ELEC 210 ELECTROMAGNETICS SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2017/18
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ELEC 210
SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2017/ 18
ELECTROMAGNETICS
1. a) Explain what is meant by the following terms in electromagnetics:
ii) electrical potential,
iii) drift velocity.
b) A charge of 30 nCis situated at the point (x, y, z) = (0, 2, 0) m and a charge of-30 nC at the point (0, -2, 0) m. Find E at point C = (4, -2, 4) m (εr = 1).
c) Find the total charge in a cube defined by the six planes for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 3, 0 ≤ y ≤ 3, 2 ≤ z ≤ 5, if
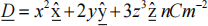
i) Calculate the capacitance.
ii) What charge will appear on the plates if a potential difference of 120 V is applied?
Total 32
2. a) Starting with Maxwell's equations in vacuum (no materials, no currents, no charges) derive the wave equation for the magnetic field.
b) Three very long wires, all parallel to the z-axis, carry current I as shown in Figure Q2b. One wire passes through the origin, and the others pass through the points y = b and x = ±a. The wire located at the origin carries current into the page, and the other two carry current out of the page.
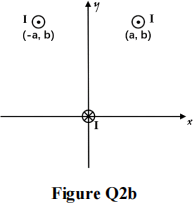
Figure Q2b
![]() i) Determine the magnetic field at the origin due to the two wires located at (a, b) and (-a, b), as shown in Figure Q2b.
i) Determine the magnetic field at the origin due to the two wires located at (a, b) and (-a, b), as shown in Figure Q2b.
![]() ii) Determine the force per unit length on the wire located at the origin due to the magnetic field determined in i).
ii) Determine the force per unit length on the wire located at the origin due to the magnetic field determined in i).
c) A uniform magnetic field is generated by a time-varying source as shown in Figure Q2c. A stationary square loop is placed such that its plane is perpendicular to the magnetic flux density B. Assuming B = B0sin(ωt) [T] with B0 = 0.1 T, ω = 100π rad/s, a = 0.1 m and b = 0.1 m.
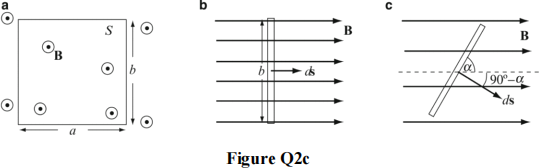
Figure Q2c (a) A square loop with its plane perpendicular to a uniform, time- dependent magnetic flux density; (b) Side view of the figure in (a); (c) A square loop with its plane at an angle α to a uniform, time-dependent magnetic flux density
i) Calculate the induced electromotive force (emf) in the loop.
ii) What is the induced emf if the loop is made of N = 100 turns, placed in the same location?
iii) Calculate the induced emf in the loop if the loop is at an angle α relative to the field.
Total 34
3. a) Explain what is meant by the following terms in electromagnetics:
i) magnetic flux density,
ii) displacement current,
iii) transmission line.
b) i) By considering a transmission line as a four terminal network, develop an expression for the transmission line wave equation in the lossless case.
ii) What is the velocity with which the electromagnetic wave propagates along this line?
c) A signal of 10 V is applied to a 50 Ω co-axial transmission line terminated in a 200Ω load. Calculate:
i) the voltage reflection co-efficient.
ii) the magnitude of the reflected voltage.
iii) the magnitude of the reflected current.
iv) the voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR).
i) The attenuation constant of the line.
ii) The characteristic impendence of the line.
Total 34
2023-08-29