ELEC 202 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2018/19
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ELEC 202
SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 2018/19
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
1. a) Give three characteristics of a good communications system. 5
b) A 12 kHz audio message is sampled at 20 kHz prior to digitisation. In order to avoid aliasing effects, a low pass filter is to be used. Explain whether it would be preferable to apply this filter before or after the sampling process, referring to the amount of the message bandwidth that can be recovered in either case. 5
c) Suggest a suitable communication technique (modulation scheme or format) for each of the following scenarios. Suggest suitable values for relevant parameters such as carrier frequency, bit depth, etc. 5
i) An analogue talk radio station
ii) An analogue stereo music radio station
iii) A digital land telephone line
d) Distinguish between baseband and bandpass signals, commenting also on the difference between baseband and bandpass communications. 5
e) Explain the meaning of modulation, giving two compelling reasons why it is necessary. 5
Total
25
2.
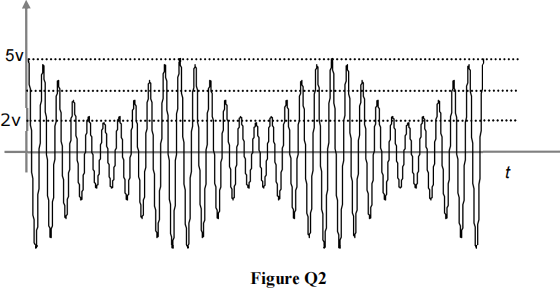
a) The carrier signal used in the AM signal shown in Figure Q2 is of frequency 100 kHz. Find the frequency of the upper sideband. 5
b) Referring to Figure Q2 above, calculate the modulation index, expressing it as a percentage. 5
c) What percentage of the total power of this AM signal is contained within the upper sideband? 5
d) Draw a circuit diagram of a suitable non-coherent demodulator for the above AM signal, suggesting suitable values for any components used. 5
e) State one advantage, and one disadvantage, of DSB-LC compared to DSB-SC, and suggest an example application in which DSB-SC would be the preferred modulation scheme. 5
Total
25
3. Figure Q3 shows how the bit error rate (BER) of selected digital transmission systems is related to the signal-to-noise ratio (Eb/No).

Figure Q3 – Bit error rate of selected digital transmission systems. BBB = bipolar baseband; UBB = unipolar baseband
![]() a) For a given signal-to-noise ratio (Eb/No), which coding format would produce more desirable results in terms of error rate: unipolar or bipolar signalling? Explain how you used Figure Q3 to reach your answer.
a) For a given signal-to-noise ratio (Eb/No), which coding format would produce more desirable results in terms of error rate: unipolar or bipolar signalling? Explain how you used Figure Q3 to reach your answer.
b) If PSK modulation is used in a particular communication system, and the signal is amplified so as to increase the signal-to-noise ratio from 4 dB to 12 dB, what will the corresponding reduction in bit error rate be? 5
c) A coherent DSB demodulator suffers a sudden fault which introduces a constant frequency error of 2 Hz in the carrier recovery circuit. What is the effect on the receiver output? How would this compare with a π/2 rad phase error in the local carrier? 5
d) The FM output signal of an angle modulator is given as: 5
x(t) = 10 cos(2 × 10଼ πt + 2π sin[1000πt])
Find the modulation index β, and determine whether this is narrow-band or wide-band FM.
e) State Carson’s bandwidth rule, and use it to estimate the effective bandpass bandwidth of x(t). 5
Total
25
4. a) The digitally modulated signal shown in Figure Q4, of amplitude 3 V, is the result of critically sampling a 10 kHz audio message, followed by a uniform quantiser. What is the bit-depth of the quantiser (i.e. how many bits are used to encode each sample?) 5
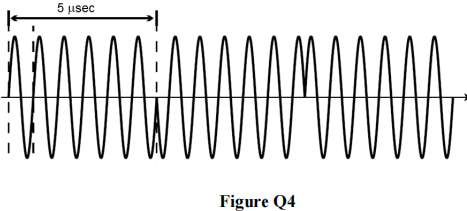
b) Referring to the signal described in part (a) above and shown in Figure Q4, determine the power of the modulated signal. 5
c) What is the name of the digital modulation scheme shown in Figure Q4? Sketch the spectrum of this bandpass signal. 5
d) How much bandwidth is required to frequency-division multiplex 5 user channels, each of bandwidth 6 kHz, with 1 kHz guard bands between channels, using : 5
i) SSB
ii) DSB
iii) FM, with β = 5
e) Consider a time-division multiplex system with n signals, each bandlimited to 5 Hz and quantized to 16 levels. If the transmission system can handle 400 bits per second, how many users (n) can simultaneously share the channel 5
Total
25
2023-08-23