Chapter 7 Exam Pool Questions
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Chapter 7 Exam Pool Questions
1. What is the wavelength of a photon having a frequency of 87.9 THz? (1 THz = 1015 Hz, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s)
a) 3.41 × 1015 nm
b) 5.83 × 10–23 nm
c) 1.75 × 10– 14 nm
d) 3.41 nm
e) 0.293 nm
2. The relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic radiation in vacuum is
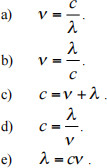
3. What is the frequency of a photon having a wavelength of 602.5 nm? ( c = 3.00× 108 m/s , h = 6.63× 10−34 J .s )
a) 9.09 × 1026 Hz
b) 3.30 × 10–37 Hz
c) 4.98 × 10–4 Hz
d) 3.30 × 10– 19 Hz
e) 4.98 × 1014 Hz
4. Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the longest wavelength?
a) gamma rays
b) x rays
c) blue light
d) red light
e) microwaves
5. Rank the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of decreasing frequency. X rays, Microwaves, Infrared, Ultraviolet
a) x rays, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet
b) microwaves, ultraviolet, infrared, x rays
c) microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, x rays
d) infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, x rays
e) x rays, ultraviolet, infrared, microwaves
6. A photon of blue light has a _______ frequency and a _______ wavelength than a photon of red light.
a) lower, longer
b) higher, longer
c) lower, lower
d) higher, shorter
e) lower, shorter
7. When a particular metal is illuminated with photons, one electron is observed for each absorbed photon. What effect would decreasing the wavelength and number of photons have on the electrons leaving the surface?
a) They would have higher kinetic energy.
b) There would be more electrons.
c) The electron velocity would be lower.
d) The kinetic energy of the electrons would be lower.
e) Two photons might be required to eject the electrons.
8. Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the highest energy?
a) radio waves
b) x rays
c) blue light
d) red light
e) gamma rays
9. What is the energy of a photon of electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 5.98 × 1014 Hz? (c = 3.00 ×
108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s)
a) 1.79 × 1023 J
b) 3.96 × 10– 19 J
c) 1.19 × 10– 10 J
d) 5.02 × 10–7 J
e) 3.30 × 10–40 J
10. What is the wavelength of a photon that has an energy of 4.28 × 10– 18 J? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-
34 J • s)
a) 1.28 × 100 nm
b) 6.46 × 1015 nm
c) 46.4 nm
d) 4.28 × 10–9 nm
e) 0.00 × 100 nm
11. What is the wavelength of photons that have molar energy of 541 kJ/mol? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol- 1)
a) 3.68 × 10–22 nm
b) 8.99 × 10– 10 nm
c) 221 nm
d) 1.36 × 106 nm
e) 2.21 × 105 nm
12. What is the frequency of photons that have a molar energy of 255 kJ/mol? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol- 1)
a) 7.80 × 10–31 Hz
b) 1.27 × 10– 10 Hz
c) 2.13 × 106 Hz
d) 4.24 × 10– 19 Hz
e) 6.39 × 1014 Hz
13. What is the energy per mole of photons with a wavelength of 482.6 nm? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-
34 J • s, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol- 1)
a) 2.91 × 1014 kJ/mol
b) 4.12 × 10– 19 kJ/mol
c) 3.74 × 1035 kJ/mol
d) 2.48 × 102 kJ/mol
e) 6.22 × 1014 kJ/mol
14. What is the energy per mole of photons having a frequency of 5.38 × 1013 Hz? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol- 1)
a) 2.15 × 101 kJ/mol
b) 3.70 × 10–30 kJ/mol
c) 3.36 × 1024 kJ/mol
d) 2.23 × 10–9 kJ/mol
e) 5.58 × 103 kJ/mol
15. Whose postulates account for the line spectrum of an atom?
a) Rutherford
b) de Broglie
c) Bohr
d) Thomson
e) Heisenberg
16. Who postulated that energy is radiated only when an electron falls from a higher-energy level to a lower- energy level?
a) Einstein
b) Rutherford
c) Heisenberg
d) Millikan
e) Bohr
17. In Bohr's atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus,
a) energy is emitted.
b) energy is absorbed.
c) no change in energy occurs.
d) light is emitted.
e) none of these
18. From the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, we can conclude that the energy required to excite an electron from n = 8 to n = 9 is ___________ the energy required to excite an electron from n = 9 to n = 10.
a) less than
b) greater than
c) equal to
d) either equal to or less than
e) either equal to or greater than
19. What is the wavelength of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from level n = 9 to level n = 4? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s), RH = 2.179 × 10- 18 J)
a) 5.49 × 105 m
b) 1.09 × 10– 19 m
c) 1.65 × 1014 m
d) 3.64 × 10–28 m
e) 1.82 × 10–6 m
20. What is the frequency of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes a transition from level n = 6 to level n = 3? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s), RH = 2.179 × 10- 18 J)
a) 2.74 × 1014 Hz
b) 1.82 × 10– 19 Hz
c) 1.65 × 1027 Hz
d) 9.13 × 105 Hz
e) 1.10 × 10–6 Hz
21. The electron in a hydrogen atom, originally in level n = 10, undergoes a transition to a lower level by emitting a photon of wavelength 1739 nm. What is the final level of the electron? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h =
6.63 × 10-34 J • s), RH = 2.179 × 10- 18 J)
a) 1
b) 5
c) 10
d) 11
e) 4
22. Consider the following energy-level diagram for a particular electron in an atom.
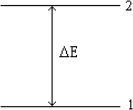
Based on this diagram, which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) If the electron is in level 1, it may jump to level 2 by absorbing a photon with energy of ∆E.
b) If the electron is in level 2, it may jump to level 1 by emitting a photon with energy of |∆E |.
c) If the electron is in level 1, it may jump to level 2 by absorbing any photon having energy of at least ∆E.
d) We would observe an electron jumping from level 2 to level 1 as a single line in a line spectrum.
e) The wavelength of a photon emitted by the electron jumping from level 2 to level 1 is given by
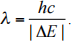
23. The contribution for which de Broglie is best remembered in modern science is
a) his statement that an electron can exist in an atom only in discrete energy levels.
b) his statement that no electron can have identical values for all four quantum numbers.
c) his proposal that particles of matter should be associated with wavelike behavior.
d) his statement that elements show periodic repetition of properties.
e) his statement that electrons occupy all the orbitals of a given sublevel singly before pairing begins.
24. What is the wavelength of a 148-g baseball traveling at 94.5 mph? (1 mi = 1.609 km, h = 6.63× 10−34 J .s )
9.43 × 1033 m
2.95 × 10–38 m
1.06 × 10–37 m
3.39 × 1037 m
1.06 × 10–34 m
25. If the location of a particular electron can be measured only to a precision of 0.058 nm, what is the minimum uncertainty in the electron's velocity? (me = 9.109 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.63 × 10-34 J • s)
a) 1.4 × 10– 13 m/s
b) 1.0 × 106 m/s
c) 10.0 × 10–4 m/s
d) 2.2 × 105 m/s
e) 10.0 × 10–7 m/s
26. The square of the wave function, !2 , of an electron in an atom
a) describes the energy of the electron.
b) specifies the momentum of the electron.
c) gives the probability of finding the electron in a region of space.
d) is proportional to the velocity of the electron.
e) is inversely proportional to the distance between the electron and the nucleus.
Ans: c Chapter/Section: 7.4 Difficulty: easy Keyword 1: general chemistry
Keyword 2: atomic theory Keyword 3: quantum mechanics Keyword 4: wavefunctions Learning Objective: Relate the wavefunctionfor an electron to the probability offinding it at a location in
space.
27. The number of orbitals having a given value of l is equal to
a) 2l + 1.
b) 2n + 1.
c) 2ml + 1.
d) n + ml .
e) l + ml .
28. The angular momentum quantum number is best associated with the
a) energy of the orbit.
b) energy of the orbital.
c) number of orbitals in a subshell.
d) orientation in space of an orbital.
e) shape of the orbital.
29. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms) refers to a 3d orbital?
a) 2 1 0 + ½
b) 3 2 2 + ½
c) 4 2 -2 + ½
d) 4 3 2 + ½
e) 5 4 3 + ½
30. A possible value of the magnetic quantum number ml for a 5d electron is
a) –5.
b) 4.
c) 2.
d) –3.
e) 6.
31. All the following statements about the quantum numbers are true except
a) n may take integral values from 1 to ∞ .
b) l may take integral values from 1 to n – 1.
c) ml has 2l + 1 possible values.
d) ml may take integral values of +l to –l, including zero. 1 1
e) ms may take only the values of + 2 and – 2 .
32. How many values are there for the magnetic quantum number when the value of the angular momentum quantum number is 4?
a) 1
b) 4
c) 10
d) 16
e) 9
33. An orbital with the quantum numbers n = 5, l = 2, ml = 2 may be found in which subshell?
5s
5p
5d
5f
5g
34. What is the value of the spin quantum number for an electron in a 5f orbital?
a) 5
b) 3
c) + ½
d) –½
e) either + ½ or –½
35. Which of the following subshells does not exist?
2s
3p
4d
3f
6g
36. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms) is not permissible?
a) 1 0 0 + ½
b) 4 0 0 - ½
c) 2 2 1 + ½
d) 3 1 0 - ½
e) 3 2 -2 - ½
37. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) The set of quantum numbers n = 2, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = –½ is not permitted because n = l.
b) The set of quantum numbers n = 3, l = 2, ml = 3, ms = –½ is not permitted because ml exceeds l.
c) The set of quantum numbers n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = + ½ is permitted.
d) The set of quantum numbers n = 3, l = 2, ml = 0, ms = –½ is not permitted because ml = 0.
e) The set of quantum numbers n = 4, l = 3, ml = – 1, ms = 0 is not permitted because ms = 0.
|
38. How a) b) c) d) e) |
many 36 1 3 5 7 |
total orbitals are in the n = 6 shell? |
39. Which of the following is a representation of a 1s orbital?
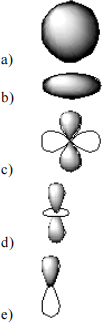
40. Which of the following is a representation of a 3dxy orbital?
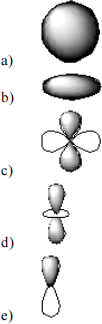
2023-07-14