ENGN4528 Computer Vision Final Examination, First Semester 2020
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ENGN4528 Final Exam
S1 2020
College of Engineering and Computer Science
Final Examination, First Semester 2020
ENGN4528 Computer Vision
Question Booklet
Reading time: 15 minutes
Writing time: 3 hours
Uploading time: 15 minutes
Allotted Time
You will have 3 hours to complete the exam plus 15 minutes of reading time. An additional 15 minutes has also been allowed to accommodate the additional task of uploading your completed exam to the final exam turnitin submission portal on the ENGN4528 Wattle site. Thus you have 3 hours and 30 minutes to complete the exam. NO late exams will be accepted. You may begin the exam as soon as you download it.
Minimal requirements:
You may attempt all questions
You SHOULD NOT include an assignment cover sheet
You must type your ANU student identification number at the top of the first page of your submission
You must monitor your own time (i.e. there is no invigilator to tell you how many minutes are left).
Your answers must be clear enough that another person can read, understand and mark your answer. 11 or 12 point font with 1.5 spacing is preferred. Scanned images of handwritten equations or diagrams must be legible and of a suitable size.
Numbering questions
● You must specify the question you are answering by typing the relevant question number at the top the page
● Each question should begin on a new page
● Multi-part questions (e.g. question 1 parts a and b) may be addressed on the same page but should be clearly labelled (e.g. 1a, 1b )
● Questions should be answered in order
You must upload your completed answers in a single document file within the allotted time using a compatible file type for Turnitin (Preference: MS Word’s .doc or .docx format) It is the student’s
responsibility to check that the file has uploaded correctly within Turnitin. No late exams will be accepted.
Academic integrity
Students are reminded of the declaration that they agree to when submitting this exam paper via Turnitin: I declare that this work:
● upholds the principles of academic integrity as defined in the University Academic Misconduct Rules;
● is original, except where collaboration (for example group work) has been authorised in writing by the course convener in the course outline and/or Wattle site;
● is produced for the purposes of this assessment task and has not been submitted for assessment in any other context, except where authorised in writing by the course convener;
● gives appropriate acknowledgement of the ideas, scholarship and intellectual property of others insofar as these have been used;
● in no part involves copying, cheating, collusion, fabrication, plagiarism or recycling.
There are 10 questions in total.
(Q1-Q10)
Please name your submission as
ENGN6528_exam_u1234567.docx
Q1: (10 marks) [basic concepts]
Answer the following questions concisely. Each of the questions must be answered in no more than 5 lines of text. Longer answers will be penalized.
(1) According to David Marr, computer vision can be separated into three layers, low-
level, mid-level and high-level vision. Image processing, filtering, and low-level edge detection such as the Sobel filter are regarded as low-level vision. Give an example of amid-level vision task. [1 mark]
(2) Consider the HSV colour space. What does H, S, and V stand for? [1 mark] Describe the information that the S channel contains.
(3) What does SVM stand for? What does RANSAC stand for? [2 marks]
(4) Using the PCA technique, any image can be represented as a linear combination of some so-called “eigenfaces”, plus a noise image. The eigenfaces can be computed by using eigen-value decomposition of certain covariance matrix A. The representation then uses the top K Eigen faces in its representation. Describe how the top K eigenfaces are chosen? [2 marks]
(5) We can represent a face image by a feature vector (w1,…,wk), which is obtained by
projecting it to the face space (u1, u2,… , uk). Mathematically, it is defined as (w1, …, wk) = (u1T(x – µ), … , ukT(x – µ)).
Explain the process of evaluating a novel face and determining if the novel image is one of the faces in the training dataset. You can choose to do this by explaining the terms u1, x, and μ and their usage, or some other way if you prefer. [4 marks]
.
Q2: (21 marks) [3D SFM and Image formation question]
Answer the following questions concisely. Write down working, and if you are unsure
about some part along the way, state your best assumption and use it for the remaining
parts. Similarly, if you think some aspect is ambiguous, state your assumption and write the answer as clearly as you can.
(a) Given two calibrated cameras, C1 and C2, C1 has focal length of 500 in x and 375 in y, the camera has resolution 512x512, and the camera centre projected to image is at (249, 251), with no skew. Suppose C2 has the same resolution and focal length as C1,but the camera centre projected to image is at (252, 252). Write down the calibration matrix K1 and K2 for C1 and C2 respectively. (Hint: please only write down the final two 3x3
matrices.) [3 marks]
(b) Suppose that a 3D world coordinate system ((X,Y,Z) coordinates as in the below
diagram from the lecture notes) is defined as aligned with the camera coordinate system of C1. More specifically, the world origin is at the camera centre of C1, the Z axis is
aligned with the optical(principal) axis and the X and Y world coordinate systems
aligned parallel with the x andy axes of the image of C1. Write down the matrices
K[R|t] which define the projection of a point in world coordinate system to the image of C1. (Hint: please only write down the final 3x4 matrix.) [3 marks]
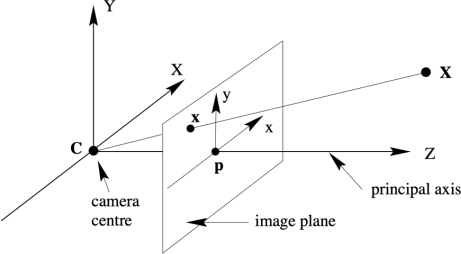
(c) Suppose that the scene has a point, P1, that in the world coordinate system defined
above that lies at (240, 235, 100). Note that the points in world coordinate system are
measured in cm. What location (to the nearest pixel) will that world point (P1) map to in the image of C1? [2 marks]
(d) Suppose that with respect to the world coordinate system that is aligned with camera C1, camera C2 begins being aligned to C1, and is then rotated by 45 degrees about its
vertical axis (Y-axis)(as shown below), and subsequently the centre of C2 is translated by 0.2 m to the left of C1 (along the X axis of C1). The two camera centres both remain on the same (X, Z) plane
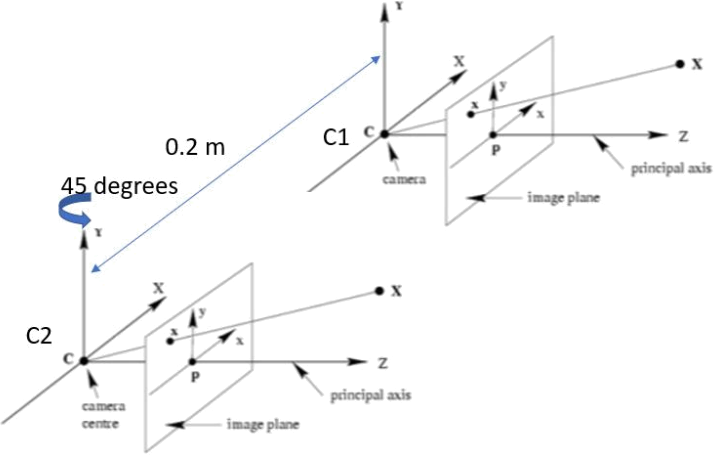
Write down the matrices K[R|t], which define the projection of points in the world system (i.e, the same coordinate system of C1) to the image of C2. (Hint: please only write down the final 3x4 matrix.) [3 marks]
(e) What is the location (to the nearest pixel) that P1 maps to in the image of Camera C2? (Hint: Please write down only the final result.) [2 marks]
(f) Define the term epipole. [2 points]
(g) For camera C1, there is an epipole (or epipolar point) that relates to Camera C2. For the two-camera setup for predicting structure from motion, what is the position of the
epipole in camera C1 of camera C2? (Hint: It is a point in the image coordinates of Camera C1). [2 points]
(h) Given a point P2 that appears in camera C1 at image location (x1, y1), and in camera C2 at image location (x2, y2). How would you find the world coordinates of point P2? [4 points]
Q3 [Camera models and SFM] (10 marks)
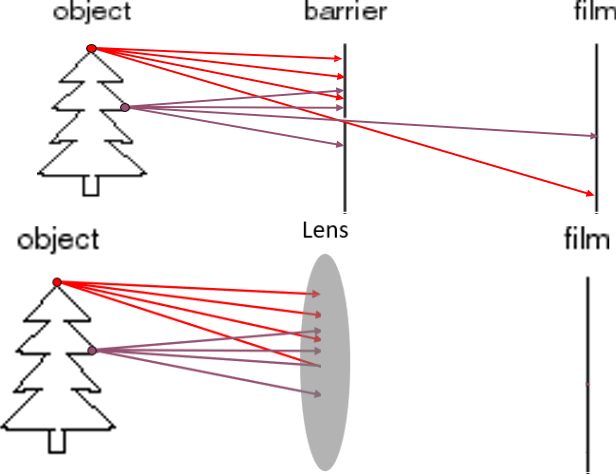
(a) The first image below is taken from the course lecture notes. It shows a pinhole
camera model, where all rays from the scene are blocked by a barrier, except those
from a single direction that pass through a pin-hole, resulting in the projection of an image (of a tree here) onto a film or ccd/CMOS sensor of a camera. However, as
shown in the second image below, many cameras include a thin lens rather than
simply a pin-hole barrier. How is the pin-hole model a good model for a camera with a lens? Explain in two or three sentences at a maximum, and/or with a diagram. [3 marks]
(b) Given two cameras with an unknown distance between them that view the same
scene. Suppose that you know the intrinsic parameters of both cameras, and they
both view a common object, for which a large number of accurately matched points are available in both images.
What information can you recover about the cameras and the scene from this
configuration up to scale? Describe what the parameters are to be recovered, and how many parameters there are. [3 marks]
(c) Suppose that you do know the intrinsic calibration parameters of both cameras,
describe a method for recovering camera and scene information given a set of point matches where a small number of the points maybe mismatched. [4 marks]
Q4: (10 Marks) [Shape-from-X, Stereo]
(a) Shape-from-Shading approaches predict the brightness of animage pixel. Given a
point light source at infinity (distant light source), write down the equation that defines the brightness at an image pixel assuming that the camera views a Lambertian surface, Please also define the terms of the equation. [2 marks]
(b) Suppose that we have used some other methods to know the brightness of the lighting, its direction and the reflectance properties of the surface in the above scenario, but we only have intensity information about this particular pixel for this surface, what can we say about the surface orientation? [2 marks]
(c) Suppose we have three images of this point from the same camera position, each taken by moving the light source to different locations. What could we then say about the
surface orientation at this point? [2 marks]
(d) The images (a and b) shown below are the left, and the right image of an ideal stereo pair,taken with two identical cameras (A and B) mounted at the same horizontal level and with their optical axes parallel.
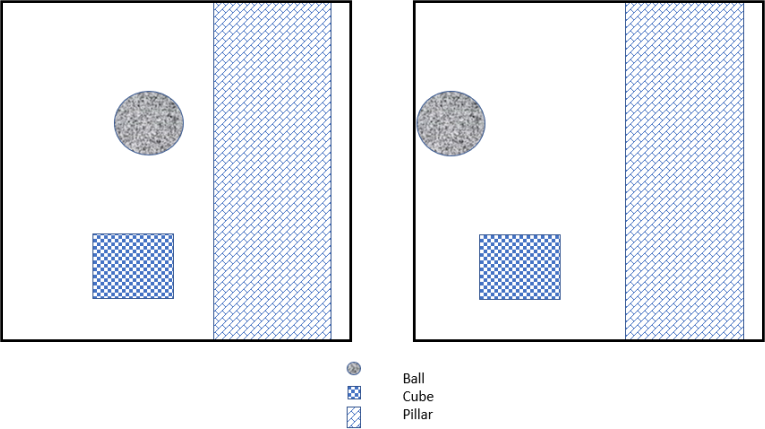
Draw a planar-view (i.e., a top-down bird-eye's view) of the scene showing roughly what the spatial arrangements of the three objects are. Only relative (rather than
accurate) positions are required. [4 marks]
Q5: (5 Marks) [Image Filtering and histogram modification]
Suppose that we have a histogram modification function as follows: (colour image)
M(v) = cv^,, where 0 <= v <= 255 (assuming pixel values for the camera are in the range of [0,255], where ,= 0.4, and c is 1.
(a) Suppose that we apply this to the following image. Describe what the effect will be on the modified histogram? [2 marks]

(b) Suppose we now use a different function that operates as follows:
M(v) = cv^,, where v < 50
M(v) = c(v-20)^,, where 50 <= v < 70
M(v) = cv^,, where v >=70
where,= 0.4, and c is 1.
Suppose that we apply this to (the histogram of) an image. What will be the effect on the histogram of the image? What will be the change to the output image? [3 marks]
Q6: (11 marks) [ Image filtering]
(a) Consider the 4 x 5 image below. The pixel grey values are indicated by the values in the cells.
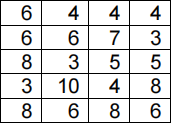
Apply the following filter to the image defined above. Note that to avoid problems at boundaries of the image you only need to calculate the filtered values for the 2x3
centred region. [4 marks]
Note: in solving this problem, please use a “correlation” rather than “convolution” operator to implement the image filtering.
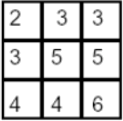
(b) The following is a separable filter. What does it mean to be a separable filter? [2 marks]
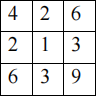
(c) Write down the separate components of the above filter. [4 marks]
(d) What is the difference between correlation and convolution? [1 mark]
Q7: (13 marks) [ Basic algorithms ]
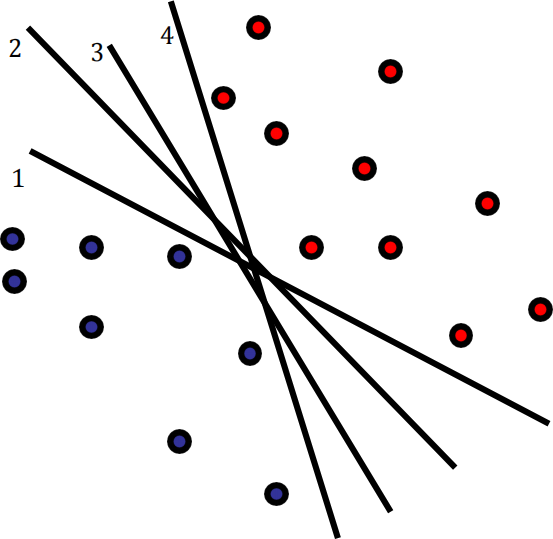
(a) Suppose that a linear support vector machine was used to classify the following
points(red vs blue are two classes). Which line (among 1, 2, 3 and 4) below defines the classifier computed based on a linear support vector machine. Your answer may be (1-4), or multiple or all of these? [1 mark]
(b) Explain (in a few words or a sentence) why you selected your answer. [2 marks]
(c) The Integral Image is apart of the Viola-Jones face detector that makes feature computation more efficient. Given an input image below, write down the corresponding integral image? [4 marks]
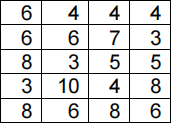
(d) Both the Viola-Jones face detector and the Histogram of Oriented Gradients detector use gradients as their basis for detection. What is the advantage of gradients over some other low-level descriptor (such as colour)? [2 marks]
(e) The Histogram of Oriented Gradients detector applies a window to determine if a
pedestrian occurs at a particular location in an image. This is broken up into 15x7
individual cells. What information does the descriptor include for each of these cells? [2 marks]
(f) The SIFT algorithm is not sensitive to the scale of the appearance of the locations
that it matches. Describe (in a few sentences) how SIFT achieves being able to match regions at a variety of scales. [2 marks]
Q8: (8 marks) [basic design problem]
Given below is a single node in a neural network. Supposing that d is 4, x={5,2,4,2}, and w={0.4,0.3,0.4,0.1}, b=0.1, and that the activation function is a standard ReLU, that is
=max(0,x), where x is the input to the activation function.
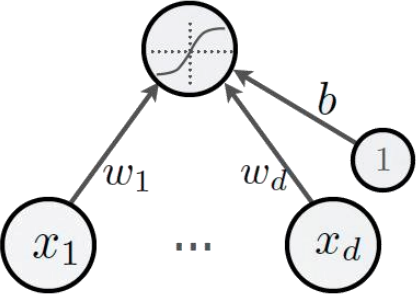
(a) What is the output of this node? [2 marks]
(b) Describe the difference between, recognition and detection in terms of how you would use a Deep Convolutional Network to solve the problem? [2 marks]
(c) In the VGG convolutional neural network, the first layer (CONV1) adopts a set of 3x3 filters for convolution, followed by a ReLU, then the second layer (CONV2) similarly adopts 3x3 Convolution filters, followed again by a ReLU. For the output of a single location (node) in CONV2, how many pixels of the input image would impact on the result? (i.e., if you changed the pixel values). [2 marks]
(d) You could remove one of these layers from the network, perhaps modifying the other. Would this have an impact on the quality of the learning? Explain your answer in at most a few sentences. (Note that multiple answers are possible to this question, state any assumptions you make). [2 marks]
Q9: (2 marks) (questions with short answers) Given adataset that consists of images of the Eiffel Tower, your task is to learn a classifier to detect the Eiffel Tower in new
images. You implement PCA to reduce the dimensionality of your data, but find that
your performance in detecting the Eiffel Tower significantly drops in comparison to
your method on the original input data. Samples of your input training images are given in the following figures. Why is the performance suffering? [hints: describe in two
sentences.]

Q10: (10 marks) (algorithm design) Turn your phone into a GPS in an art museum or a library. GPS usually does not work well in an indoor environment. The goal of designing this algorithm is to localise your position by taking a few images around you in the museum. Please Briefly describe the key steps of your method.

2023-07-24