ECN6510 Topic 3: Theory of the Firm
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Topic 3: Theory of the Firm
1. A profit-maximising firm has a production function given by:
q = ALαKβ
where α > 0, β > 0, α + β < 1, , L denotes labour and K denotes capital. The firm’s total costs are given by: WL + rK where W denotes wages, r denotes the unit price of capital. The firm sells its output at a given market price, p.
(a) Explain the difference between decreasing, constant and increasing returns to scale and indicate which describes this firm’s production function. [20%]
(b) Derive expressions for the firm’s optimal demand for labour and capital and comment on their properties. [20%]
(c) Derive the supply function of the firm and comment on its properties. Explain what happens to the supply function if α + β = 1 [20%]
(d) The firm now aims to maximise output subject to incurring costs, C*. Derive expressions for the optimal demand for labour and capital as a function of output, comment on their properties and compare the expressions to those derived in part (b). [40%]
2. A firm has a production function given by:
q = ALαKβ
where q denotes output, L denotes labour, K denotes capital, A>0 and A>0. The firm’s total costs are given by:
C = WL + rK
where w denotes wages and r denotes the unit price of capital.
(a) The producer aims to maximise output subject to total costs being equal to C*. Derive the input demand functions for L and K and comment on how realistic their properties are. [40%]
(b) Derive the cost function associated with part (a) and comment on its properties. [20%]
(c) Present a general proof of Shephard’s Lemma in the context of producer theory and comment on its role in the theory of the firm. [40%]
3. A firm has a cost function, derived via output constrained cost minimisation, given by:
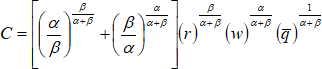
where ![]() denotes the target output level, w denotes wages, r denotes the unit price of capital, α + β = 1, α > 0 and β > 0.
denotes the target output level, w denotes wages, r denotes the unit price of capital, α + β = 1, α > 0 and β > 0.
(a) Give an example of an industry where output constrained cost minimisation might apply and analyse four properties of the above cost function. [20%]
(b) Use the above cost function to derive the conditional input demand functions for capital and labour. [40%]
(c) Analyse four properties of the conditional input demand functions derived in part (b) and comment on the realism of these properties. [20%]
(d) Comment on the significance of Shephard’s Lemma for producer theory. [20%]
4. A firm has a production function given by:
q = ALαKβ
where q denotes output, L denotes labour, K denotes capital, A>0 and α + β = 1. The firm’s total costs are given by:
C = WL + rK
where w denotes wages and r denotes the unit price of capital.
(a) Explain whether the production function has increasing, decreasing or constant returns to scale. [10%]
(c) The producer aims to minimize total costs subject to producing a target output level of ![]() . Derive the conditional input demand functions for K and L and state four properties of the conditional input demand functions. [50%]
. Derive the conditional input demand functions for K and L and state four properties of the conditional input demand functions. [50%]
(c) Derive the cost function associated with part (b) and state four of its properties. [20%]
(d) Use Shephard’s Lemma to derive the conditional input demand functions from the cost function. [20%]
2023-08-01