ST302 – Stochastic processes 2021
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
January Assessment 2021
ST302-Stochastic processes
1. Let S=(Sn)n≥o be a simple symmetric random walk. That is,So =0 and for each n≥0,Sn=Yi+Y2+ Yn,where Yi,Y2,.. is a sequence of iid random variables with P(Yi=1)= P(Yi=-1)=1/2.Let Fo ={0,2}and Fn=σ(Yi,...,Yn) for n≥1.
(a)Which of the following processes are martingales with respect to (Fn)n≥o? Justify your answers(if necessary, you can assume that the random vari- ables are integrable).
 [6 marks]
[6 marks]
(b) Let a <0 and="" b="">0integers and define the random timest = min{n≥0: Sn ま(a,b)},Tb= min{n≥0:Sn =b}and g =max{n ∈[0,1000]:Sn ま (a,b)}. Are T,To and g stopping times? Explain your answer. [3 marks]
(c)Find the covariance of S, and +(you may need to assume that the optimal sampling theorem is applicable and use the fact that E(T)=-ab and/or P(S,=a)=b/(b-a) without proof). [8 marks]
(d)Find the value of E(To)(Hint: you may need to use the fact that E(T)=-ab). [4 marks]
2.(a) Identify the transient and recurrent states, and the irreducible closed sets for the Markov chains with the following transition matrices. |[6 marks]
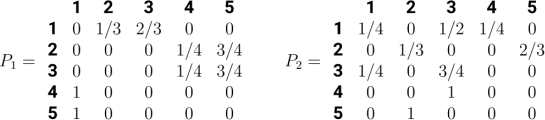
(b)A particle moves according to a Markov chain in the set E ={1,2,..,c,c+ 1,...,c+d}. If the particle is in any of the first c states, it jumps to any of the last d states with equal probability in a single step. If the particle is in any of the last d states, it moves to any of the first c states with equal probability in a single step. Show that the stationary distribution is given by
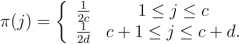
What can you say about the long term behaviour of this Markov chain? Justify your answer. [6 marks]
(c)Consider a Markov chain X=(Xn)n≥o with state space E =Z, the set of all integers, and transition probabilities
p(i,i+1)=p
p(i,i- 1)=q,
where0≤p
h(i)=P(Td
i. Calculate the value of h(i) for eachi≥ a and show that for anyi≤a-1,
h(i)=h(i+1)p+h(i- 1)q. [3 marks]
ii. Without using Optional sampling theorem, show that

Hint: Use telescopic sums for h(a)-h(i) and h(0)-h(i) fori ≤0 and use (without proof) the fact that lim;→-a h(i)=0. [6 marks]
3. Let N be a Poisson process withintensityλ> 0 which is adapted to some filtration (Fi)t≥o.Let Ti,T2,T₃,... be its arrival times.
(a) Show that Ti conditional on N =1 has uniform distribution on [0,t]. [3 marks]
(b) For any 0≤t₁≤t₂≤t,show that

where fn,r₂ N=2 is the joint density of (Ti,T₂) conditioned on Ni = 2.Hint: Find the joint probability P(t₁
(c) Assume that λ= 1 and that θ is an exponential random variable with param- eter 1, independent of N. Define the process Y = Not. Show that for any s,t≥0,
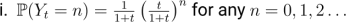
Hint: Condition on θ and you might use the fact that the density of Gamma distribution integrates to one on its domain. [3 marks]

Hint: Use similar reasoning as in part (i). [3 marks]
iii. Are the random variables Yi and Yi+s-Y independent? [2 marks]
4. Let B=(Bt)t≥o be a standard Brownian motion.
(a)Show that the following processes can be written as stochastic integrals.
i.X=xexp(at+βB:),withx>0.
ii.Yi =log(X:).
iii. ![]() for0≤t<1. [6 marks]
for0≤t<1. [6 marks]
(b)Solve the SDE
dXt =B₁Xdt+B;X;dBt,
with Xo = xo.(Hint: Try a solution of the form Xt = exp(Rt), where dRt = Fidt +GidB, for some adapted processes F and G which need to be deter- mined in terms of B.) [8 marks]
(c) Use the Feynman-Kac representation result to find a function F(t,x) that solves
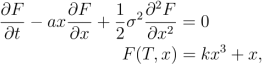
where a, k and a are real constants. You may want to use without proof that for any deterministic function f(t), the random variable ![]() normally distributed and that if X~ N(μ,σ²),then E(X³)=μ³+3μo² . [8 marks]
normally distributed and that if X~ N(μ,σ²),then E(X³)=μ³+3μo² . [8 marks]
5. Let X=(X:)t≥o be acontinuous time Markov chaintaking values in E ={0,1,2,.} with Q matrix such that Qo,o =0 and forn≥1,
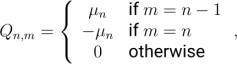
where we have that μn>0 for all n≥1.Denote (Pt)t≥o as the transition probabli- ties of this continuous Markov chain.
(a)Write down the Kolmogorov's forward equation and use it to find pr(n,n) for alln>0. [5 marks]
(b) Determine pt(n,m) in terms of p:(n,m +1) using the Kolmogorov's forward equation and use it to show that for any n≥1,
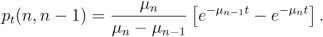 [6 marks]
[6 marks]
(c)Show that if μn =μn, for all n≥0,and for some μ>0,then

[6 marks]
2023-08-26