ECOS3022 Tutorial 4 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Tutorial 4
1. Exercise 3.4 from Lengwiler.
2. consider an economy with one good and two states.
(a) suppose we have two inancial assets and the asset markets are complete. show that a consumer,s budget constraints for S = 0, 1, 2,
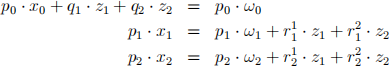
can be collapsed into one budget constraint
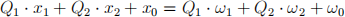
Determine Q1 and Q2 . (you may use some particular values for T 1(1) , etc.) (b) Interpret the budget constraint in a. through Arrow security prices.
(c) suppose we have one inancial assethence the asset markets are not com-plete. show that a consumer,s budget constraints for S = 0, 1, 2,
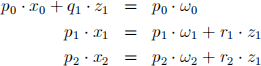
can be collapsed into two budget constraint
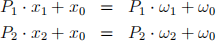
Determine P1 and P2 . (you may use some particular values for T1 , etc.)
3. suppose we have 2 inancial assets and the asset markets are complete. Formu- late the portfolio choice problem. That is consider the agent with today wealth ωo , who has access to the inancial markets with two assets with the payofs 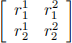 with the prices of the assets (q1 , q2 ) . (you may use some particular values for r1 1, etc.) At date 0 the agent can decide on asset holdings (z1 , z2) which determines his t = 1 wealth, call those ω1 and ω2 in the corresponding states.
with the prices of the assets (q1 , q2 ) . (you may use some particular values for r1 1, etc.) At date 0 the agent can decide on asset holdings (z1 , z2) which determines his t = 1 wealth, call those ω1 and ω2 in the corresponding states.
(a) Derive the agent,s budget constraint, that is the combinations of ω1 and ω2 that are feasible given the markets and the initial wealth.
(b) connect the no arbitrage condition to the slope of the budget constraint.
2023-09-01