CTO2 Practice Exam November 2022
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CTO2 Practice Exam November 2022
Section A
1. Which of the following is a complex network of phenolic compounds, abundant in secondary cell walls?
☐ A. Cellulose
☐ B. Collagen
☐ C. Lignin
☐ D. Pectin
☐ E. Proteoglycan
2. Which one of the following molecules interacts directly with the cytoplasmic domain of cadherins, thereby providing a connection to the cytoskeleton?
☐ A. Actin
☐ B. Catenins
☐ C. Integrin
☐ D. Laminin
☐ E. Tubulin
3. Which ONE of the following answers pairs the correct molecule with the specific type of connection between animal cells?
☐ A. Cadherins and focal adhesions
☐ B. Claudins and adherens junctions
☐ C. Connexins and gap junctions
☐ D. Integrins and adherence junctions
☐ E. Integrins and tight junctions
4. Which one of the following statements about cell junctions is FALSE?
☐ A. Adherens junctions connect actin filaments in adjacent animal cells
☐ B. Desmosomes connect intermediate filaments in adjacent animal cells
☐ C. Gap junctions seal the gap between adjacent epithelial cells to prevent leakage
☐ D. Hemidesmosomes anchor intermediate filaments in an animal cell to the extracellular matrix
☐ E. Plasmodesmata directly connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells
5. Which of the following types of intercellular junctions normally contain cadherins?
☐ A. Adherens junctions, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
☐ B. Adherens junctions only
☐ C. Both adherens junctions and desmosomes
☐ D. Both desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
☐ E. Desmosomes only
6. Which of the following statements concerning selectins is FALSE?
☐ A. Selectins are cell surface proteins that recognise and bind to carbohydrates
☐ B. Selectins are expressed by endothelial cells, which line blood vessels
☐ C. Selectins are important for co-ordinated movement of epithelial cells during neural tube closure
☐ D. Selectins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton, through specific adaptor proteins
☐ E. There are multiple types of selectins in vertebrates
7. Extracellular matrix from which ONE of the following tissues contains the highest proportion of glycosaminoglycans?
☐ A. Bone
☐ B. Cartilage
☐ C. Skin
☐ D. Tendon
☐ E. Vitreous humour
8. Which one of these statements concerning the basal lamina is FALSE?
☐ A. It contacts the apical side of an epithelium
☐ B. It contains laminin
☐ C. It contains type IV collagen
☐ D. It is also known as the basement membrane
☐ E. It is produced in part by overlying epithelial cells and in part by underlying stromal cells
9. Cell proliferation can be controlled by a number of different signalling systems. Which one of these is NOT scale-invariant?
☐ A. All of these options are scale-invariant
☐ B. Mechanical tension
☐ C. Morphogen gradient
☐ D. Planar cell polarity
☐ E. Systemic hormones
10. Which of the following mutations/pathologies results in a body with markedly non-Vitruvian proportions?
☐ A. Achondroplasia
☐ B. Alon syndrome (growth hormone receptor mutation)
☐ C. Insulin deficiency
☐ D. Pituitary insufficiency
☐ E. Pituitary tumours of childhood
11. Which of the following options best describeshow the two hind-legs of a rabbit come to be the same size?
☐ A. Mechanical load reduces leg growth, so a longer leg, which will reach the ground and bear the animal's weight, stops growing until the other leg has caught up to share the load.
☐ B. The growing legs continually signal their size to one another, and the larger (if either happens to be larger) slows its growth to allow the smaller to catch up.
☐ C. The growing legs continually signal their size to one another, and the smaller (if either happens to be smaller) accelerates its growth to catch up.
☐ D. The legs grow independently and the larger the leg bone has grown, the less sensitive it becomes to growth-promoting hormones.
☐ E. The legs grow independently of one another at a rate directly controlled by circulating growth-promoting hormones; as these hormones reach both legs, they end up the same length.
12. Which one of the following options correctly describes the chain of causation in mammalian growth control?
☐ A. The liver makes Growth Hormone, which signals to the pituitary gland, which responds by making IGF I/II, which signal to other growing tissues
☐ B. The liver makes IGF I/II, which signal to the pituitary gland, which responds by making Growth Hormone, which signals to other growing tissues
☐ C. The pituitary gland makes Growth Hormone, which signals to the liver, which responds by making IGF I/II, which signal to other growing tissues
☐ D. The pituitary gland makes IGF I/II, which signal to other growing tissues, which produce Growth Hormone to give feedback to the pituitary gland and the liver
☐ E. The pituitary gland makes IGF I/II, which signal to the liver, which responds by making Growth Hormone, which signals to other growing tissues
13. There are 5 basic zones of a growth plate in bones: which one of the following options lists them in anatomical order from distal to proximal position in the bone?
☐ A. Proliferative zone, zone of cartilage maturation, zone of cell enlargement, zone of cartilage death, replacement of cartilage with bone
☐ B. Proliferative zone, zone of cell enlargement, zone of cartilage maturation, zone of cartilage death, replacement of cartilage with bone
☐ C. Zone of cartilage maturation, proliferative zone, zone of cell enlargement, zone of cartilage death, replacement of cartilage with bone
☐ D. Zone of cell enlargement, zone of cartilage maturation, proliferative zone, zone of cartilage death, replacement of cartilage with bone
☐ E. Zone of cell enlargement, zone of cartilage maturation, zone of cartilage death, replacement of cartilage with bone, proliferative zone
14. In the lectures, we discussed ways in which limitations to the size of an individual cell can be circumvented in some organisms. Which of the following does NOT result in there being
more than two copies of each nuclear gene in a cell's cytoplasm?
☐ A. Cell fusion
☐ B. Chromosome endoreduplication
☐ C. Formation of a syncytium
☐ D. Formation of a vacuole (plant cells)
☐ E. Formation of polytene chromosomes
15. Which one of the following statements about cyclins is TRUE?
☐ A. Cyclins all rise in concentration at the start (M-G1 transition) of the cell cycle
☐ B. Cyclins are protein kinases
☐ C. Cyclins bind to cdks
☐ D. No cyclin is present in mitosis
☐ E. No cyclin is present in S phase
16. Which one of the following options best summarizes the trophic hypothesis?
☐ A. Each cell type of a mature body depends for its survival on signals from other cell types
☐ B. Elective cell death is a normal feature of human development
☐ C. Elective cell death of one cell can be triggered by signals from other cell types
☐ D. Overall tissue growth is a balance between proliferation and death
☐ E. The future vas deferens will die in female bodies because of the lack of testosterone
17. Where in the cell would you most likely find a transcription factor located?
☐ A. ECM
☐ B. Endoplasmic reticulum
☐ C. Golgi apparatus
☐ D. Nucleus
☐ E. Plasma membrane
18. Concerning the concept of ‘gene constancy’, which statement is FALSE?
☐ A. A frog skin cell can generate an entire organism when grown in isolation
☐ B. A nucleus from a differentiated cell can support development of a whole embryo under some conditions
☐ C. Cells generally differ in their gene expression rather than gene content
☐ D. Gene constancy is a feature of both plants and animals
☐ E. With few exceptions, all cells in the body generally contain a full complement of genes
19. During muscle differentiation, which of the following best describes the function of growth factors?
☐ A. They cause MyoD to be phosphorylated, leading to its degradation
☐ B. They cause MyoD to be phosphorylated, stimulating its activity
☐ C. They cause Pax3 to be phosphorylated, allowing it to regulate the MyoD gene
☐ D. They inhibit proliferation of the myoblasts
☐ E. They stimulate the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes
20. The following are statements concerning the process of pancreas development. Which of these statements is FALSE?
☐ A. Activation of Pdx1 transcription factor is a key event in forming the pre-pancreatic region
☐ B. In the gut, transcription factor Sox17 provides the potential to regulate Pdx1
☐ C. Pancreas formation requires interaction between mesodermaland endodermal tissues
☐ D. Part of the gut endoderm locally secretes FGF2, which induces pancreas formation in the mesoderm
☐ E. Transcription factor Ngn3 is required for all endocrine cell differentiation
21. Which statement best describes the regulation of the MyoD gene by Myf5 and Pax3?
☐ A. MyoD gene transcription is activated by either Myf5 or Pax3
☐ B. MyoD gene transcription is activated by Myf5 and Pax3 working together
☐ C. MyoD gene transcription is activated by Myf5 but inhibited by Pax3
☐ D. MyoD gene transcription is inhibited by Myf5 or Pax3
☐ E. Pax3 activates transcription of the Myf5 gene, and then Myf5 activates MyoD gene transcription
22. Which of the following is correct concerning embryonic germ layers?
☐ A. Muscle and neurons both arise from the mesoderm
☐ B. Muscle and pancreas both arise from the mesoderm
☐ C. Muscle arises from the mesoderm; neurons arise from the ectoderm
☐ D. Muscle can arise from ectoderm, mesoderm, or endoderm
☐ E. Neurons arise from the mesoderm, pancreas arises from the endoderm
23. Which ONE of the following is most likely to be a housekeeping protein?
☐ A. Haemoglobin
☐ B. Insulin
☐ C. MyoD
☐ D. Trypsin
☐ E. Tubulin
24. Which ONE pair of transcription factors is involved in the erythroid/myeloid decision process in haematopoiesis?
☐ A. GATA1 and PAX6
☐ B. GATA1 and PU.1
☐ C. MYF5 and GATA1
☐ D. MYF5 and PAX3
☐ E. PO.1 and GATA2
Section B
25. An organ in the organism you are studying consists of three regions containing populations of distinct differentiated cell types – A, B and C (Figure 1).
The expression patterns of two transcription factors were determined in this organ (TF1 and TF2) (Figure 2).
Use this information to infer how different genes might be regulated, as given in the questions.
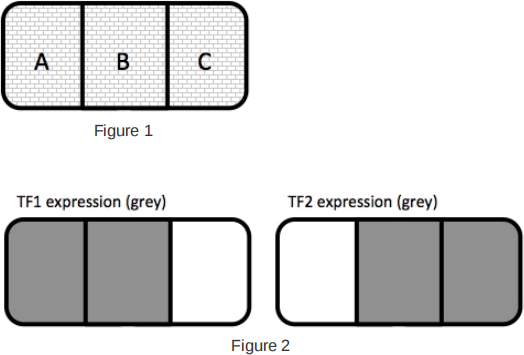
1) Gene X is found to be exclusively transcribed in cells of type ‘A’. Which statement describes the most plausible mechanism by which Gene X transcription is regulated by TF1 and TF2?
☐ Both TF1 and TF2 together are required to activate Gene X
☐ Either TF1 or TF2 are sufficient to activate Gene X
☐ TF1 activates Gene X, TF2 has no role in regulating Gene X
☐ TF1 activates Gene X but TF2 prevents this
☐ TF2 represses Gene X but TF1 prevents this
2) If TF1 were rendered non-functional due to mutation, in which cells would Gene X be transcribed?
☐ A cells
☐ All the cells
☐ B cells
☐ C cells
☐ None of the cells
3) A different gene, Gene Y, is found to be exclusively expressed in ‘B’ cells. Which statement describes the most plausible mechanism by which Gene Y transcription is regulated by TF1 and TF2?
☐ Both TF1 and TF2 together are required to activate Gene Y
☐ Either TF1 or TF2 are sufficient to activate Gene Y
☐ TF1 activates Gene Y; TF2 has no role in regulating Gene Y
☐ TF1 activates Gene Y but TF2 prevents this
☐ TF2 represses Gene Y but TF1 prevents this
4) The mRNA product of yet another gene, Gene Z, is present in ‘A’ and ‘B’ cells, but Gene Z protein is only present in ‘B’ cells. Which statement best describes the transcriptional
regulation of Gene Z by TF1 and TF2?
☐ Both TF1 and TF2 together are required to repress transcription of Gene Z
☐ Either TF1 or TF2 are sufficient to activate transcription of Gene Z
☐ TF1 activates transcription of Gene Z
☐ TF1 activates transcription of Gene Z but TF2 prevents this
☐ TF2 activates transcription of Gene Z
26. In the development of the kidney, groups of cells aggregate together and, when each
aggregate is large enough, the cells in it go on to differentiate into epithelial vesicles. The
cells produce a signalling molecule X and also receptors for the same molecule. A researcher proposes a hypothesis that molecule X is used by the cells for quorum sensing.
To test this, the researcher decides to treat kidneys developing in culture (a) with a
pharmacological antagonist of X, or (b) with exogenous X. In a control experiment, kidneys treated with nothing were found to develop normally.
For the two experimental conditions, which of the following sets of results would most support the researcher’s hypothesis?
☐ Kidneys treated with the antagonist develop small vesicles and do so early; those treated with exogenous X develop large vesicles and do so late.
☐ Kidneys treated with the antagonist develop small vesicles and do so early; those treated with exogenous X develop unusually large aggregates but do not develop vesicles.
☐ Kidneys treated with the antagonist develop unusually large aggregates but do not develop vesicles; those treated with exogenous X develop large vesicles and do so late.
☐ Kidneys treated with the antagonist develop unusually large aggregates but do not develop vesicles; those treated with exogenous X develop normally
☐ Kidneys treated with the antagonist develop unusually large aggregates but do not
develop vesicles; those treated with exogenous X develop small vesicles and do so early
27. As we saw in the lectures, the neural crest is a migratory population of cells that arises in the dorsal part of the neural tube. The cells undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition then leave the neural tube and migrate in a loose mass to distant parts of the embryo, where they can clump together tightly to form groups of sensory neurons (ganglia).
During this process, neural crest cells express different cadherin molecules in a particular order (Figure 1). Specifically:
![]() Presumptive neural crest cells in the neural tube express cadherin-6B, but down- regulate its expression immediately before migrating
Presumptive neural crest cells in the neural tube express cadherin-6B, but down- regulate its expression immediately before migrating
. After leaving the neural tube, migrating cells express cadherin-7.
. When they have reached their final destination, they activate N-cadherin expression.
Given these expression patterns, predict the MOST LIKELY consequence of each of the following experimental manipulations.
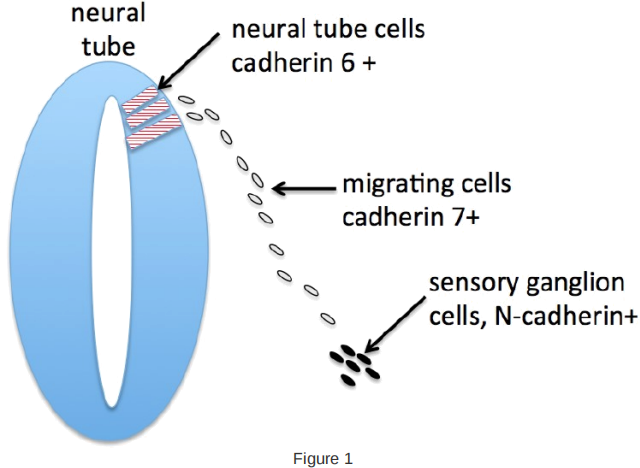
1) Increased expression of cadherin-6B in the neural tube would most likely lead to which outcome?
☐ Migrating cells clump together less tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migrating cells clump together more tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migration of neural crest cells from the neural tube is completely blocked
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally, but fail to clump together to form ganglia
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally and clump together very tightly to make abnormally small ganglia
2) Decreased expression of cadherin-6B in the neural tube would most likely lead to which outcome?
☐ A decreased number of neural crest cells migrate from the neural tube
☐ All neural crest cells die, leading to a much smaller neural tube
☐ An increased number of neural crest cells migrate from the neural
☐ Migration of neural crest cells from the neural tube is completely blocked
☐ No effect on neural crest cell migration
3) Decreased expression of cadherin-7 in migrating neural crest cells would most likely lead to which outcome?
☐ Migrating cells clump together less tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migrating cells clump together more tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migration of neural crest cells from the neural tube is completely blocked
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally, but fail to clump together to form ganglia
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally and clump together very tightly to make abnormally small ganglia
4) Deleting the N-cadherin gene entirely, such that no N-cadherin is made in neural crest cells would mostly likely lead to which outcome?
☐ Migrating cells clump together less tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migrating cells clump together more tightly after leaving the neural tube
☐ Migration of neural crest cells from the neural tube is completely blocked
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally, but fail to clump together to form ganglia
☐ Neural crest cells migrate normally and clump together very tightly to make abnormally small ganglia
2023-08-04