ACC41020 Accounting Technology
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ACC41020 Accounting Technology
Accounting Information Systems (AIS) Take Home Assignment
Please expand text boxes if necessary.
Q1. Define an Accounting Information System and list its functions.
Accounting Information System is a system that accumulates, records, stores, and processes data to produce information for decision-makers. It comprises personnel, procedures and instructions, data, software, IT infrastructure, and internal controls and security measures.
The functions of an accounting information system include:
Collect and store data about organisational activities.
Transform data into information so management can plan, execute, regulate, and assess activities, resources, and personnel.
Provide sufficient safeguards to protect the organisation's assets and data.
Q2. Describe the high-level elements of the revenue business process.
The revenue business process is a fundamental aspect of any organisation, as it entails the activities associated with generating income from selling products or services. It consists of a series of interconnected processes, beginning at the customer orders and continuing through deposit cash receipts. Here are the most critical components of the revenue business process:
Take customer orders: The procedure involves receiving a consumer order, which can occur via multiple channels, including online sales, sales representatives, and customer service departments.
The customer indicates a desire to buy products or services.
Sales Order Processing: The organisation processes the customer's order once received, including validating product availability, pricing, and discounts and ensuring the order is accurate and complete.
Deliver or ship order: Following the processing of the sales order, the organisation fulfils the order by either delivering the tangible products to the customer or providing the specified services.
Recognising Revenue: Recognising revenue is a crucial phase in the revenue business process, especially for companies that adhere to accrual accounting principles. Revenue is recorded when earned, and ownership risks and benefits are transferred to the customer. The timing of revenue recognition can vary depending on variables such as the nature of the product or service and the contractual terms.
Receive Cash: When a consumer receives goods or services from a company, they are required to make payment for them using one of several different payment methods, such as money in hand, a cheque, a credit card, or one of several other possibilities.
Deposit cash receipts: After receiving payment from a customer, the organisation is required to promptly deposit the funds into its designated bank account. This practice ensures that all sales-related cash inflows are accurately and promptly recorded in the company's financial records. By promptly depositing cash receipts, the organisation maintains an accurate and current representation of its financial position, enhancing transparency and facilitating effective financial management.
Q3. Describe an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system and explain how it differs from an Accounting Information System.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software solution. It offers a unified framework for integrating organizational activities, including production, payroll, sales, purchasing, and financial reporting. The main purpose of an ERP system is to increase organizational efficiency of an organization by managing and improving how company resources are utilized.
Accounting Information Systems (AIS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve diverse purposes and have distinct functions. The following describes their distinctions:
1. Functionality:
AIS: Manages the financial aspects of an organisation, including financial transactions, reporting, payroll, and tax compliance.
ERP: Provides an end-to-end business management solution, integrating departments and functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and sales, among others. It’s a standardization of procedures and reports.
2. Application and Integration:
AIS: Primarily focuses on accounting and financial processes, frequently to the exclusion of other business functions.
ERP: Integrates multiple departments and functions, facilitating streamlined data flow and communication across the organisation.
Integrated enterprise-wide allowing for better flow of the information as it’s stored in a centralized database and can be access by various departments which also improves customer service.
3. Industry-Particular Adaptation:
AIS: Typically a stand-alone product with few industry-specific modifications.
ERP: Many ERP vendors offer industry-specific solutions tailored to satisfy various industries' specific requirements.
4. Data Flow:
AIS focuses primarily on the passage and processing of financial data.
ERP: Facilitates the passage of data across all departments, ensuring a unified and consistent database. Data captured once (i.e., no longer need sales to enter data about a customer and then accounting to enter same customer data for invoicing).
5. Users
• AIS: Used primarily by accounting and finance professionals.
• ERP: Used by employees from different departments to manage modules pertinent to their responsibilities.
6. Ease of Use:
• AIS: Generally straightforward and easier to implement, with a concentration on standard accounting processes.
• ERP: Comprehensive and potent, but may require implementation and support expertise (learning new things are sometimes hard for employees). And it requires significant amount of time to implement.
Q4. This flowchart is for an engineering company that sends out engineers to fix machines. Describe the accounting system that is depicted in the following flowchart.
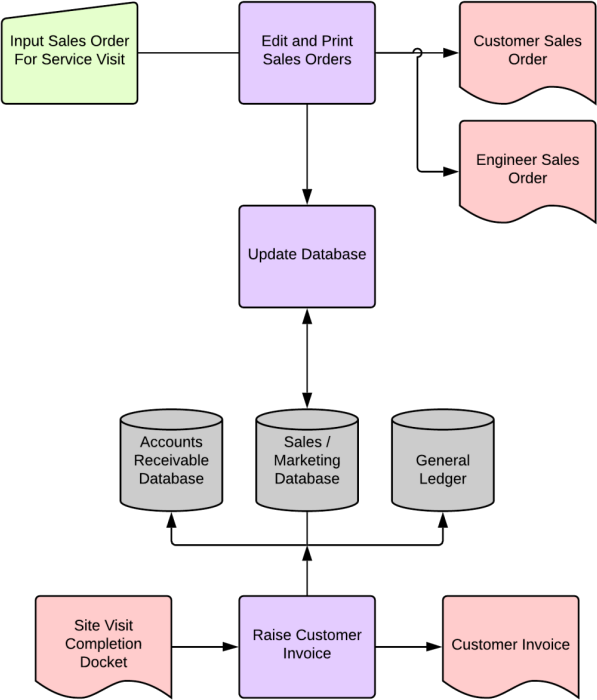
Q5. List the things that could go wrong in an invoicing system and suggest controls that could be used to manage that risk.
Q6. (a) Identify and describe the document below.
(b) When is this document prepared?
(c) Explain how it will be processed through an accounting system (such as SAP) and reflected in the financial statements.

2023-07-24