ELEC209P 2016 Exam
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ELEC209P
Answer any THREE questions out of FOUR
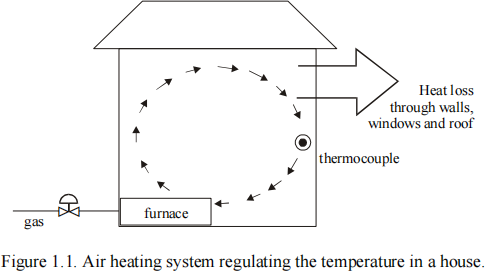
1. Figure 1.1 shows an air heating system used to regulate the temperature in a house. It is a warm air system in which air warmed by a furnace is circulated round the house driven by a fan. The furnace is fuelled by gas. It has an on-off characteristic such that if the gas valve is opened the furnace is on and when the gas valve is closed the furnace switches off.
(a) Identify the following sets of features of the control system (2 marks awarded for each of the three sets of features):
(i) Control objective(s) and disturbances
(ii) Sensors(s) and actuator(s) needed to achieve the control objective. Distinguish between those which are essential and those which might be useful for enhanced performance.
(iii) Manipulated variable(s) needed to achieve the control objective [6 marks]
(b) Is the system class zero or class one? Explain your answer.
Hint: Newton’s law of cooling (and common sense) tells us the house will lose heat through its walls and that the rate of heat loss is proportional to temperature. [8 marks]
(c) Draw the block diagram for a basic feedback control system. Explain how your controller would manage the on-off characteristic of the furnace. [8 marks]
(d) Discuss whether a feedforward configuration has anything to offer to this control system. [3 marks]
2.
(a) State the final value theorem and explain its derivation. [6 marks]
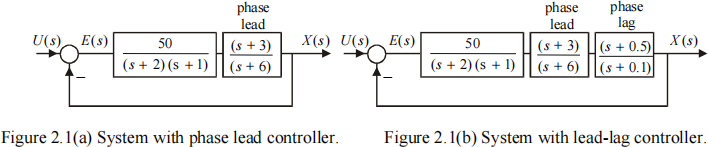
(b) The feedback control systems shown in Figure 2.1(a),(b) have a controlled system Go(s) together with a lead compensator and, in the case of Figure 2.1(b), a lag compensator. Based on Figure 2.1, show that the poles of the closed loop systems are the values of s that satisfy the following polynomial equations. Do not attempt to find the numerical values of the poles from these equations [they are given in part (c)].
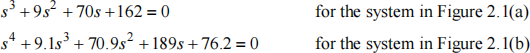 [8 marks]
[8 marks]
(c) The closed loop poles of the system are:
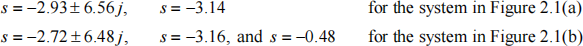
Find the numerical values of the zeros of the transfer functions E(s) U(s)![]() for the two systems. Plot pole-zero diagrams for the transfer functions E(s) U(s) for the two systems
for the two systems. Plot pole-zero diagrams for the transfer functions E(s) U(s) for the two systems![]() . Highlight any closed loop pole and zero that originates from the phase lag compensation. [8 marks]
. Highlight any closed loop pole and zero that originates from the phase lag compensation. [8 marks]
(d) If the input is a unit step, show that the use of the phase lag compensator gives the benefit of reducing the steady state error by a factor of 4.7 compared to the case when there is no phase lag compensation.
3. (a) In Figure 3.1(a), the displacement of the block on the lefthand side of the spring is x 1 and the displacement of the block on the right hand side is x 2 . Both displacements are measured from the equilibrium positions of the blocks and they are applied such that the spring is compressed from both sides. The spring constant is K . Write down the expressions for the force exerted by the spring on each of the two blocks. [6 marks]
(b) In Figure 3.1(b) the velocity of the block on the lefthand side of the damper is dx 1 ![]() dt and the velocity of the right hand block is dx 2
dt and the velocity of the right hand block is dx 2 ![]() dt . The damping coefficient is B . Write down the expressions for the force exerted by the damper on each of the two blocks.
dt . The damping coefficient is B . Write down the expressions for the force exerted by the damper on each of the two blocks.
[8 marks]
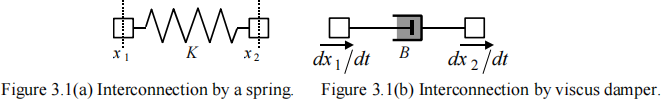
(c) Show that the transfer function for the car suspension system shown in Figure 3.2 is:
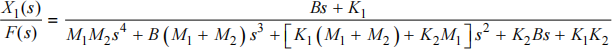
where x 1 is the deviation of mass M1 from its equilibrium position and f(t) is the force on mass M2 .
Hints:
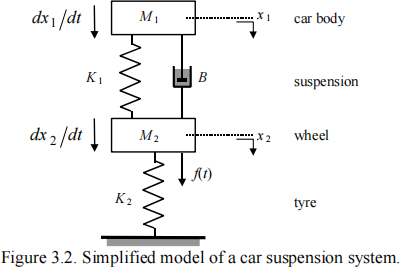
1. Useful intermediate results to consider (which must be proven before being used in your answer) are:
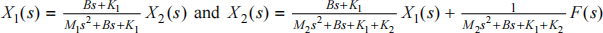
2. Do not include the force due to gravity in the analysis. Gravity determines the equilibrium position, but does not influence deviations from equilibrium.
4. (a)
(i) By making use of Euler's theorem to decompose cos (t ) and sin (t ) into complex exponentials, or otherwise, prove that the Laplace transforms of cos (t ) and sin (t ) (t 之 0) are, respectively:
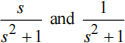
(ii) Explain what is wrong with the following reasoning:
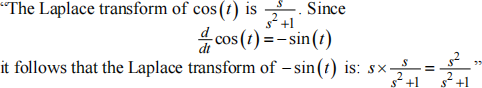
[6 marks]
(b) Use a partial fraction expansion to determine the time domain signal y (t ) whose Laplace transform is:
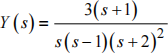
What is the value of y (t ) as t → ∞ ? [8 marks]
(c) Determine the steady state value for y (t ) by application of the final value theorem to the expressio→n for Y (s ) in Q4(c) above. Explain why the final value theorem gives a misleading result in this case. [8 marks]
(d) Prove that the Laplace transform of a time delay is e-sTd , where Td is the delay.[3 marks]
2023-07-19