SPH3U: FINAL EXAM
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
SPH3U: FINAL EXAM
Overall Expectations
A) Scientific Investigation Skills and Career Exploration
A.1) demonstrate scientific investigation skills (related to both inquiry and research) in the four areas of skills (initiating and planning, performing and recording, analysing and interpreting, and communicating);
A.2) identify and describe careers related to the fields of science under study, and describe the contributions of scientists, including Canadians, to those fields.
B) Kinematics
B.1) analyse technologies that apply concepts related to kinematics, and assess the technologies’ social and environmental impact;
B.2) investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, uniform and non-uniform linear motion, and solve related problems;
B.3) demonstrate an understanding of uniform and non-uniform linear motion, in one and two dimensions.
C) Forces
C.1) analyse and propose improvements to technologies that apply concepts related to dynamics and Newton’s laws, and assess the technologies’ social and environmental impact;
C.2) investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, net force, acceleration, and mass, and solve related problems;
C.3 demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between changes in velocity and unbalanced forces in one dimension.
D) Energy and Society
D.1) analyse technologies that apply principles of and concepts related to energy transformations, and assess the technologies’ social and environmental impact;
D.2) investigate energy transformations and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems;
D.3) demonstrate an understanding of work, efficiency, power, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, nuclear energy, and thermal energy and its transfer (heat).
E) Waves and Sound
E.1) analyse how mechanical waves and sound affect technology, structures, society, and the environment, and assess ways of reducing their negative effects;
E.2) investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the properties of mechanical waves and sound, and solve related problems;
E.3) demonstrate an understanding of the properties of mechanical waves and sound and of the principles underlying their production, transmission, interaction, and reception.
F) Electricity and Magnetism
F.1) analyse the social, economic, and environmental impact of electrical energy production and technologies related to electromagnetism, and propose ways to improve the sustainability of electrical energy production;
F.2) investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, magnetic fields and electric circuits, and solve related problems;
F.3) demonstrate an understanding of the properties of magnetic fields, the principles of current and electron flow, and the operation of selected technologies that use these properties and principles to produce and transmit electrical energy.
Knowledge: 23 Thinking: 14 Communication: 13 Application: 15
Section A: Multiple choice
(K:8, T:0, C:0, A:0)
1) Which of the following quantities is a scalar?
a. distance
b. displacement
c. velocity
d. acceleration
e. none of the above
2) A pilot flies to a destination due north from the departure point. During the flight there is a wind blowing from the west. What direction must the pilot point the plane during the flight?
a. due east
b. due west
c. east of north
d. west of north
e. due north
3) A construction worker does 450 J of work in lifting a load of bricks from the ground to a support stand 1.50 m from the ground. What was the mass of the bricks she lifted?
a. 300 kg
b. 0.327 kg
c. 3.06 kg
d. 30.6 kg
e. 68.9 kg
4) The speed of any mechanical wave as it propagates through a medium is dependent mainly on the
a. frequency of the wave source
b. wavelength
c. period of the wave
d. type of medium through which the wave travels
e. amplitude
5) A standing wave with three loops is generated in a string. If the wavelength is 10 cm, how far apart are the nodes created?
a. 2.5 cm
b. 20 cm
c. 5.0 cm
d. 30 cm
e. 10 cm
6) Magnetic field lines
a. show the strength of a magnetic field
b. show the direction of a magnetic field
c. become more widely spaced as the magnetic force weakens
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
7) The SI unit for measuring charge is the
a. coulomb
b. joule
c. ampere
d. watt
e. volt
8) What is the length of a closed column that produces the fundamental frequency of a wave with wavelength 2.50 m? Assume speed of sound in air is 323 m/s.
a. 62.5 cm
b. 1.25 m
c. 64 m
d. 2.5 m
e. 6 cm
Section B: Short answer
(K:6, T:6, C:6, A:6)
8) A cart with a mass of 2.0 kg is pulled across a level desk by a horizontal force of 4.0 N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0. 12, what is the acceleration of the cart? (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
9) With a power rating of 345W, how far will a force of 115.0N push an object in 5.00s? (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
10) Beryllium- 11 has a half-life of 13.81 s. What percent of the initial sample will remain after 30.0 s? (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
11) A sound wave travels with a speed of 334 m/s through air with a frequency of 172 Hz. How far apart are the wave crests? (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
12) The potential difference across the terminals of a light bulb is 120 V. If the bulb uses 540 J of energy, how much total charge is moved across the terminals? (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
13) A power plant produces power at a current of 3.0 kA. If the total resistance in the transmission wire is 0.40 ohms, what is the total power loss due to transmission through the wire (K:1, T:1, C:1, A:1)
Section C: Long answer
(K:9, T:8, C:7, A:9)
14. 1) During the opening kickoff of a college football game, the kicker kicks a football with an initial velocity of 27.5 m/s at an angle of 41° above horizontal.
a. What is the time of flight for the ball?
b. How far does it travel before hitting the ground?
c. What is the maximum height the football reaches? (K:3, T:3, C:3, A:4)
15) The cart in the figure below has a mass of 0.4 kg and is attached, by a string and a pulley, to a weigh that has a mass of 0.20 kg.
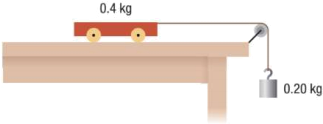
a. Calculate the acceleration of the cart, assuming there is no friction.
b. Calculate the acceleration of the cart if there is a frictional force of 0.10 N acting on the cart.
c. Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the cart going to the pulley then tension in the pulley going to the hanging mass assuming there is no friction.
18) A police car is approaching at a speed of 20.0 m/s with its siren emitting a frequency of 1.0 kHz. What frequency does a stationary observer detect? The speed of sound in this case is 330 m/s. (K:2, T:1, C:1, A:2)
2023-07-16