Fundamental Mechanics – ENGG 1300
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Department of Civil Engineering
Fundamental Mechanics – ENGG 1300
Assignment - Axially loaded structures & statically determinate structures
Please submit the answers of Q6 to Q10 by 29 October 2023.
Q1
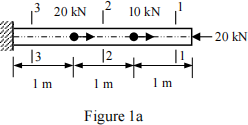
(a). Axial forces are acted on a straight bar of length L = 3 m as shown in Figure 1a. The cross- section area is A = 400 mm2. Determine the axial stresses on sections 1- 1, 2-2 and 3-3 respectively. (Answers: σ1 = -50 MPa, σ2 = -25 MPa and σ3 = 25 MPa)
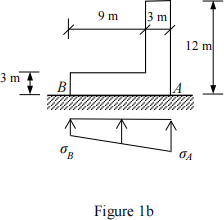
(b). An L-shaped concrete block rested on ground is shown in Figure 1b. The width of the block is 2 m. The concrete density is ρ = 2250 kg/m3. Determine the stresses at A and B. (g = 10 m/s2) (Hint: the stress along AB is a trapezoid distribution). (Answers: σA = 232 kPa and σB = 4.22 kPa)
Q2
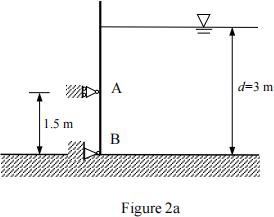
(a). Figure 2a shows a gate holding 3 m depth of water behind it. The width of the gate is 2 m. The density of the water is ρ = 1000 kg/m3. Determine the reaction forces of the gate at A and B. (g = 10 m/s2) (Answers: RA = 60 kN and RB = 30 kN)
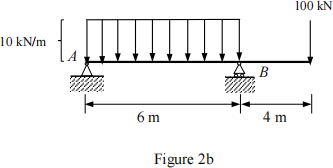
(b). For the beam as shown in Figure 2b, determine the reaction forces at A and B respectively. (Answers: RA = -36.7 kN and RB = 196.7 kN)
Q3
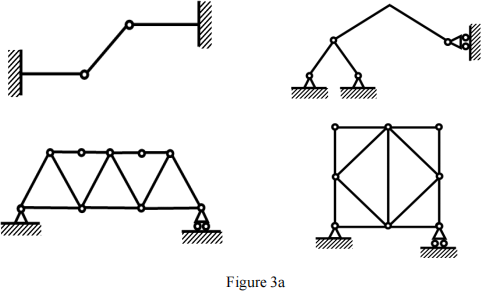
(a). How many stable structure(s) are shown below? (Answers: 2)
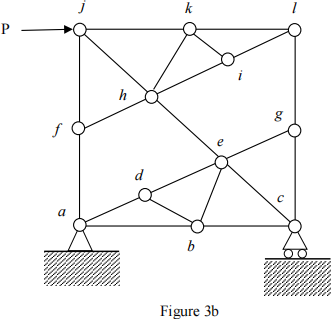
(b). Find all the zero-force members in Figure 3b.
(Answers: zero-force members: ad, db, de, be, eg, cg, lg,fh, hi, il, kl, ki, kh, and jk)
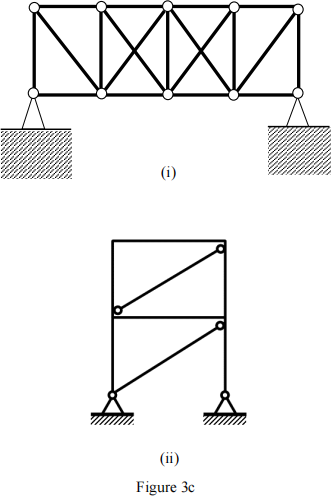
(c). Calculate the degrees of indeterminacy of the structures in Figure 3c.
(Answers: degrees of indeterminacy: (i) 3 and (ii) 6)
Q4
(a). Determine all the internal forces of the truss by the method of joints.
(Answers: FAB = FDE = 96 kN (C); FAH = FEF = 75 kN (T); FBC = FCD = 75 kN (C); FBH = FDF = 60 kN (T); FCH = FCF = 48 kN (C) and FGH = FGF = 112.5 kN (T))
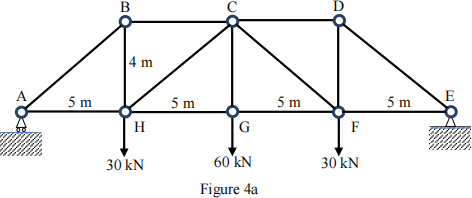
(b). Compute the member forces ofCE, CF and DF by the method of sections.
(Answers: FCE = 1 kN (T),FCF = 1.414 kN (T) and FDF = 2 kN (C))
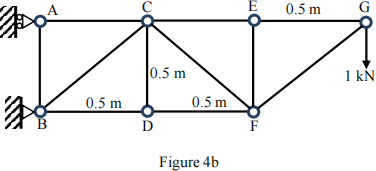
Q5
Determine all the reactions and the distance yc of the cable structure.
(Answers: HA = 3.17 kN, VA = 3.96 kN, HD = 3.17 kN, VD = 2.84 kN andyc = 3.60 m)
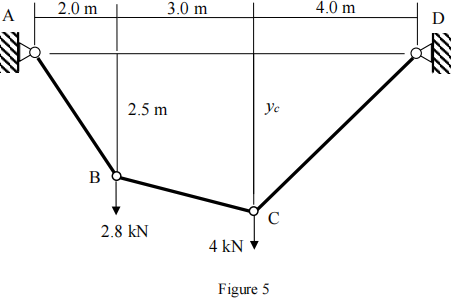
Q6
(a). Find the tensile force required to close the 6 mm gap for the system as shown in Figure 6a.

The material and sectional properties of the two bars are as follows: E1 = 100,000 MPa, E2 = 150,000 MPa, L1 = 2 m, L2 = 4 m, A1 = 300 mm2 and A2 = 200 mm2.
(b). A concrete column rested on ground is shown in Figure 6b. Three point loads are applied on the top of the column. The width of the block is 2 m. The concrete density is ρ = 2450 kg/m3. Determine the stresses at A and B. (g = 10 m/s2).
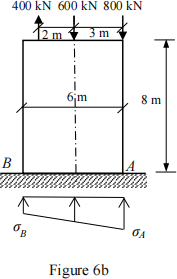
Q7
Figure 7 shows a gate holding 2m depth of water behind it. The inclination angle of the gate is 45。 to the horizontal. The width of the gate is 4 m. The density of water is ρ = 1000 kg/m3. The weight of the gate can be ignored. Determine the reactions at A and B. (g = 10 m/s2)
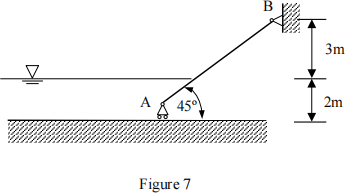
Q8
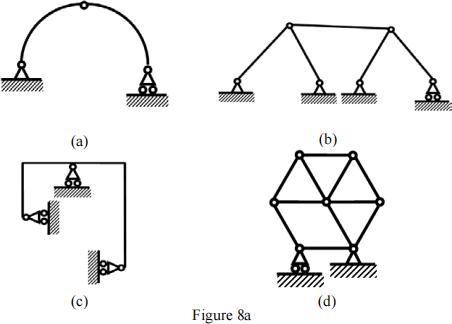
(a). Find all the stable structure(s) as shown in Figure 8a.
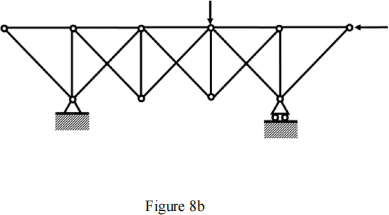
(b). Determine all the zero force members in Figure 8b.
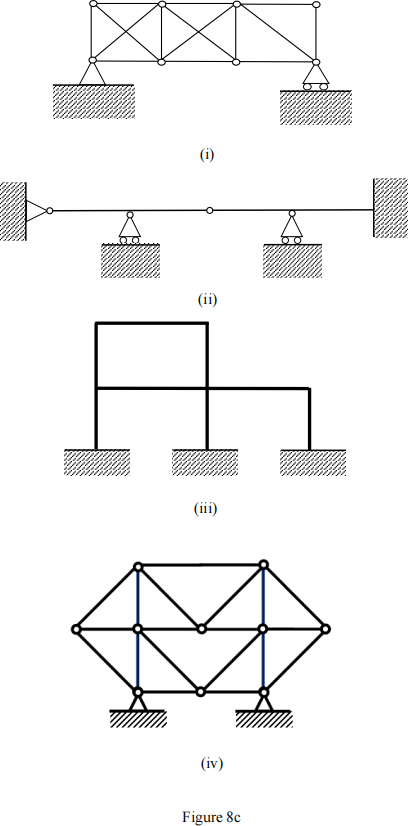
(c). Find the degree of indeterminacy of the structures in Figure 8c.
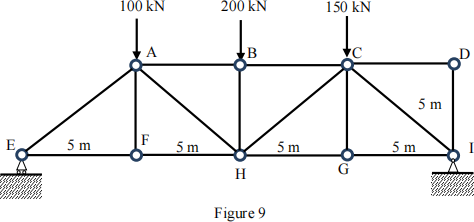
Q9
Find the internal forces in members AB, BC, BH, CH and HG. Please note that compression is positive.
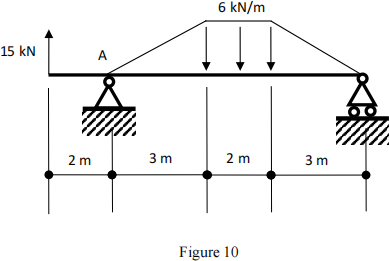
Q10
Determine the reaction force at A (Note: upward reaction is positive).
2023-10-21
Assignment - Axially loaded structures & statically determinate structures