Astro 7N — Sample Questions for Test 1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Astro 7N — Sample Questions for Test 1
1. What two properties of a planet affect the gravity we feel on its surface?
A: radius and distance from the Sun
B: radius and temperature
C: mass and distance from the Sun
➔ D: mass and radius
E: mass and temperature
2. Two planets have the same radius. If Planet A is 5 times more massive than Planet B, how does gravity differ on the surfaces of the two planets?
A: gravity is 5 times stronger on Planet B
➔ B: gravity is 5 times stronger on Planet A
C: gravity is 25 times stronger on Planet A
D: gravity is 25 times stronger on Planet B
E: gravity is equal on Planet A and Planet B
3. Say that there were a planet X in our Solar System with a mass 1/4 the mass of Earth and a radius 1/2 the radius of Earth. How will the gravity on its surface compare to the surface gravity of Earth?
A: surface gravity on planet X is 2 times weaker than on Earth
B: surface gravity on planet X is 2 times stronger than on Earth
➔ C: surface gravity on planet X is the same as on Earth
D: surface gravity on planet X is 8 times stronger than on Earth
E: surface gravity on planet X is 4 times weaker than on Earth
4. A planet in a nearly circular orbit with its rotation axis tilted by 5 degrees relative to its orbital plane around its star would ...
A: have longer days and nights than those of Earth
B: have very severe seasons compared to Earth
C: have shorter years than those of Earth
D: have shorter days and nights than those of Earth
➔ E: have seasons that are not very different from each other as compared to Earth's.
5. The rotation axis of the Earth is ...
A: tilted so that it is always pointed directly at the Sun
B: is sometimes parallel and sometimes perpendicular to the axis of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
➔ C: tilted at about 23 degrees relative to the axis of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
D: perpendicular to the axis of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
E: parallel to the axis of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.

6. In the diagram above, what season and planet is being represented by thered X on the planet on the left in orbit around the Sun?
A: winter on Earth
B: summer on Earth
C: winter on Venus
D: winter on Uranus
➔ E: summer on Uranus
7. When is the waning gibbous moon highest in the sky?
A: about 9:00am
➔ B: about 3:00am
C: about noon
D: about midnight
E: about 3:00pm

8. What phase is the Moon in, when observed by the person standing on the Earth in the diagram above?
A: New
➔ B: Third Quarter
C: Waning Gibbous
D: Full
E: First Quarter
9. At what time will the Moon set on the day of a Solar eclipse?
A: Sunrise.
B: Noon.
➔ C: Sunset.
D: Midnight.
E: It will not set at all. It will be up for 24 hours.
10. Stars that are in the same constellation ...
A: appear in all different directions around the sky.
B: are all at close to the same distance from us.
➔ C: are likely to beat very different distances from us.
D: are all in our Solar System.
E: are all in orbit around the same larger star.
11. The "North Star" is a star in the constellation of Ursa Minor, which lies just above the North pole of Earth. Which of the following is true?
A: Ursa Minor is a Zodiac constellation in the winter but not in the summer.
B: Ursa Minor is a Zodiac constellation in the summer but not in the winter.
➔ C: Ursa Minor is not a Zodiac constellation.
D: The Zodiac constellations are located near the axis below the South pole.
E: Ursa Minor is a Zodiac constellation all year.
12. A particular Zodiac constellation is high in the sky at midnight in April. Where will it be in October?
A: high in the sky at midnight
➔ B: near the Sun in the daytime sky
C: near the horizon a couple of hours after sunset
D: near the horizon a couple of hours before sunrise
E: visible at midnight, but only from the Southern hemisphere
13. What do you expect the spectrum of an object that is 1,000,000 Kelvin to be like?
A: It should peak at radio wavelengths.
B: It should peak at violet wavelengths.
➔ C: It should peak at X-ray wavelengths.
D: It should give off less total light than the Sun.
E: It should give off about 10 times more total light than the Sun.
14. As compared to a cool star, a hotter star emits ...
A: shorter wavelength, lower frequency, bluer color
➔ B: shorter wavelength, higher frequency, bluer color
C: longer wavelength, higher frequency, bluer color
D: shorter wavelength, higher frequency, redder color
E: shorter wavelength, lower frequency, redder color
15. Radio waves can travel large distances without interference because ...
A: they have shorter wavelengths than visible light
B: they have higher energies than visible light
➔ C: they have longer wavelengths than visible light
D: they travel at the speed of light
E: they travelslower than the speed of light
16. Compared to ultraviolet radiation, X-rays have a wavelength that is ...
A: the same
B: longer
➔ C: shorter
D: sometimes shorter and sometimes longer
E: zero
17. Star A is 4000 K, and Star B is 8000 K. Which of the following is true?
A: The wavelength of the dominant light from Star A is shorter than that from Star B.
B: The color of Star A is bluer than Star B.
➔ C: The color of Star A is redder than Star B.
D: The two stars have the same color.
E: The frequency of the dominant light from Star A is larger/higher than that from Star B.

18. In the diagram above, what is happening in the box in the center?
A: helium gas is emitting photons at specific wavelengths
B: a continuous spectrum is being produced
C: electrons are being absorbed by hydrogen gas
➔ D: hydrogen gas is absorbing photons at specific wavelengths
E: photons are being emitted at specific wavelengths
19. A star is a hot, dense gas surrounded by a cooler, low density atmosphere. What type of spectrum will a star create?
A: blackbody spectrum
➔ B: absorption spectrum
C: continuous spectrum
D: hydrogen spectrum
E: emission spectrum
20. What makes a transition from a lower energy state to a higher energy state when a photon is absorbed into an atom?
A: proton
B: photon
C: neutron
➔ D: electron
E: graviton
21. An emission line is produced when:
A: a proton passes from a higher to a lower energy level.
B: a proton passes from a lower to a higher energy level.
C: an electron passes from a lower to a higher energy level.
➔ D: an electron passes from a higher to a lower energy level.
E: radiation passes through the outer layers of a star.
22. Bright lines in an emission spectrum represent:
➔ A: particular energies of light that are emitted from a distant object
B: photons absorbed when an electron jumps from a higher to a lower energy
C: flaws in the telescopes and spectroscopes that astronomers use to measure spectra
D: regions from which light travels more rapidly and reaches us more quickly
E: photons absorbed when an electron jumps from a lower to a higher energy level
23. The faintness of an object that a telescope can observe is mostly determined by the ...
A: wavelength of light being observed
B: eyepiece it uses
C: the expertise of the astronomer in focusing light
➔ D: diameter of the opening of the telescope
E: magnification of the telescope
24. In what ways does a 5 meter telescope outperform a 1 meter telescope?
A: All objects observed by the 5 meter will appear larger.
➔ B: Its images are 25 times brighter than a 1 meter.
C: It will produce better "seeing" than the 1 meter.
D: It can observe light with a wavelength 5 times longer than the 1 meter.
E: It will not suffer from spherical aberration like the 1 meter.
25. A mountaintop is a good location for optical telescopes because the site ...
A: has cold weather which improves the performance of the instruments
B: is closer to astronomical objects
C: has warm weather which improves the performance of the instruments
➔ D: is above much of the atmosphere
E: has high altitude which expands the glass in the mirror and makes it smoother
26. Which statement about the rotation of the Inner planets is true?
➔ A: Venus rotates in the opposite direction from the three others.
B: All rotate in the same direction.
C: The rotation periods of all of them are the same — i.e., 1 Earth day.
D: All have rotation periods of 365 Earth days.
E: All have rotation periods about equal to their periods to orbit the Sun.
27. Which of the following is TRUE?
A: The average surface temperature of Venus is about 30 degrees Fahrenheit.
B: Mercury has a very thick atmosphere made mostly of carbon dioxide.
C: The runaway greenhouse effect causes the present temperatures on Mars to exceed those on Earth.
➔ D: Mercury rotates exactly one and a halftimes for every one revolution around the Sun.
E: Venus has no volcanoes on its surface.
28. Why do the orbits of the planets all lie in nearly the same plane?
A: Collisions between planetesimals destroyed all planets that would have been elsewhere.
B: The Sun’s gravity forced them into these orbits.
➔ C: The early solar nebula flattened into a disk.
D: The angular momentum of the solar system was kept to a minimum this way.
E: This happened purely by chance.
29. Of these choices, which planet has the most moons?
|
A: |
Earth |
|
B: |
Mercury |
|
➔ C: |
Saturn |
|
D: |
Mars |
|
E: |
Venus |
30. Venus is visible to us ...
➔ A: only near sunrise or sunset.
B: only during the several hours around midnight.
C: only in the winter.
D: only in the summer.
E: only during its new phase.
31. A planet is in orbit around the Sun. The semimajor axis of the orbit is 5 Astronomical Units (AU).
Use P 2 = a 3 to calculate the period of the orbit, in years.
|
A: |
5 years |
|
B: |
0.2 years |
|
C: |
135 years |
|
D: |
125 years |
|
➔ E: |
11.2 years |
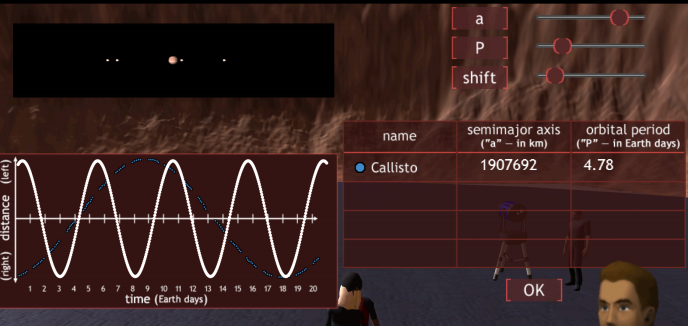
32. In the above diagram, how should the parameters of the white curve be changed in order that it matches the observed distance versus time graph of Callisto?
A: increase a and decrease P
➔ B: increase P and shift the curve
C: decrease a and decrease P
D: shift the curve and increase a
E: decrease P and decrease a
33. How do most craters on moons form?
|
|
A: B: C: D: |
by volcanic activity running water by seismic activity (earthquakes) earthquakes |
|
➔ |
E: |
impact of asteroids |
34. Which planet has a temperature of 800 degrees Fahrenheit on the side facing the Sun and –290 degrees Fahrenheit on the side opposite the Sun?
|
A: |
Mars |
|
B: |
Venus |
|
C: |
Earth |
|
D: |
Jupiter |
|
➔ E: |
Mercury |
35. How many Earth years does it take Uranus to orbit the Sun?
➔ A: 84
B: 1
C: 0.48
D: 2.4
E: 0.27
36. Meteors are ...
➔ A: asteroids or comet debris that pass into Earth’s atmosphere and burn up
B: a group of rocky objects between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn
C: comets that are vaporized when they pass very close to the Sun
D: comets that escape the Solar System without being vaporized by the Sun
E: a group of rocky objects between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter
37. Which feature of Neptune is most responsible for its blue color?
➔ A: methane in its atmosphere
B: auroral activity due to its strong magnetic field
C: excess energy emitted by the interior
D: winds blowing at speeds almost that of sound
E: large oceans covering most of the surface
38. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A: Neither Uranus or Neptune have ring systems.
➔ B: The planet Saturn has more than 30 moons.
C: There is no evidence to suggest that either Jupiter or Saturn has a liquid metallic or rocky core beneath its gas layers.
D: The Great Red Spot is a dust storm near the South polar cap of Mars.
E: Jupiter’s solid surface lies just below the cloud layers visible from Earth.
39. The surface of Venus is hotter than the surface of Mercury because ...
A: Venus is closer to the Sun than Mercury.
B: Mercury’s atmosphere prevents radiation from penetrating through to its surface.
C: of the volcanic activity that occurs on Venus.
➔ D: Venus is more massive and is able to retain a thick atmosphere.
E: Venus is smaller than Mercury so it does not require so much energy to heat it.
40. Which of the following is moving fastest in the orbit?
➔ A: Venus at its perihelion (closest point to Sun)
B: Venus at its aphelion (farthest point from Sun)
C: Mars at its perihelion (closest point to Sun)
D: Mars at its aphelion (farthest point from Sun)
E: Neptune at its aphelion (farthest point from Sun)
41. Which of the following is FALSE?
A: Venus has a density of 5.2 grams per cubic centimeter
B: All Terrestrial planets have densities much higher than the density of water
➔ C: Saturn has a density of 4.8 grams per cubic centimeter, similar to metals like aluminum and iron
D: The density of Jupiter is 1.3 grams per cubic centimeter, similar to the density of milk.
E: The density of Mercury is greater than the density of Uranus.
42. Which of the following objects have a dark/black sky, even in the daytime?
A: both Venus and Mars
B: both Mercury and Mars
C: both the Moon and Earth
➔ D: both the Moon and Mercury
E: both Earth and Titan
43. Which of the following is the largest distance?
➔ A: the distance from Jupiter to Saturn
B: the distance from the Sun to the Earth
C: the distance from the Earth to the Moon
D: the distance from Earth to Mars
E: the distance from Mercury to Venus
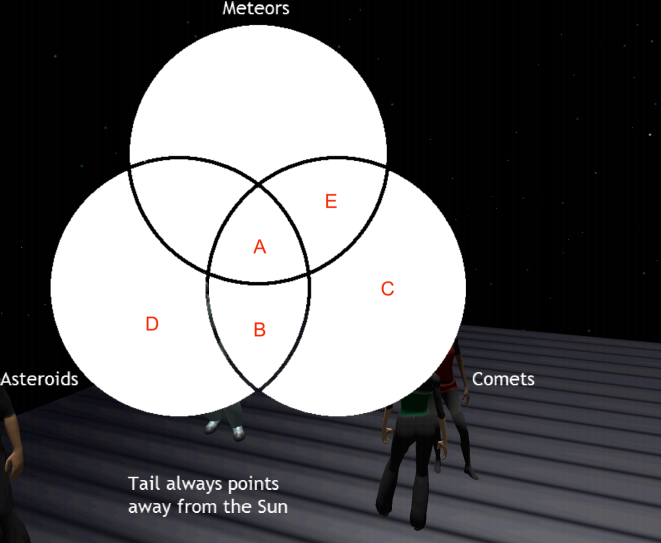
44. Where on the Venn diagram, above, does the clue
“Tail always points away from the Sun” belong?
A
B
➔ C
D
E
45. Which of the following is NOT required in order to classify a Solar System object as a planet (instead of a dwarf planet)?
A: It must not be a moon around another object.
B: It must be massive enough to be nearly round.
C: It must orbit the Sun.
D: It must clear the region around its orbit.
➔ E: It must be larger than all of the moons in the Solar System
46. Which of the following planets looks the most like the&
2023-08-08