BPS1022: WORKSHOP 1: Amines
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BPS1022: WORKSHOP 1: Amines
Supporting resources
To complete this workshop, you may find it useful to review Discovery 1.1 and Interactive Lectures 1.1-1.2.
Brown, WH & Poon, T. (2016). Introduction to Organic Chemistry (6th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons
McMurry, J. (Ed.). (2016). Organic chemistry (9th ed.). Boston, MA: Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning
There are two parts to be completed in this workshop.
There will also be assessable questions to be completed in the last part of this workshop.
Part 1
ANSWERS
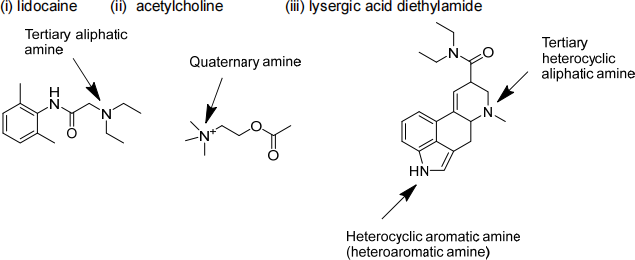
1. Look up the following compounds, draw their structures in skeletal form and classify the amines within their structures as primary, secondary, tertiary, aliphatic, aromatic, heterocyclic, etc. Very briefly give the pharmacology of the agent and/or it’s mechanism of action.
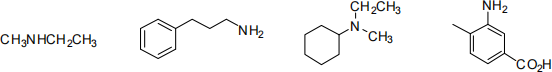
2. Name the following compounds according to IUPAC rules:
3. Draw structures of the following compounds:
(i) N-ethyl-3-methylpentanamine (or N-ethyl-3-methylpentan-1-amine)
(ii) 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine
(iii) (R)-2-butanamine
(iv) Benzyltrimethylammonium hydroxide
4. Explain the relative basicity of the following on the basis of the stability of their conjugate acid.
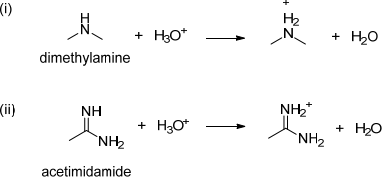
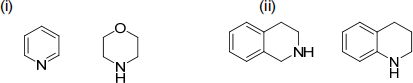
5. Select the stronger base from the following pairs of compounds. Justify your choices. (i)
6. 1-Propanol boils at 97oC, 1-propanamine boils at 49oC and butane boils at 0oC. These compounds represent three different families, but their molecular weights are similar. Although you might expect their boiling points to be similar clearly they are not. Explain this trend in boiling point.
7. Devise a synthesis of 3-methylbutanamine from: 3-methylbutanamide
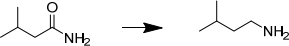
8. Devise a synthesis of 3-methylbutanamine from: 1-bromo-3-methylbutane
NOTE: Remember that reactions of amines with alkyl halides often produces
quaternary amines. Consider carefully your choice of reagents/reactants and bear in mind that this synthesis may require more than one step.
9. Explain how you synthesise 3-bromobenzoic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid and 3-cyanobenzoic acid from toluene via a diazonium salt.
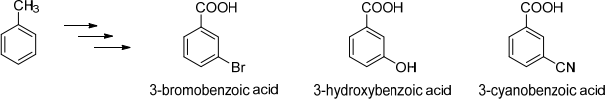
Part 2.
Second activity – useful amines
1. Tyramine is a natural product found in cheese and red wine. It has sympathomimetic action and can regulate blood pressure. It is derived from tyrosine by the action of the enzyme tyrosine decarboxylase.
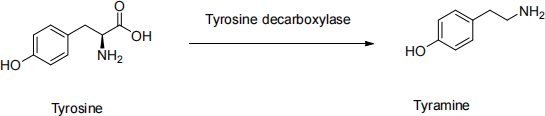
Explain how tyramine can be synthesize using the Gabriel synthesis and from what starting material.
2. Chlorpromazine is an anti-psychotic medication that can be used in the treatment of psychotic disorder, like schizophrenia or manic depression, or anxiety before surgery by inducing calmness without sedation. It works by blocking the dopamine receptor. It can be synthesised from the reflux of 2-chlorophenothiazine and 3-chloropropyl-dimethylamine in toluene and sodamide.
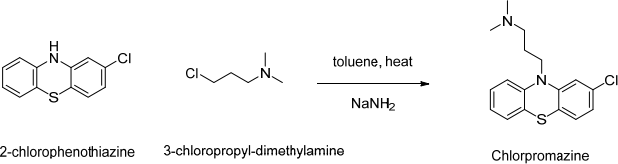
What is the purpose of the base (sodamide)? Chlorpromazine is subjected to metabolism; suggest possible products.
Base is used to remove HCl to move the reaction forward.
2023-08-21