 [18 marks]
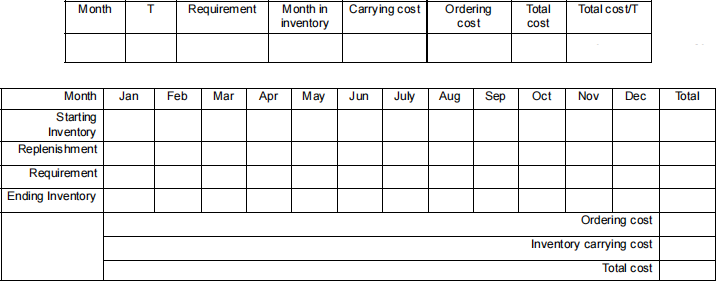
A paper production company sells Bond papers to some publishers in NZ. The total demand that the company expects from these publishers varies by month. The table below shows the estimated monthly demand (in boxes) for next year. The company itself procures the papers from a downstream supplier. The company pays $50 for each box of Bond papers . In addition, there is a fixed ordering cost of $300 each time the company places an order from the supplier. Assume there is no lead time for the supplier, no shortages are acceptable by the publishers , and any leftover inventory in the company at the end of a month will be carried over to the following month. The company keeps its inventories in-house and incurs a monthly holding cost equivalent to 2% of the production cost of each box .

a) The company currently uses a rather naïve ordering policy where it covers the demand for the next four months every time it orders from the supplier. What is the total inventory cost (i.e., ordering cost plus inventory holding cost) for the next year under this policy? (Use the table below to give your answer.) [6 marks]

b) The company has recently hired a supply chain manager. The manager suggests that the overall inventory strategy for the company should aim at having minimum inventory cost per month. What would be the improvement in the total inventory cost for the next year if the company uses this strategy? (Use the tables below for calculations and to give your answer.) [12 marks]
Question 6 [10 marks]
SunTiers is a tier supplier for car manufacturers . It has five production plants located near each other. SunTiers has recently received work orders from five manufacturers for five different cars , which need different tiers . The table below shows production costs of processing each order at each plant.
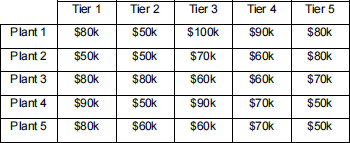
What is the optimal allocation of the orders to the plants? What is the total optimal cost of processing the orders? (Use the tables below to give your answer.) [10 marks]

Question 7 [16 marks]
Two suppliers collaborate on preparing semi-finished products for a manufacturer. Suppliers need to perform two sequential tasks on
each product: supplier one does the initial cutting, and after that, supplier two performs brushing. The suppliers need to prepare six
variants of such products for the manufacturer. From their experience, the suppliers have come up with estimates of the time required to finish each task on each product. The table below shows the estimates:
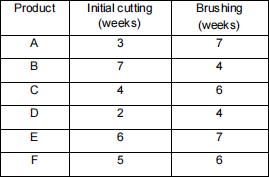
a) Using the Johnson’s rule, optimally schedule the products . [5 marks]
b) Compute the minimum makespan time? (Use the table below to show your calculations .) [6 marks]
Initial cutting
Brushing
c) Image the suppliers decide to merge into one big supplier, by which they can combine the initial cutting and brushing into one task.
The merger of such kind improves the performance such that the total time required to finish the combined task is reduced. At the same time, the manufacturer has set a preferred deadline for each product. There will be a fee for products with more than a month delay. The table below shows the estimated work time for each product together with the manufacturer’s preferred deadline:
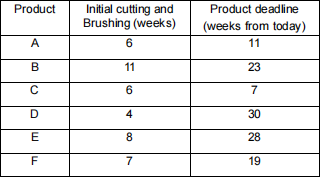
Using the Critical Ratio (CR) rule, optimally schedule the products and indicate which products will incur the delay fee. (Use the table below to show your calculations .) [5 marks]

2023-10-31