Chapter 8 Exam Pool Questions
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Chapter 8 Exam Pool Questions
1. The Pauli exclusion principle states that
a) both the position of an electron and its momentum cannot be known simultaneously very accurately.
b) the wavelength and mass of a subatomic particle are related by 入 = h/ mv .
c) the wavelength of a photon of light times its frequency is equal to the speed of light.
d) no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
e) an electron can have either particle character or wave character.
2. Which of the following orbital occupancy designations is incorrect?
a) 2s1
b) 3d10
c) 4p7
d) 4f7
e) 2p6
3. The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in an f subshell is
a) 1.
c) 2.
c) 14.
d) 6.
e) 10.
4. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state?
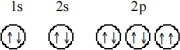
a) Pauli exclusion principle
b) Aufbau principle
c) Hund's rule
d) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
e) No rules or principles are violated by this orbital diagram.
5. Which of the following electron configurations is impossible, according to the Pauli exclusion principle?
a) 1s22s22p4
b) 1s22s22p5
c) 1s22s22p2
d) 1s22s4
e) 1s22s22p63s2
6. Which principle or rule is violated by the following orbital diagram of an atom in its ground state?
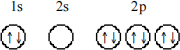
a) Pauli exclusion principle
b) Building-up principle
c) Hund's rule
d) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
e) No rules or principles are violated by this orbital diagram.
7. Which of the following electron configurations represents an excited state of the indicated atom?
a) He: 1s2
b) Ne: 1s2 2s2 2p6
c) Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
d) P: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 4s1
e) N: 1s2 2s2 2p3
8. The ground-state valence-shell configuration of a particular atom is 4f146s2 . The element to which this atom belongs is a
a) noble gas.
b) s-block main-group element.
c) transition element.
d) inner transition element.
e) p-block main-group element.
9. Which of the following statements is true concerning the electron configuration [Ne]3s13p1?
a) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Na+ cation.
b) It may represent an excited-state electron configuration of a Mg atom.
c) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Al+ cation.
d) It may represent an excited-state electron configuration of a Ne– anion.
e) It may represent a ground-state electron configuration of a Mg+ cation.
10. All of the following ground-state electron configurations are correct except
a) Ca: [Ar]4s2 .
b) Ti : [Ar]4s24d2 .
c) Cu: [Ar]3d104s1 .
d) Sn: [Kr]4d105s25p2 .
e) Xe: [Kr]4d105s25p6 .
11. How many valence electrons does an arsenic atom have?
a) 2
b) 5
c) 6
d) 33
e) 7
12. What is the ground-state electron configuration of terbium (Tb)?
a) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d104f145s25p3
b) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p65d96s2
c) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p65d106s 1
d) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d104f95s25p66s2
e) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d94f105s25p66s2
13. The elements that are filling the 5f subshell are called
a) lanthanides.
b) main-group elements.
c) transition elements.
d) alkali metals.
e) actinides.
14. The quantum numbers of an atom's highest-energy valence electrons are n = 5 and l = 1. The element to which this atom belongs could be a
a) transition metal.
b) inner transition metal.
c) alkali metal.
d) s-block main-group element.
e) p-block main-group element.
15. Which of the following sets of four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms) correctly describes an electron occupying a d orbital of an element in the third row of the transition metals?
a) 5 0 0 -½
b) 4 1 1 + ½
c) 5 2 1 -½
d) 4 2 2 + ½
e) 5 3 - 1 - ½
16. An element that has the same valence-shell configuration as tin is
a) antimony.
b) tellurium.
c) indium.
d) selenium.
e) germanium.
17. What is the valence-shell electron configuration for the fourth-period element in Group VA?
a) 5s25p5
b) 4s25p3
c) 4s24p3
d) 5s24p5
e) 4s23d3
18. The statement that "the lowest-energy configuration for an atom is the one having the maximum number of unpaired electrons allowed by the Pauli principle in a particular set of degenerate orbitals" is known as
a) the Aufbau principle.
b) Hund's rule.
c) Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
d) the Pauli exclusion principle.
e) the quantum model.
19. The element whose atoms in the ground state have two half-filled orbitals is
In.
Bi.
Ca.
Cs.
Po.
20. Fe has __________ that is(are) unpaired in its d orbitals.
a) 1 electron
b) 2 electrons
c) 3 electrons
d) 4 electrons
e) none of these
21. An atom of which of the following elements is not diamagnetic in the ground state?
a) Ba
b) Kr
c) Hg
d) Pt
e) All are diamagnetic.
22. Which of the following orbital diagrams represent(s) a paramagnetic atom?
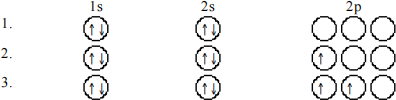
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) 3 only
d) 1 and 2 only
e) 2 and 3 only
23. Which of the following orbital diagrams represents a paramagnetic atom?
24. Which of the following atoms is paramagnetic in its ground state?
Fe
Ne
Be
Cd
Sr
25. When arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the elements exhibit periodicity for all the following properties except
a) ionization energy.
b) atomic radius.
c) electron configuration.
d) electron affinity.
e) atomic mass.
26. In general, atomic radii
a) decrease from left to right in a period and increase down a group.
b) increase from left to right in a period and decrease down a group.
c) increase from left to right in a period and increase down a group.
d) decrease from left to right and decrease down a group.
e) do not change across a period or a group.
27. A section of the periodic table with all identification features removed is shown below.
|
V |
W |
X |
|
|
Y |
Z |
Which element has the smallest atomic radius?
a) V
b) W
c) X
d) Y
e) Z
28. An atom of which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius?
Bi
Sb
P
N
As
29. An atom of which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
C
Ge
Si
Sn
Pb
30. The statement that the first ionization energy for an oxygen atom is lower than the first ionization energy for a nitrogen atom is
a) consistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right because it is easier to take an electron from an oxygen atom than from a nitrogen atom.
b) consistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right because it is harder to take an electron from an oxygen atom than from a nitrogen atom.
c) inconsistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right and due to the fact that the oxygen atom has two doubly occupied 2p orbitals and nitrogen has only one.
d) inconsistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right and due to the fact that oxygen has one doubly occupied 2p orbital and nitrogen does not.
e) incorrect.
31. The change in energy for which of the following processes represents the first ionization energy of iodine?
a) I(g) → I+(g) + e–
b) I–(g) → I+(g) + 2e–
c) 2I–(g) → I2(s) + 2e–
d) I(g) → I2+(g) + 2e–
e) I(g) + e– → I–(g)
32. The change in energy for which of the following processes corresponds to the second ionization energy of calcium?
a) Ca(g) → Ca+(g) + e–
b) Ca(g) + e– → Ca–(g)
c) Ca+(g) → Ca2+(g) + e–
d) Ca–(g) → Ca(g) + e–
e) Ca(g) → Ca2+(g) + 2e–
33. An atom of which of the following elements has the highest fourth ionization energy?
Al
Ga
Se
As
Si
34. An atom of which of the following elements has the largest ionization energy?
a) At
b) Po
c) Bi
d) Pb
e) Cs
35. An atom of which of the following elements has the smallest first ionization energy?
a) Be
b) Ba
c) Mg
d) Sr
e) Ca
36. An atom of which of the following elements has the largest second ionization energy?
Li
C
F
Be
O
37. Which of the following ground-state electron configurations corresponds to an atom having the largest ionization energy?
a) [Ne]3s23p2
b) [Ne]3s23p3
c) [Ar]3d104s24p3
d) [Kr]4d105s25p3
e) [Xe]4f145d106s26p3
38. The electron affinity value expected for the process
Cl(g) + e– → Cl–(g)
would be
a) a large negative number.
b) a small negative number.
c) zero.
d) a small positive number.
e) a large positive number.
39. The change in energy for which of the following processes corresponds to the electron affinity of iodine?
a) I(g) + e– → I–(g)
b) I2(g) → 2I(g)
c) I(g) → I+(g) + e–
d) I–(g) → I(g) + e–
e) I+(g) + I–(g) → I2(s)
40. Which of the following ground-state electron configurations corresponds to an atom that has the most negative value of the electron affinity?
a) 1s22s22p63s1
b) 1s22s22p63s23p5
c) 1s22s22p63s23p2
d) 1s22s22p63s23p63d54s2
e) 1s22s22p6
2023-07-14
