ENGR 145 Homework unit 4
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ENGR 145
Homework unit 4
1. Complete the following table:
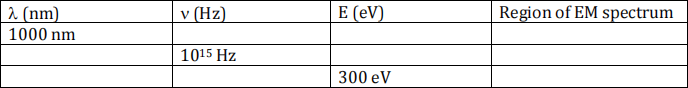
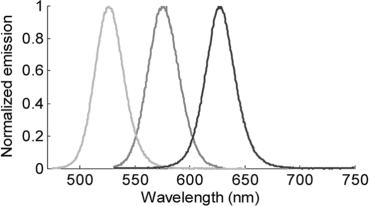
2. The energy levels for the hydrogen atom are given by 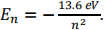 For the following transitions, determine the wavelength of the photon that is emitted and its region of the EM spectrum.
For the following transitions, determine the wavelength of the photon that is emitted and its region of the EM spectrum.
a. n=2 to n=1
b. n=3 to n=2
c. n=4 to n=3
3. The figure below shows the emission spectra for three quantum dots that have the same chemical composition.
a. What is the color or region of the electromagnetic spectrum in which these quantum dots emit?
b. What is the energy difference (in eV) between the relevant energy states in each quantum dot?
c. Sketch (very qualitatively) the one-dimensional potential energy diagrams that give rise to the relevant energy states in each quantum dot. What is the difference in the potential energy diagrams for these three quantum dots? Explain the physical basis of the potential energy diagrams.
4. The picture below shows the emission of six quantum dots that have the same chemical composition.
a. Which quantum dot is largest in size, and which is smallest?
b. Sketch emission spectra for the left-most and right-most materials (put the spectra for both materials on the same plot; use the experimental emission spectrum in problem 3 as a model)

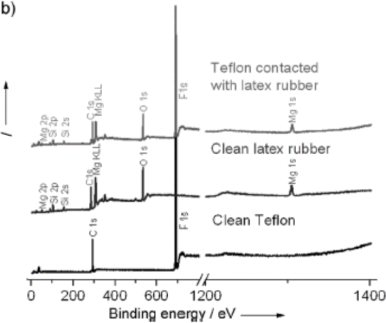
5. Use the x-ray photoelectron spectra below (from one of Prof. Lacks’s papers) to answer these questions (estimate binding energies for the peaks from the graph):
a. What are the binding energies of the 1s electrons of C, O, F and Mg? What is the physical basis for the relative magnitudes of these binding energies?
b. What is the maximum wavelength of a photon that can remove an electron from the 1s orbital of oxygen?
c. What are the binding energies of the 2s and 2p electrons in Si? What is the physical basis for the relative magnitudes of these binding energies?
d. What is the wavelength of the photon emitted when an electron goes from the 2p to the 2s state of Si?
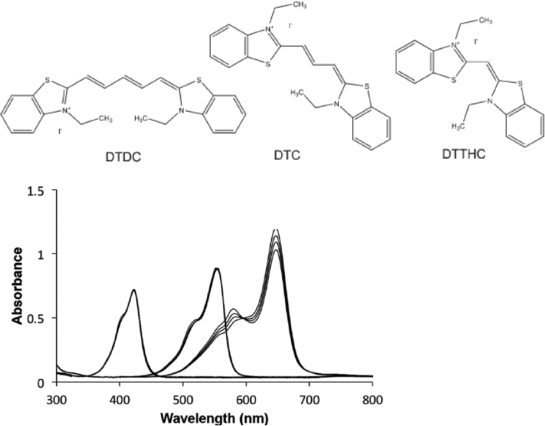
6. The absorbance spectra is shown for the three dye molecules below.
a. Describe qualitatively the energy states are involved in the electron transitions that lead to the absorbance peaks for each molecule.
b. Indicate the molecule that corresponds to each absorbance peak.
c. Which dye molecule will look bluish when white light shines on it?
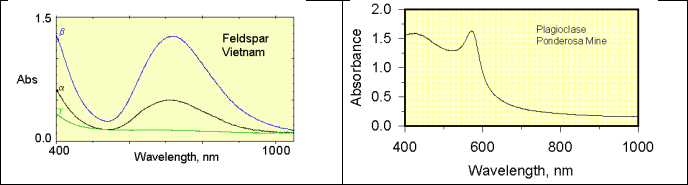
7. The absorbance spectra are shown for two minerals.
a. What color is each mineral?
b. The absorbance is due to an energy transition between two states. For each of these two states, sketch one of the orbitals in that energy state. What is the characteristic that differentiates the orbitals in these two states?
8. Callister 19.14
9. Callister 19. D1. Also, explain why you would expect the band gap to be larger for GaP than for GaAs.
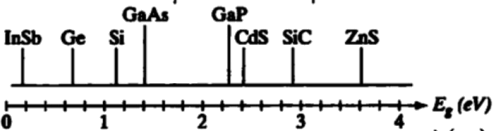
10. Using the band-gap data below.
a. On the graph, write the wavelengths corresponding to Eg = 1, 2, 3 and 4 eV, and use this as a guide to answer the questions below.
b. Which semiconductor would be best for converting UV to violet light?
c. Which semiconductors, if any, are transparent to visible light?
d. Which semiconductors, if any, are transparent to red light but absorb blue and green light?
e. Which semiconductors, if any, are transparent to blue light but absorb green and red light?
2023-07-13