Practice test 1 2022
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Practice test 1 2022
SECTION A
1 The following are statements about plant cell walls. Which of the statements is TRUE?
a. All plant cell walls are rigid and are not deposited until the cells have stopped growing
b. Lignin is a linear polymer that adds flexibility to cell walls
c. Pectin gives cell walls their tensile strength
d. The microtubule cytoskeleton directs the orientation in which cellulose is deposited in the cell wall
e. The main structural components of cell walls are proteins not polysaccharides
2 Which of the following molecules is LEAST able to pass through gap junctions?
a. cAMP
b. Na+ ions
c. Cl- ions
d. Water
e. Proteins
3 Which ONE of these statements regarding integrins is FALSE?
a. They change their conformation in response to signals
b. They can be regulated by extracellular signals
c. They can be regulated by intracellular signals
d. They form a connection between the intracellular cytoskeleton and extracellular pectin
e. They are transmembrane heterodimers
4 Which of the following statements concerning glycosaminoglycans is TRUE?
a. They are positively charged
b. They are built up from repeating trisaccharide units
c. They are responsible for repelling water molecules from the extracellular matrix
d. They help maintain a high concentration of cations in the extracellular matrix
e. They are found only in the extracellular matrix of epithelial cells
5 Which of the following statements concerning gap junctions is FALSE?
a. They allow unrestricted movement of small water-soluble molecules from cell to cell
b. They contain connexon proteins
c. They consist of small regions where the plasma membranes of two cells are very closely apposed
d. They are important for electrical coupling between cardiac muscle cells
e. They allow waves of electrical stimulation to spread synchronously throughout the heart
6 What is the best explanation of why the rate of growth of rabbit limb long bones slows and ceases?
a. The level of systemic growth hormone falls with time.
b. The level of pituitary hormone falls with time.
c. Proliferating cells no longer make receptors so have to share them between daughters on ever division.
d. Signalling within the growing bone becomes less efficient as bone growth separates the periosteum from the growth plate more and more.
e. As cells multiply, they accumulate an enzyme that destroys growth hormone.
7 Colonies of Bacillus subtilis take the form of branched structures when in agar under low concentrations of nutrients. Which one of the following correctly describes the conditions under which the branching will be most sparse (fractal dimension lowest)?
a. Low agar stiffness, lowest concentration of nutrients
b. Low agar stiffness, highest concentration of nutrients
c. High agar stiffness, lowest concentration of nutrients
d. High agar stiffness, highest concentration of nutrients
e. Mid agar stiffness, middle concentration of nutrients
8 Which of these statements provides the BEST definition of ‘terminal differentiation’?
a. The state a cell takes after it stops dividing
b. Differentiation that results in cell death
c. The process by which a cell ceases to be a stem cell
d. The binary choice between two different cell types
e. Differentiation to give the final specialised cell type
9 The transcription factor, GATA1, drives the differentiation not only of erythrocytes but also megakaryocytes and eosinophils. How can it achieve these different cell fate outcomes?
a. Different forms of GATA1 protein are expressed in the precursors of these cells
b. These cell types are closely related and so express the same genes
c. GATA1 only triggers the process of differentiation, it does not regulate the specific target genes expressed in these different cell types
d. Phosphorylation of GATA1 protein enhances its activity only in erythrocytes
e. In each cell type, GATA1 protein functions in combination with a different group of transcription factors
10 Which statement about the phosphorylation of transcription factors is FALSE:
a. During protein synthesis, phosphoserine can be incorporated instead of serine
b. Phosphate is transferred from ATP to a serine residue by a kinase enzyme
c. Phosphorylation can cause a conformational change of the transcription factor
d. Phosphorylation is an example of a post-translational modification
e. Phosphorylation can result in activation, inhibition or degradation of a transcription factor
11 Which ONE of the following is an embryonic germ layer?
a. Pachyderm
b. Epiderm
c. Hypoderm
d. Ectoderm
e. Ecoderm
12 To which family of transcription factors does GATA1 belong?
a. Zinc finger
b. Myb
c. MADS
d. Homeodomain
e. bHLH
13 Which ONE of the following transcription factors is NOT involved in muscle development?
a. MyoD
b. Pax6
c. Pax3
d. Mrf4
e. Myogenin
14 Which ONE of the following is most likely to be a housekeeping protein?
a. Haemoglobin
b. MyoD
c. Insulin
d. Cyclin A
e. Trypsin
15 Which of these proteins phosphorylates transcription factors?
a. MAP kinase kinase
b. Phosphofructokinase
c. Adenylate cyclase
d. MAP kinase
e. GATA1
16 Which of the following BEST defines the term 'paracrine signal'?
a. A signal that acts on the cell type that produces it
b. A signal that acts parallel to another signal
c. A signal that acts on a cell type other than the one that produces it
d. A signal that operates at long range
e. A signal that triggers parturition
17 Which best describes how sex phenotype in chickens is determined?
a. By a combination of an environmental signal and a genetic signal
b. By an environmental signal acting cell autonomously
c. By an environmental signal acting cell non-autonomously
d. By a genetic signal acting cell autonomously
e. By a genetic signal acting cell non-autonomously
18 Some strains of dog have disproportionately short legs compared to their wolf-like ancestors. What has happened somewhere in the process of dog-breeding to cause this:
a. Contact mediated repulsion
b. Lateral inhibition
c. Ectopic gene expression
d. The ‘French Flag’ model
e. Cell-autonomous signalling
19 In an experiment, a ureteric bud from a green mouse (all cells are tagged with green
fluorescent protein) is cultured with metanephric mesenchyme from a red mouse (all cells are tagged with red fluorescent protein). Which one of the following outcomes might you expect to see after a few days in culture?
a. A kidney containing red collecting ducts and green nephrons
b. A kidney containing green collecting ducts and red nephrons
c. A kidney containing red collecting ducts and red nephrons
d. A kidney containing green collecting ducts and green nephrons
e. A kidney in which the red and green cells are distributed evenly between collecting ducts and nephrons
20 Which statement is correct? The kidneys of a sprouty homozygous knockout mutant mouse would:
a. Be too big
b. Be too small
c. Be polycystic
d. Develop with supernumerary ureteric buds
e. Not develop at all
21 Nephron and collecting duct morphology are influenced by:
a. Oriented cell division only
b. Directed cell intercalation only
c. Oriented cell division and directed cell intercalation
d. Differential growth with respect to the surrounding mesentery
e. None of the above
22 Which of the following tissues are NOT renewed by stem cells?
a. Blood
b. Gut
c. Skin
d. Inner cell mass
e. Drosophila germline
23 Where are the stem cells for the epidermis of the skin located?
a. Basal layer
b. Cornified layer
c. Suprabasal layer
d. Dermis
e. Villus
24 The ability of the mammalian gut to regenerate after damage such as that caused by irradiation depends on:
a. Stem cells being kept ‘hidden’ from damage in the niche
b. Partially differentiated cells de-differentiating and repopulating the niche
c. Cells from the haematopoietic system repopulating the niche
d. Pluripotent stem cells throughout the body repopulating the niche
e. Niche cells forming stem cells
25 Understanding how part of the neural tube develops into the midbrain and then into specific neuronal cell types within it has aided regenerative medicine strategies for Parkinson’s
disease. During development, which of the following signal combinations instructs the formation of the midbrain as a whole?
a. Presence of uniformly high Shh and low FGF8
b. Presence of FGF8 and medium Wnt
c. Presence of FGF8 and high Wnt
d. Presence of FGF8 and absence of Wnt
e. Presence of FGF8, high Wnt and high Shh
26 Which one of the following statements best describes WNT signalling in early embryos of bilaterally symmetrical animals?
a. WNT ligands and WNT inhibitors are both expressed in the anterior region of the embryo, but at different protein concentrations
b. WNT inhibitors are expressed in the anterior region, and WNT ligands are expressed in the posterior region of the embryo
c. WNT ligands are expressed in the anterior region, and WNT inhibitors are expressed in the posterior region of the embryo
d. WNT ligands are uniformly expressed along anterior-posterior axis, while WNT inhibitors are expressed highest in the anterior region
e. WNT signalling specifies the most anterior part of bilateral organisms
27 Which type of unicellular organism is thought to resemble the ancestral cells that gave rise to metazoan animals?
a. Choanoflagellates
b. Choanocytes
c. Biflagellates
d. Ciliated protozoans (Paramecium)
e. Collared cells
SECTION B
A.
Cyclopamine is a potent toxin produced by the skunk cabbage plant that specifically inhibits the function of Sonic hedgehog (Shh).
1. If cyclopamine is injected into a chicken egg at the time when limb development was underway, what would you expect the resulting chick’s wings to look like?
a. Wings with extra digits in a perfect mirror image digit pattern
b. Wings with extra digits in a partial mirror image digit pattern
c. Wings with missing digits
d. Chick legs
e. A severely truncated wing with barely recognisable bone structure
B.
In an experiment to understand how chicken wings develop, the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) was surgically removed after 3 days of development. After a few more days of development, a severely truncated wing was observed. In a control experiment, removing the AER and then immediately replacing it did not impair subsequent wing development.
2. What conclusion can be drawn from this experiment alone?
a. AER signals to nearby cells, which differentiate into a limb.
b. Nearby cells signal to AER, which differentiates into a limb.
c. AER grows to form the limb without signalling to/from nearby cells.
d. The AER is important for wing formation but it is not possible to conclude how
e. The AER is completely dispensable for wing formation.
C.
The following diagram shows the influence of four factors (1-4) on progression through the G1-S transition of the cell cycle. The identity of factors 1-4 is not important here, just the logic of their regulatory interactions. The other named things are proteins we met in a very similar diagram in the lectures.
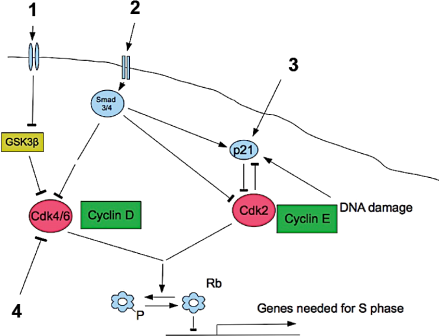
Factors 1, 2, 3 and 4 could each be needed for entry to S phase, or alternatively they could block entry to S phase.
3. Which of the following statements about Rb protein is FALSE?
a. Is the abbreviation for Retinoblastoma protein
b. Is regulated by phosphorylated
c. Inhibits transcription of genes required for S phase progression
d. Is regulated by cyclins
e. Is not influenced by external cellular signals
4. By following the connections of the diagram, determine whether each factor encourages or inhibits entry to S phase
a. Encourages, inhibits, inhibits, inhibits
b. Encourages, encourages, encourages, encourages
c. Inhibits, inhibits, inhibits, inhibits
d. Inhibits, encourages, encourages, inhibits
e. Inhibits, inhibits, encourages, encourages
D.
In human erythrocytes, the majority of haemoglobin is a tetramer consisting of two α globin chains
and two β globin chains (α2 β2). However, in the erythrocytes of a human foetus, the β chain is replaced by a related γ globin chain (α2γ2). α2γ2 haemoglobin has different oxygen binding characteristics from α2 β2, which allows efficient transfer of oxygen across the placenta from maternal blood to foetal blood. This set of questions concerns γ and β globin gene regulation.
The following transcription factor interactions describe how these two globin genes are regulated. Although based on real transcription factors, names have been changed (apart from GATA1 which you will recognise from the lectures).
Take a moment to deduce from these schematics the progression of gene regulation that is likely to occur first in the foetus (expresses the γ globin gene) and then after birth (expresses the β globin gene).
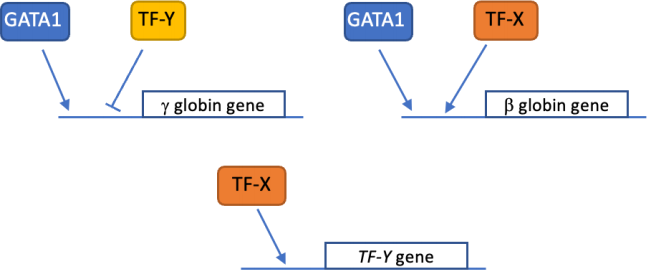
5. At which stage do you deduce that TF-Y is present in erythrocyte precursor cells?
a. In the foetus only
b. After birth only
c. At all developmental stages
d. At no stage is TF-Y present
e. There is not enough information to deduce TF-Y's expression
6. Which option MOST LIKELY describes the logic for the regulation of the β globin gene by the transcription factors?
a. GATA1 and TF-X
b. TF-X or GATA1
c. GATA1 and not TF-Y
d. TF-X and not γ GLOBIN
e. TF-X and not TF-Y
7. If the TF-Y gene is mutated so that it does not produce functional protein, what would be observed during development? (Assume that the only function of TF-Y is as shown here.)
a. The switch from γ to β globin synthesis would happen normally
b. At birth, β globin synthesis will begin normally but γ globin synthesis will not be switched off.
c. Excess γ globin synthesis will occur, which will harm the foetus
d. β globin synthesis will begin prematurely in the foetus
e. The switch from γ to β globin synthesis would be reversed
2023-08-04