HW 2: Mathematics of Cable Equation
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
HW 2: Mathematics of Cable Equation
September 23, 2023
1. The heat equation describes the diffusion of heat. Modeling an infinite straight rod by a line along the x-axis, we denote the temperature of the rod at time t ≥ 0 at x ∈ R by u(x,t). If u0 (x) is the temperature at t = 0, the function u satisfies the heat equation,
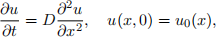
where D > 0 is the diffusion constant. Consider now the cable equation,
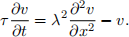
Assuming that v(x,t) satisfies the cable equation, define the function u by
u(x,t) = µ(t)v(x,t), (1)
where µ(t) > 0 is some function satisfying µ(0) = 1. Find a function µ(t) such that the new function u defined above satisfies the heat equation. What is D in this case in terms of τ and λ? (Hint: Plug in the definition (1) in the heat equation and use the fact that v satisfies the cable equation. This leads to a condition giving D and another giving µ.)
2. Prove that the function

satisfies the heat equation simply by plugging it in. The function K is known as the heat kernel. By the previous problem, you therefore get a solution of the cable equation of the form
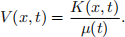 (2)
(2)
How does the solution behave for large t?
3. The solution V defined in (2) corresponds to an initial value that is not a classical function, but a generalized function known as Dirac’s delta,
 (3)
(3)
which is formally defined as an object that has the property

for all continuous functions φ . Heuristically, Dirac’s delta represents a point mass accumulated at a single point x = 0. As an initial value for the cable equation, you can think that we load a “voltage spark” at time t = 0 at the origin, and then watch how the voltage propagates along the cable. To prove (3), proceed as follows: Let φ be a continuous function. For t > 0, write the integral
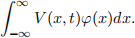
Now, make the change of variables in your integral, defining the new variable as
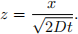
Then, let the parameter t go to zero in the integral, and use the fact that
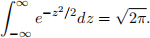
2023-10-19