MATH 3527 - Problem Set 7
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATH 3527 - Problem Set 7
1. (a) If 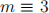 (mod 4), prove that with the usual definitions of addition and multipli-cation, the set
(mod 4), prove that with the usual definitions of addition and multipli-cation, the set
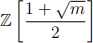
fails to be a ring.
Hint: Find 2 elements of the set which when multiplied result in a complex number not included in the set.
(b) When 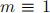 (mod 4), the set
(mod 4), the set 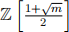 with the usual notions of addition and multiplication is an integral domain. In this case, show that the set can be written as
with the usual notions of addition and multiplication is an integral domain. In this case, show that the set can be written as
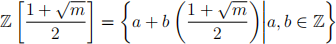
Hint: Use the fact that 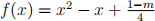 is an integer polynomial having
is an integer polynomial having
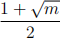
as a root.
(c) Prove that the integral domain 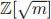 is a subring of
is a subring of 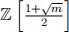 .
.
2. (a) Suppose 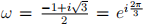 , a cube root of unity. Then the ring of Eisenstein integers is defined
, a cube root of unity. Then the ring of Eisenstein integers is defined 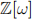 . Show that any Eisenstein integer
. Show that any Eisenstein integer 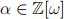 can be written in the form
can be written in the form 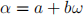 for integers a and b.
for integers a and b.
Hint: What quadratic polynomial with integer coefficients is 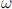 a root of?
a root of?
(b) In the Eisenstein integers, show that the usual notion of the norm map for a subring of C, the magnitude of a complex number squared, results in the formula
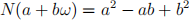
(c) Show that 13 is not prime in the Eisenstein integers by producing an explicit fac-torization into non-unit elements.
3. Prove that a prime number p can be written as a sum of squares,
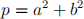
if and only if 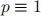 (mod 4) using the following steps:
(mod 4) using the following steps:
(a) Show that p is not a prime element in 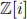 .
.
Hint: Start by showing that p divides 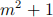 for some integer m using quadratic reciprocity.
for some integer m using quadratic reciprocity.
(b) Deduce that p can be factored in 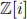 into exactly 2 irreducible factors.
into exactly 2 irreducible factors.
4. Show that 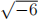 is not prime in
is not prime in 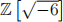 , but that is it irreducible.
, but that is it irreducible.
5. (the Dirichlet ring) Consider the set of all arithmetic functions, R, with the oper-ations of convolution and point-wise addition, that is, for arithmetic functions f and g define a new arithmetic function (f + g)(n) = f(n) + g(n). This makes R a ring, called the Dirichlet ring.
(a) Prove that
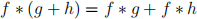
(b) Prove that a f is a unit of R if and only if 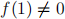 .
.
(c) Does the subset of multiplicative functions form a subring of R? Justify your an-swer.
2021-08-19