ELEC 202 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS SECOND SEMESTEREXAMINATIONS 2021/22
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ELEC 202
SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2021/22
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
Q1. a) A carrier signal of frequency 99 MHz is frequency-modulated by a message signal of bandwidth 5 kHz such that the largest frequency deviation is 0.1 MHz. Determine whether this is narrow-band FM (NBFM) or wide-band FM (WBFM) and estimate the bandpass bandwidth.
b) Show that the NBFM expression for a single tone message can be written as a scaled version of
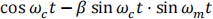
Sketch the above signal in the time and frequency domains, and comment on the bandpass bandwidth.
c) Draw the block diagram of a coherent DSB detector and discuss whether this could be used to recover the baseband message from aNBFM signal. Use appropriate diagrams, signal sketches and mathematical steps to support and illustrate your answer.
d) Using a table, compare the main features of frequency modulation with those of the various forms of amplitude modulation. These features should include power efficiency, bandpass bandwidth, complexity, and example applications.
Total 25
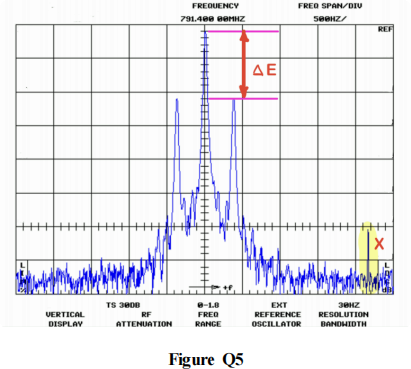
Q2. A spectrum analyser is used to display a bandpass signal as shown in Figure Q5 below, where the horizontal axis is frequency and the vertical axis is 20log10 E, where E is the magnitude of the signal spectrum at any given frequency.
a) Explain why a logarithmic scale is often used in such displays.
b) Given that the modulation index can be expressed as a ratio of the (linear) amplitudes of the sideband and carrier peaks, respectively ESB and EC , as follows:
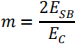
show that the modulation index m can be found from the instrument display by
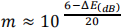
c) Using the value of ΔE = 5.1 dB, estimate what percentage of the signal’s total power is contained within the upper sideband.
d) Is this signal over-modulated, under-modulated or perfectly-modulated? Explain your answer
e) What does the peak labelled X represent? Explain where this may have originated from and what affect it may have, if any, on the recovered signal.
Total 25
Q3. a) The digitally modulated signal shown in Figure Q3a, of amplitude 5 V, is the result of critically sampling a 10 kHz audio message, followed by a uniform quantiser. The duration T shown in the figure is 10 μs.

i) What is the bit-depth of the quantiser (i.e. how many bits are used to encode each sample?)?
ii) Referring to the signal described and shown in Figure Q4a, determine the power of this signal.
iii) What is the name of the digital modulation scheme shown in Figure Q4a? Sketch the spectrum of this bandpass signal, indicating clearly the carrier frequency.
b) How much bandwidth is required to frequency-division multiplex 5 user channels, each of bandwidth 6 kHz, with 1 kHz guard bands between channels, using :
i) SSB
ii) DSB
iii) FM, with β= 5
c) Consider a time-division multiplex system with n signals, each bandlimited to 5 Hz and quantized to 16 levels. If the transmission system can handle 400 bits per second, how many users (n) can simultaneously share the channel
Total 25
Q4. a) Consider the following scenario:
You work in a laboratory containing digital microscopes connected to legacy computing equipment. You need to transmit a series of 12 megapixel images from one of these old computers to another, but there is no way to directly connect the two computers. Neither computer has any wired or wireless connectivity options. Each computer has an integrated keyboard, monitor, speaker and microphone, but no serial or parallel ports and no removable storage. You can write and execute software on the computers, but you cannot open or alter the hardware in any way, and do not have access to any technical equipment other than the above.
Describe how you would go about achieving this task, including as much technical detail as possible, including time and error considerations,
justifying any design choices and including illustrations and calculations in your design as appropriate.
b) The Internet backbone refers to one of the principal data routes between large, strategically interconnected networks and core routers on the Internet. It is a very high-speed data transmission line (typically a fiber optic trunk line) that provides networking facilities to Internet service providers all around the world.
Using your knowledge of communications, explain why the Internet backbone consists of cables rather than wireless connections, even though wireless signal propagation is considerably faster. Use relevant theorems and communication principles to support your answer.
c) Broadband over power lines (BPL) is a communication method that allows digital data transmission over the network of public electricity power distribution cables over long distances. BPL employs a carrier in the MHz region, utilising frequencies that are part of the radio spectrum allocated to over-the-air communication services.
Explain why BPL may not be very suitable for the distribution of high-speed internet traffic in urban areas (such as cities).
Total 25
2023-08-31