Quiz-2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
1. Consider the linearised quantum circuit from Quiz 1 Problem 4 with the state-space equation:
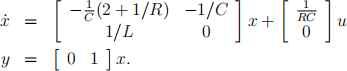
Let C = 0.5 F, L = 0.2 H and R = 2 ohms.
(a) Using the Ackermann’s formula twice, design a linear output feedback control law with gain K and a Luenberger observer with gain L so that the closed-loop system (consisting of system + output feedback + observer) has the characteristic polynomial cAcl(s) = (s2 + 6s + 13)(s + 2)(s + 3), with the observer contributing only real eigenvalues (recall that Acl denotes the closed-loop A matrix).
(b) Sketch a block diagram of the closed-loop system.
2. For the same circuit as in Problem 1, consider the infinite horizon LQR cost
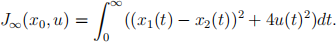
Answer the following questions:
(a) Verify that the infinite horizon problem has a solution.
(b) Compute the unique solution of the CARE equation satisfying P > 0 and determine the optimal control law uopt .
3. Consider the system
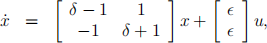
where x = (x1 ,x2 )T , and δ and ϵ are unknown real parameters. Answer the following questions:
(a) Show that the system is not controllable for any value of the parameter ϵ .
(b) Show that there is a linear combination of x1 and x2 that evolves independently of the input u.
(c) Using the result of sub-problem (b) and WITHOUT computing the charac-teristic polynomial of A − BK (you may, however, compute the characteristic polynomial of A), show that there is an eigenvalue of A that cannot be moved by any linear state feedback law u = −Kx (that is, for any choice of K , A − BK will always have this eigenvalue).
2023-07-16