ELEC 207 INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2017/18
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ELEC 207
SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2017/18
INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL
PART A
1. a) Define the accuracy and precision of a measurement instrument. Which of them takes into account systematic errors?
b) Repeated measurements of a constant current, affected only by random noise with Gaussian probability distribution, provide the following results: 2.55 A, 2.68 A, 2.27 A, 2.59 A, 2.53 A.
i) Write the expression and calculate the value of the best estimate of the current that can be obtained from the provided measurement results.
ii) Write the expression and calculate the value of the standard uncertainty of the provided measurement results.
iii) Write the expression and calculate the value of the standard uncertainty of the best estimate of the current calculated in question b.i) above.
c) The noise in question b) above is the result of electromagnetic interference produced by a strong time-varying magnetic field created by a nearby power circuit. Illustrate and explain a possible solution to decrease the electromagnetic interference in the measurement circuit without using any additional device.
d) A current transducer provides an output voltage that varies from 0 to 10 V when the current to be measured varies from 0 to 25 A. The current-voltage relationship is linear. Calculate the sensitivity of the transducer.
Total 16
![]() 2. a) A half bridge that employs two active strain gauges (of nominal resistance R and
2. a) A half bridge that employs two active strain gauges (of nominal resistance R and
gauge factor G) is shown in Figure Q2. The operating (source) voltage of the bridge is Vs. Derive the following relationship between the applied strain e and the bridge
output voltage Vout = VB – VA :

b) Explain why the half bridge configuration in question a) above can achieve automatic temperature compensation.
c) Each strain gauge in Figure Q2 above has a nominal resistance R = 80 Ω and a gauge factor G = 2.0. Calculate the resistance variation ΔR that each strain gauge experiences when a strain of 1500 microstrain is applied.
d) A thermistor has a resistance R0 = 25 kΩ at temperature T0 = 25 ºC (298 K), and its resistance at different temperatures is described by the following relationship:

where β = 2000 K and all temperatures are expressed in K. Calculate the measured temperature when the resistance is 10 kΩ.
e) A temperature sensor, initially at 20 ºC, is introduced into a room at 35 ºC. The sensor has a first-order transient response, with a time constant of 4 s. Calculate the waiting time required for the sensor to reach a temperature of 34 ºC.
Total 17
3. a) With the aid of a diagram, briefly explain the working principle of a Successive Approximation Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC).
![]() b) An ADC has to be designed to convert voltages in the range from -5 V to +5 V, with a resolution below (better than) 1 mV. What is the minimum number of bits required to meet this design specification?
b) An ADC has to be designed to convert voltages in the range from -5 V to +5 V, with a resolution below (better than) 1 mV. What is the minimum number of bits required to meet this design specification?
![]() c) An ADC has to be designed to convert input voltage signals with frequency components less than or equal to 250 Hz. Which of the following sampling frequencies can be used to correctly sample the input signals, without aliasing errors? Why?
c) An ADC has to be designed to convert input voltage signals with frequency components less than or equal to 250 Hz. Which of the following sampling frequencies can be used to correctly sample the input signals, without aliasing errors? Why?
i) 100 Hz;
ii) 125 Hz;
iii) 250 Hz;
iv) 500 Hz;
v) 2.5 kHz.
![]() d) The input signal in question c) above is affected by noise at frequencies above
d) The input signal in question c) above is affected by noise at frequencies above
10 kHz. An analog filter has to be designed to decrease such noise before the signal is sampled by the ADC. Which of the following types of filters can be used for this purpose?
i) Low-pass filter;
ii) High-pass filter;
iii) Band-pass filter;
iv) Band-stop filter.
e) The Hamming code is used to transmit a digital word of 20 bits. Determine the number of parity check bits (included in the 20 bits) required to detect and correct single bit errors.
Total 17
PART B
4. You are designing a remote-controlled drone. The dynamics of the drone can be approximated to be a second order system.
a) Sketch the time response to a unit step for an under-damped second order system.
Annotate the sketch to clearly indicate the peak time, settling time, percentage overshoot and anon-zero steady-state error. Label the axes.
b) The overshoot is to be 50% or less. Write an inequality involving the damping co-efficient.
c) Solve the inequality to deduce a range of values for the damping co-efficient.
d) The settling time needs to be less than 10 seconds. What values can the natural frequency take if the overshoot is 50%?
e) What is the resulting inequality on the peak time if the overshoot is 50%?
f) Write the transfer function for a generalised second order system. Ensure that the gain is unity at low frequencies.
g) You have been told to manufacture the drone with an overshoot of 50%, a settling time of 10 seconds and unity gain at low frequencies. Write the transfer function for the manufactured drone.
Total 17
5. A milling machine has the following open-loop transfer function:

a) Draw a block diagram describing a negative feedback system that includes a plant with transfer function of G1(s) and a cascade proportional controller with a gain of K.
b) Write the closed-loop transfer function for such a negative feedback system
c) The plant has poles that are solutions to P(s) = 0 and zeros that are the solutions to Z(s) = 0. Write an equation involving K, P(s) and Z(s) that holds for the closed-loop poles.
d) By substituting in for P(s) and Z(s) or otherwise, deduce the position of the closed-loop poles when K=0.
e) Draw the root locus for G1(s). Clearly indicate the positions of the closed-loop poles when K is infinite.
f) Is the closed-loop system stable for all values of K?
Total 17
6. a) Draw the bode plot for a system with the following open-loop transfer function:

b) Using Routh-Hurwitz or otherwise, determine if the following closed-loop transfer functions describe stable systems:
i) 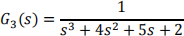
ii) 
c) The Nyquist plot of an open-loop transfer function circles the s = -1 point twice anticlockwise. The same open-loop transfer function has three open-loop poles with positive real parts. How many unstable closed-loop poles does the transfer function have?
Total 16
2023-09-01