Astro 7N — Sample Questions for Test 2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Astro 7N — Sample Questions for Test 2
1. A high-luminosity star ...
A: is always at a larger distance than a low-luminosity star
B: emits more light than a low-luminosity star
C: is always redder than a star with a lower luminosity
D: is at a lower temperature than a low-luminosity star
E: is always at a smaller distance than a low-luminosity star
2. If a red giant appears the same brightness as a red main sequence star, which one is farther away?
A: the red giant
B: we cannot tell
C: it depends on the phase of the Moon
D: the main sequence star
E: they are at the same distance
3. The heaviest nuclei of all are formed ...
A: during helium burning
B: as part of the p-p chain
C: during carbon burning
D: during a supernova explosion
E: during all stages of stellar evolution of massive stars
4. Fill in the blank in the following chemical reaction that occurs in the Sun: Hydrogen-2 + proton = + energy:
|
A: |
Hydrogen-2 |
|
B: |
Hydrogen-1 |
|
C: |
Helium-3 |
|
D: |
Carbon-12 |
|
E: |
Helium-4 |
5. Which of the following has the smallest radius?
A: type A main sequence star
B: main sequence star with surface temperature 8000 K
C: type K main sequence star
D: white dwarf
E: neutron star
6. Why does the main sequence part of a star’s life end?
A: The Helium in the core is exhausted.
B: The gravitational force is no longer large enough to balance the pressure.
C: The Hydrogen in the core is exhausted.
D: The temperature drops so that nuclear reactions are no longer possible.
E: Much of the mass of the star has evaporated.
7. Which of the following will have the shortest lifetime on the main sequence?
A: main sequence star with surface temperature 20000 K
B: main sequence star with surface temperature 3000 K
C: main sequence star with luminosity one tenth that of the Sun
D: the Sun
E: main sequence star with mass 2 times the Sun's
8. Many of the brightest 100 stars viewed from Earth are not on the main sequence (even though most stars are) because ...
A: only high mass stars formed near to us in the Galaxy.
B: the most luminous stars are giants and supergiants that have already finished their main sequence lifetimes.
C: our region of the Galaxy is very young.
D: the main sequence is the shortest part of a star’s life so stars do not spend much time there.
E: our region of the Galaxy is very old.
9. A 2-solar-mass main sequence star is at the same distance as a 0.2-solar-mass main sequence star. Which star appears brighter?
A: depends on the phase of the Moon
B: the 2 solar mass main sequence star appears brighter
C: the stars are approximately the same brightness
D: the 0.2 solar mass main sequence star appears brighter
E: we cannot tell with the information given
10. The temperature of the photosphere of the Sun is closest to ...
|
A: |
107 Kelvin |
|
B: |
106 Kelvin |
|
C: |
100 Kelvin |
|
D: |
600,000 Kelvin |
|
E: |
6000 Kelvin |
11. An estimate of the number of communicating / technological civilizations that we expect in our Galaxy would be a larger number if ...
A: the average lifetime of a communicating civilization were smaller
B: the star formation rate in our Galaxy were smaller
C: the average number of planets that could support life for each star were larger
D: it were more difficult for life to develop intelligence, once life had formed
E: a smaller percentage of stars formed planets
12. If the Sun had twice its mass, then which of these planets would be in its habitable zone?
|
A: |
Mercury |
|
B: |
Venus |
|
C: |
Earth |
|
D: |
Neptune |
|
E: |
Jupiter |

13. What is the exoplanet's orbital period, and the percent brightness drop in light, for
the case in the image above from the Kepler Exoplanet Transit Hunt activity?
A: 60 days and 0.15%
B: 20 days and 0.15%
C: 10 days and 0.15%
D: 5 days and 0.30%
E: 60 days and 0.30%
14. How do astronomers measure the temperature of stars?
A: The inverse square law is used.
B: Temperature is determined from the radius of the star that is measured by radar.
C: By looking at which absorption lines are present in the star’s spectrum.
D: The rate of change of the color of the star is measured.
E: By comparing the luminosity and apparent brightnesses.

15. In the inverse square law activity above, what would the wattage of the top
lightbulb need to be, such that it appeared as bright as the bottom lightbulb which is a 25-Watt bulb?
|
A: |
400 Watts |
|
B: |
100 Watts |
|
C: |
50 Watts |
|
D: |
25 Watts |
|
E: |
20 Watts |
16. The largest fraction of nearby stars (e.g., within 100 light years) are ...
A: neutron stars
B: Sun-like stars
C: blue main sequence stars
D: red main sequence stars
E: blue supergiants
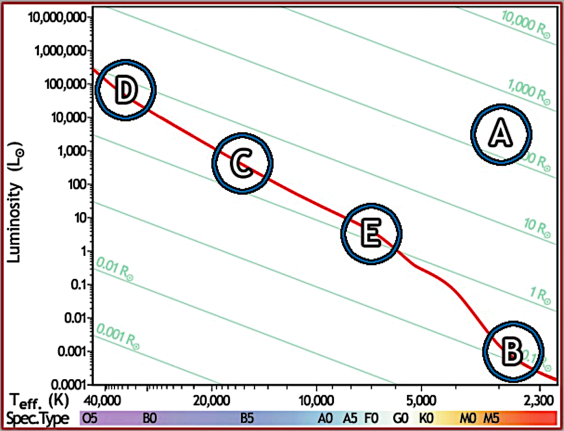
17. Which of the stars, in the diagram above, is the hottest?
A: A
B: B
C: C
D: D
E: E
18. If they were all formed at the same time, which of the stars in the diagram above will live the longest?
A: A
B: B
C: C
D: D
E: E
19. The parallax angle of a nearby star is measured to be 0.02 arcseconds. What is the distance to the star?
|
A: B: |
20 parsecs 2 light years |
|
C: D: E: |
50 parsecs 0.2 light years 200 light years |
20. Which of the following is the sequence of events for a 40-solar mass star (one of the most-massive stars)?
A: planetary nebula, protostar, Sun-like star on main sequence, blue giant, red giant
B: stellar nursery, protostar, Sun-like star on main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf
C: stellar nursery, blue giant, Sun-like star on main sequence, red giant, Type II supernova, neutron star
D: stellar nursery, protostar, bluestar on main sequence, Type II supernova, black hole
E: black hole, neutron star, white dwarf, Sun-like star on main sequence, red giant, Type II supernova
21. Star A is 9 times as luminous as Star B. The two stars appear the same brightness. What is true about their distances?
A: Star A is 9 times farther away than Star B.
B: Star B is 9 times farther away than Star A.
C: Star A is 3 times farther away than Star B.
D: Star B is 3 times farther away than Star A.
E: Stars A and B are at the same distance.
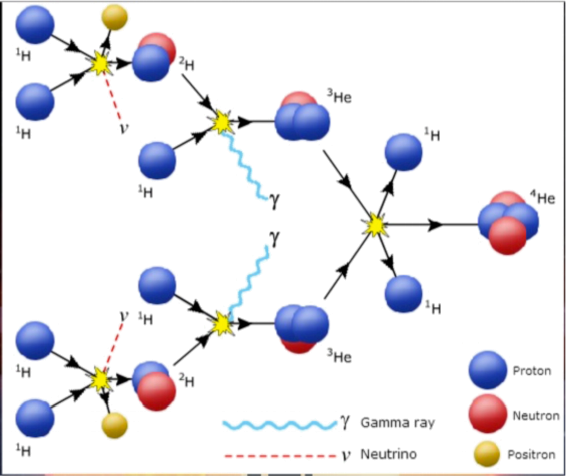
22. In the p-p chain, shown in the above diagram, what particles must be input in order to produce one4 He nucleus?
A: 8 protons, but 2 of them are returned when the 4 He is produced
B: 6 protons, but 2 of them are returned when the 4 He is produced
C: 2 photons and 2 positrons
D: 2 protons and 4 neutrons
E: 4 neutrons
23. What is the name of the slightly cooler layer of the Sun just outside the photosphere?
A: core
B: corona
C: convective zone
D: chromosphere
E: radiative zone
24. How does a star move on the H-R diagram during the period of time it is converting hydrogen to helium in itscore?
A: It moves from the far lower right corner of the diagram to the far upper left corner of the diagram, along the main sequence.
B: It moves from the upper left of the diagram to the lower right of the diagram, along the main sequence.
C: It remains nearly fixedat a certain point on the main sequence and does not move on the H-R diagram.
D: It moves from the upper right of the diagram to the lower left of the diagram.
E: It moves from the lower left of the diagram to the upper right of the diagram.
25. If the entire mass of Earth were concentrated in a region the size of a marble, the resulting object would be ...
A: a Sun-like star
B: a white dwarf
C: a neutron star
D: a black hole
E: a planetary nebula
26. Which is the smallest object?
A: a neutron star
B: the Solar System
C: the Sun
D: a dwarf galaxy
E: the Eagle nebula
27. A galaxy has an H-alpha emission line observedat a wavelength 10 percent larger than the rest wavelength of H-alpha. What is the redshift of the galaxy?
|
A: |
10 |
|
B: |
0.001 |
|
C: |
0.1 |
|
D: |
1 |
|
E: |
-0.001 |
28. What is in this image? (right)
A: supernova remnant
B: irregular galaxy
C: planetary nebula
D: globular star cluster
E: star forming region

29. Which is the most luminous?
|
A: |
nova |
|
B: |
supernova |
|
C: D: E: |
quasar the Sun white dwarf |
30. Which contains the most stars?
A: an open star cluster
B: a globular star cluster
C: a spiral galaxy
D: the Solar System
E: the alpha Centauri star system
31. Galaxy A appears twice the angular size of Galaxy B. Assuming the two galaxies
have the same physical size in kiloparsecs, which of the following is true?
A: Galaxy A is 2 times farther away than Galaxy B.
B: Galaxy B is 2 times farther away than Galaxy A.
C: Galaxy A and B are at the same distance.
D: Galaxy A is 4 times farther away than Galaxy B.
E: Galaxy B is 4 times farther away than Galaxy A.
32. What fundamental particles make up a Helium-3 atom?
A: 2 up quarks, 1 down quark, 1 electron
B: 6 up quarks, 6 down quarks, 2 electrons
C: 3 up quarks, 3 down quarks, 3 electrons
D: 1 proton, 2 neutrons, 1 electron
E: 5 up quarks, 4 down quarks, 2 electrons
33. In what box does the galaxy in the bottom center belong in this Hubble tuning fork diagram?

|
A: |
E1 |
|
B: |
Irr |
|
C: |
Sc |
|
D: |
SBb |
|
E: |
SBc |
34. Which statement is FALSE?
A: planetary nebulae can have layers because of pulsating stars
B: planetary nebulae usually last tens of thousands of years
C: a planetary nebula will be part of the end state of the Sun
D: planetary nebulae usually have black holes at their centers
E: planetary nebulae are a few light years in size
35. Which statement is TRUE?
A: Stars form in molecular clouds, where temperatures are about 10 Kelvin.
B: A cloud will collapse and form stars if its mass is a lot less than its Jeans mass.
C: A nova outburst typically only happens once in a star’s life.
D: Stars usually form in isolation, far away from other stars
E: The Crab supernova, in our galaxy, went off about 8 years ago.
36. How tiny a spot is the Hubble Deep Field?
A: About 1/2 of the entire sky.
B: About 1/5 of the entire sky.
C: About 1/10 of the entire sky.
D: About 1/50 of the entire sky.
E: The size of President Roosevelt’s eye on a dime held at arm’s length.
37. Among these choices, what is the last thing that happens in the history of the Universe?
A: electrons join with nuclei to make atoms
B: quarks join together to make protons and neutrons
C: nucleosynthesis
D: the Planck epoch
E: the Big Bang expansion begins
38. If a galaxy had no dark matter, we would observe ...
A: the entire galaxy would approach us at a faster velocity, and we would observe a redshift
B: the entire galaxy would recede from us at a faster velocity, and we would observe a redshift
C: the rotation velocity would remain constant with increasing distance
D: the rotation velocity would decrease with increasing distance like the Keplerian curve in our Solar System
E: the rotation velocity would increase with increasing distance like the Keplerian curve in our Solar System
39. How many times bigger is the Local Group of galaxies in which the Milky Way resides than the Milky Way itself?
A: it is not bigger than the Milky Way
B: about 100 times bigger
C: about 1040 times bigger
D: about 1010 times bigger
E: about 1 million times bigger
40. Which one of the following is FALSE?
A: Irregular galaxies, although small, often have a lot of star formation taking place in them.
B: Barred spiral galaxies have similar properties to normal spirals, except for the “bar” feature.
C: Galaxy collisions destroy most of the stars in the galaxies involved.
D: Most galaxies appear to be receding from the Milky Way Galaxy.
E: Most elliptical galaxies contain only old stars.
41. If a galaxy is moving away from us the wavelength of the light it emits will be ...
A: unaffected.
B: blueshifted.
C: increased.
D: decreased.
E: distorted.
42. The stars in the halo of our Milky Way Galaxy are ...
A: in a very flat distribution.
B: very close together compared to stars in the disk.
C: older and bluer than those in the disk.
D: never in globular clusters.
E: older and redder than those in the disk.
43. The supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way has a mass of ...
A: 10 solar masses
B: 1,000 solar masses
C: 4 million solar masses
D: 100 billion solar masses
E: 100 solar masses

2023-08-08