MBA662 HW1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MBA662 HW1
1. Multiple choices (1.5 points)
1.1 Which of the following constraints, applied collectively, does not contribute to defining the feasible region? (hint: desmo)
a) X1 + X2 <= 10
b) X1 – X2 <=10
c) X1 + 3X2 <= 20
d) X1, X2 >= 0
1.2 The feasible region does not include:
a) interior points.
b) boundary points.
c) points at which at least one of the decision variables is zero.
d) points which violate at least one of the functional or non-negativity constraints.
1.3 Squire Leathers produces two sizes of wallets from cowhide. The first requires 60 square inches of cowhide and the second requires 100 square inches. The company has 1000 square feet of cowhide. Part of the model is (hint 1 square foot is 144 square inches):
a) 60X1 + 100X2 >=144,000
b) 60X1 + 100X2 <=144,000
c) 60X1 + 100X2 = 144,000
d) 60X1 <=144,000 and 100X2 <=144,000
1.4 The functional constraints of a linear model with nonnegative variables are 3X1 + 5X2 <=16 and 4X1 + X2 <=10. Which of the following points could not be an optimal solution for the model? (hint: desmo)
a) X1 = 2.5, X2 = 0
b) X1 = 0, X2 = 3.2
c) X1 = 1, X2 = 2.25
d) X1 = 2, X2 = 2
1.5 The effect of deleting a linear constraint from a linear programming model depends on whether or not that constraint:
a) has positive RHS value.
b) has negative coefficients
c) is binding
d) is a “<=” or a “>=” constraint
1.6 Refer to the excel table below on the Kings Department jewelry problem. How many of the following statements below are correct?
· In cell F7, the excel function sumproduct() is not only convenient but also necessary.
· If I deleted the content in F10 to F12, solver will still work;
· If I deleted the content in G10 to G12, solver will still work.
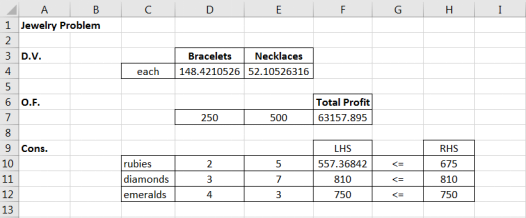
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
2. Extel Industries (1.5 points)
Extel Industries produces integrated circuit components for use in the next generation of automobiles. In particular, it can make the AT50 unit that can control the air temperature in the car, the V35 unit that monitors vibration and makes adjustments accordingly, and the GM30 that regulates the engine so that the car provides maximum efficiency. The unit profits on these units are $84, $112, and $126, respectively. Each of these units uses different quantities of three computer chips (as shown below), which Extel purchases from a Taiwanese distributor.
chips: (the materials)
C101 H122 P043
circuit: (the product) AT50 1 1 1
V35 1 1 2
GM30 1 2 1
Each week Extel receives 350 C101’s, 300 H122’s, and 400 P043’s. Formulate a linear programming model and use excel solver to help Extel decide how many units of each product to produce weekly to maximize profit. (Decision variables, Objective function and constraints.)
(hint: you should realize this is exactly the same as the jewelry example.)
3. Anderson & Blount (A&B) Woodworks (3 points)
(Adapted from Lawrence and Pasternack, Chapter 2 Problem 5)
Anderson & Blount (A&B) Woodworks makes tables and chairs from 30-inch wide mahogany sheets that it purchases the linear foot. It can purchase whatever mahogany it desires for $10 per linear foot up to 2250 linear feet per week. Each table requires 9 linear feet and each chair 3 linear feet (including waste). Each chair also utilizes a soft cushion. Up to 500 cushions can be purchased each week for $25 each. Other required hardware (supports, braces, nuts, bolts, etc.) averages $45 for each table and $25 for each chair. A&B sells the tables to retailers for $300 each and each chair for $150 each.
The 10 craftsmen employed by A&B are salaried workers. To produce a table requires 1 hour of a craftsmen's time, whereas each chair requires only 36 minutes. Each craftsman averages 37.5 productive work-hours per week. Company policy mandates that the ratio of chairs to tables must be between 4 to 1 and 6 to 1.
a. Develop a linear programming model for A&B. The objective function should maximize its weekly profit (revenue less the variable costs of wood, cushions and other materials). Express the feasible region by the non-negativity constraints and a set of five functional constraints (wood and cushion availability, the minimum and maximum chair to table ratios, and the maximum weekly production time).
Hints on ratio constraints: if you define # of chairs as C, # of tables as T, then the minimum ratio will be expressed as C/T >= 4, which is equivalent to C >= 4T (by multiplying both side by T) then to C - 4T >= 0 (by moving 4T from right to left).
b. Apply graphical analysis to draw each constraint and identify the resulting feasible region and the optimal solution with the line of same profit method.
c. Use solver add-in to solve the problem.
2023-08-28