ACW1100 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING – PAPER 1 Semester One 2017
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Semester One 2017
Examination Period
Faculty of Business and Economics
Department of Accounting
ACW1100
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING - PAPER 1
3 hours writing time
10 minutes
Question 1
Your uncle Graham has prepared atrial balance for his supermarket business, Graham Trading, but he is puzzled as his trial balance does not balance. After learning ACW1100, you think that he might have made some errors and/or omitted some transactions. You volunteer to assist in correcting the errors. Graham Trading’s financial year ends on June 30.

Question 1 (cont’d)
Additional information:
. Each of the above listed accounts has a normal balance per the general ledger.
. Equipment is depreciated using the straight-line method. It is anticipated to have a useful life of 10 years and a residual value of $2,000.
. Graham recalled that he has not recorded a transaction:
On 16 June 2016, Graham took a carton of canned drinks from his stock for his son’s birthday party. The carton of canned drinks had a cost price of $200 and a retail price tag of $400.
. A physical stock take on 30 June 2016 revealed that inventory on hand at cost is $4,200.
. The Bank loan was borrowed on 1 May 2016, with interest being payable at 9% per annum for the year. No payment has been made to date.
. Prepaid administrative expense of $1,200 was wrongly recorded as administrative expense.
Required:
(a) Prepare the necessary general journal entries for the year ended June 30, 2016 by
taking into account the additional information (ignore narrations).
(b) Prepare the adjusted trial balance as at June 30, 2016.
(c) Prepare the Income Statement for the year ended June 30, 2016 using classification of Revenue and Expenses (ignore Goods and Service Tax and income tax).
(5 + 10 + 5 = 20 marks)
Question 2
(a) Kenny Ltd’s financial year ends on December 31.
Kenny Ltd purchased equipment on January 1, 2013, at a cost of $60,000. The
equipment was originally estimated to have a residual value of $5,000 and an
estimated life of 10 years. Depreciation has been recorded using the straight-line method.
On 1 January, 2017, the estimated residual value was revised to $6,000 and the estimated useful life of the equipment was revised from 10 years (original) to 8 years.
Required:
Calculate Kenny Ltd’s Depreciation Expense for 2017. Show all workings.
(b) Lukas Ltd’s financial year ends on June 30 and they value their assets using the fair value basis in accordance with AASB 116 Property, Plant and Equipment.
On July 1, 2013, Lukas Ltd acquires a piece of land at a cost of $500,000 and a
building at a cost of $195,000, both for cash. The company uses the straight-line method of depreciation and the useful life of the building is 10 years.
On June 30, 2015, the landis revalued to $650,000.
On June 30, 2016, the building is revalued to $130,000.
Required:
Prepare the necessary journal entries of Lukas Ltd for years 2013 to 2016 including depreciation. Show all your workings clearly. Narrations are not required.
(4 + 10 = 14 marks)
Question 3
The following information relates to Veryrich Ltd, a restaurant.
(7+2=9 marks)
Question 4
The equity section of Silverflower Ltd as at July 1, 2015 is as follows:
Share Capital (100,000 shares) $200,000
General Reserve $15,000
Retained Earnings $50,000
During the year ended June 30, 2016, the following transactions occurred:
July 1, 2015 Issued 2,000 ordinary shares at par value each by private placement.
October 1, 2015 An interim dividend of $0.10 per share was declared and paid.
June 30, 2016 A final dividend of $0.12 per share was declared.
The final dividend is paid on August 1, 2016.
Profit for the year is $20,000.
Required:
(a) Prepare journal entries for the above transactions (ignore narrations).
(b) Prepare a statement of changes in retained earnings for the year ended June 30, 2016.
(4 + 3 = 7 marks)
Question 5
(a) Mother & Baby Magazine received in June 2016 atotal of $3,600 in subscriptions for magazines to be delivered once per month for the next 12 months.
Required:
Explain whether you would recognise the subscription monies of $3,600 as revenue in the statement of profit or loss for the year ended June 30, 2016. Refer to the recognition criteria outlined in the AASB118 Revenue to support your answer.
(b) Brewery Ltd uses the aging of accounts receivable method to record their bad debt expense for the year ended June 30, 2016. The balance of accounts receivable at the year-end was $600,000 and the allowance for doubtful debts had a credit balance of $20,000 before any adjustments. The company estimates that 2% of accounts
receivable will become uncollectable.
Required:
(i) Determine the total estimated amount of uncollectable accounts receivable for June 30, 2016.
(ii) Construct the ‘Allowance for Doubtful Debts’ account as at June 30, 2016.
(iii) Prepare the adjusting journal entries to record bad debts expense for the year ended June 30, 2016. Ignore narrations.
(iv) Show the extract of the accounts receivable account in the Balance Sheet of Brewery Ltd as at June 30, 2016.
(5 + [1 + 3 +2 + 1] = 12 marks)
Question 6
(a) The balance of two accounts as at June 30, 2016 areas follows:
|
Account Name |
Balance as at 30/6/2016 |
|
Wages Payable |
$3,000 Cr |
|
Wages Expense |
$4,800 Dr |
The balance of the Wages payable account as at June 1, 2016 was $7,000.
Required:
Construct the Wages Payable account and determine how much cash was paid for wages in the month of June 2016.
(b) Kiwi Ltd offers a 12-month warranty to its customers with the electrical appliances that it sells. Warranty liabilities are estimated at 10% of sales for the previous 12 months.
On July 1, 2015, the balance of the Warranty Provision account was $10,000.
During the year ended June 30, 2016, warranty repair cost is $7,500, of which $4,000 was for inventory parts and $3,500 was for wages.
Revenue from the sale of electrical appliances in the current financial year is $60,000. There have been no changes in suppliers, product quality or prices.
Required:
(i) Construct the Warranty Provision account.
(ii) Prepare the journal entries to record the warranty claims during the year ended June 30, 2016. Ignore narrations.
(iii) Prepare the journal entries to record the balance-day adjustments to the Warranty Provision account. Ignore narrations.
(iv) Do you think the warranty provision of $10,000 as at July 1, 2015 is adequate to cover warranty claims made during the financial year ended June 30, 2016? Give reason(s) for your answer.
(4 + [4 + 3 + 1 + 1] = 13 marks)
Question 7
Below is the information for Simone Ltd required for the preparation of their bank reconciliation for July 31, 2016.
(i) The bank statement balance as at July 31, 2016 is $3,426 (Cr).
(ii) The Cash at bank ledger account balance (unadjusted) as at July 31, 2016 is $6,930 (Dr).
(iii) The total amount of unpresented cheques is $585.
(iv) Cash of $1,175 deposited into the bank on July 31 was recorded in the company’s general ledger but this amount does not appear on the bank statement.
(v) The bank statement shows a bank service charge of $25 debited by the bank on July 30, 2016.
(vi) Two errors were noted. A cheque for $98 for supplies was recorded as $89 in the general ledger. A cheque received from customer was entered in the cash book as $3,200 instead of $320.
Required:
(a) Determine the adjusted cash at bank account as at July 31, 2016 in Simone Ltd’s general ledger.
(b) Prepare the monthly bank reconciliation statement as at July 31, 2016.
(c) List three (3) internal control principles that would reduce the probability of errors occurring in the processing of cash transactions.
(4 + 4 + 3 = 11 marks)
Question 8
(a) Distinguish three key differences between the periodic and perpetual inventory methods.
(b) Pokaman Ltd uses the periodic inventory method with its year-end falling on December 31. The following inventory information is available:
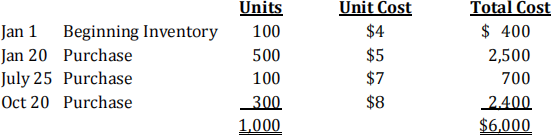
A physical count of inventory on December 31, 2015 revealed that there were 350 units on hand.
Required:
Answer the following independent questions and show computations supporting your answers.
(i) Assume that the company uses the average cost method. The value of the ending inventory as at December 31, 2015 is $ .
(ii) Assume that the company uses the LIFO method. The value of the ending inventory as at December 31, 2015 is $ .
Question 8 (con’t)
(c) Puriflower sells air purifiers and its financial year ends on June 30. The business uses a perpetual inventory system and FIFO inventory cost flow method.
On June 1, 2016, Puriflower has an inventory of 400 units of air purifiers at a cost of $150 each.
During the month of June, the following transactions occurred:
June 6 – Purchased 280 units of air purifiers at $160 each on credit.
June 16 – Sold 300 units of air purifiers for cash at $500 each.
June 20 – Sold 240 units of air purifiers on credit at $550 each.
June 30 – A physical stock count revealed that there were 136 units of air purifiers left in the warehouse.
The total net realisable value for air purifiers as at June 30, 2016 is $22,000.
Required:
(i) Construct the ‘Inventory’ account for the month of June 2016.
(ii) Determine the cost of goods sold for air purifiers as at June 30, 2016.
(iii) What should be the reported value of ending inventory for air purifiers as at June 30, 2016? Give reasons for your answer.
(3+ (1 + 1) + (6 + 1 + 2) = 14 marks)
2023-08-05