Physics 1/1L – 114051 Final Exam A
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Physics 1/1L – 114051
Final Exam A – 07/02/2023 – 14:00-17:00
1. Question 1
A girl throws a ball of mass m from the origin upward with velocity v0 ![]() . While the ball is in the air, a force
. While the ball is in the air, a force ![]() = Fx
= Fx ![]() + Fy
+ Fy ![]() acts on the ball where the horizontal direction Fx = avy (t) (Where vy is the y component of the velocity) and Fy = −mg. At which point x will the ball hit the ground?
acts on the ball where the horizontal direction Fx = avy (t) (Where vy is the y component of the velocity) and Fy = −mg. At which point x will the ball hit the ground?

2. Question 2
A father and son of masses M and M/2 ,respectively, are standing on the left side of a boat of mass M and length L . At a certain moment both begin to walk towards the right side, but the son’s speed relative to the boat is twice the father’s speed.
If the friction between the boat and the water is negligible, what is the distance the boat will move when the son reaches its right side?
a. |Δxboat | = 2L/3
b. |Δxboat | = L/3
c. |Δxboat | = L/4
d. |Δxboat | = 3L/5
e. |Δxboat | = 2L/9
f. |Δxboat | = 2L/5
3. Question 3
A children swing was built using two ropes of length 2 m each. The swing is able to hold a mass at rest of no more than 50 kg before the ropes will break.
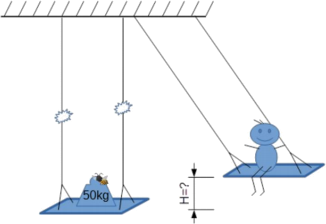
A boy of mass 30 kg wants to use the swing. What is the maximal height H the boy can swing above the lowest point before the ropes will break?
Assume that the boy can be treated as a point mass and that the mass of the swing is negligible relative to the mass of the boy.
a. H = 0.8 m
b. H = 0.3 m
c. H = 0.75 m
d. H = 0.666 m
e. H = 4 m
f. There is no limit for the height.
4. Question 4
A rugby player runs with the ball directly toward his opponent’s goal, along the positive direction of an X axis. He can legally pass the ball to a teammate as long as the ball’s velocity relative to the field does not have a positive X component!
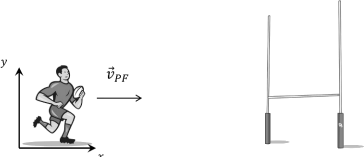
Suppose the player runs at velocity ![]() PF of magnitude 4 m/S relative to the field while he passes the ball with velocity
PF of magnitude 4 m/S relative to the field while he passes the ball with velocity ![]() BP relative to himself. If
BP relative to himself. If ![]() BP has magnitude 6 m/S, what is the smallest angle (as measured from the positive x axis) it can have for the pass to be legal?
BP has magnitude 6 m/S, what is the smallest angle (as measured from the positive x axis) it can have for the pass to be legal?
a. θ = 56.3∘
b. θ = 60 ∘
c. θ = 130 ∘
d. θ = 50 ∘
e. θ = 33.7∘
f. θ = 40 ∘![]()
![]()
5. Question 5
Particle A and B traveling along the x axis with speed 4c/5 and 3c/5, respectively, relative to the lab frame. Particle C is placed between particles A and B, as seen in the figure.

At which velocity particle C should travel, relative to the lab frame, so that it will measure that particle A and B travel towards particle C at the same speed?
6. Question 6
A car is moving along a straight line at constant speed v0 and at t = 0 it begins to brake (slow down). Knowing that the ‘deceleration’ depends on the speed as a = −b√v, where b is a known positive constant, find the time it takes the car to stop, tstop .
7. Question 7
Two masses m1 and m2 are connected by a massless spring passing through a massless and frictionless pulley connected to a table that stands on a frictionless floor. Mass m1 is resting on the top of the table and mass m2 is hanging and in contact with the table. Between the table and the masses there is friction with friction coefficient u .
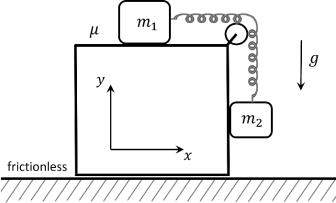
Choose the one correct statement for the system consisting of the table, two masses and the spring:
a. Mechanical energy and linear momentum are conserved in the system.
b. Mechanical energy is conserved in the system, but linear momentum along the y axis is not conserved.
c. Linear momentum is conserved in the system, but mechanical energy is not conserved.
d. Mechanical energy is not conserved in the system, and only linear momentum along the x axis is conserved.
e. Mechanical energy is conserved in the system, but linear momentum along the x axis is not conserved.
f. Mechanical energy is not conserved in the system, and only linear momentum along the y axis is conserved.
8. Question 8
An Alien plays ball in a spaceship of proper length L0 that is traveling to the right with speed U = 0.6c relative to its home planet.

At time t = t ′ = 0, the alien stands on the left side of the spaceship (point A) and throws the ball at speed v = 0. 1c (relative to the spaceship) at point B at the other side of the spaceship. At what time t1 and at what location x1 the ball will hit point B according to an observer on the planet?
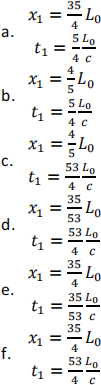
9. Question 9
In a certain one-dimensional physical system, particles can move along the X axis where a single external conservative force is acting on the particles:
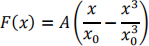
Where A and X0 are known positive constants.
Assume that there are two identical particles of mass m in this one-dimensional system. The first particle is released from rest at X = −X0 and the second particle is released from rest at X = −aX0 with a being a non-negative constant. It is given that if the particles collide, they stick together after the collision.
What is the minimal a so that after the collision the two particles can arrive at the position X = +X0 ?

10. Question 10
A particle is moving clockwise along a circular path and is slowing down (that is, the magnitude of angular velocity is decreasing) as shown in the left drawing below.
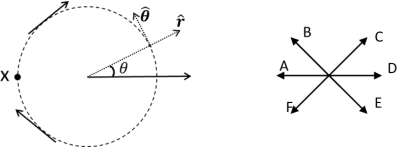
Which arrow in the right drawing best represents the acceleration vector of the particle at point X?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
e. E
f. F
11. Question 11
A particle of mass m is at rest in the lab’s reference frame. A second particle of mass 2m with velocity v (in the lab reference frame) close to the speed of light. At a certain moment the two particles collide, both disappear, and 4 new particles of mass m are created.
What is the minimum kinetic energy (as measured in the lab) of the second particle that allows the creation of the 4 new particles?
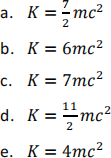
12. Question 12
Three particles of masses: m1 = m2 = m and m3 = m/2 are placed on a horizontal and frictionless table and connected by massless rods of length L each. At moment t0 a particle of mass m/2 of velocity v in direction of positive x axis collides with m3 and sticks to it.

What is angular velocity ![]() with which the system will rotate after the collision?
with which the system will rotate after the collision?
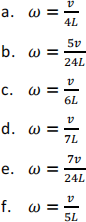
13. Question 13
A ball of mass m1 = 1 kg is traveling with velocity of v1 = 10 m/S to the left and hits a box of mass m2 = 50 kg which is resting on the floor.

After the collision, the ball moves to the right with the same speed as before and the box slides on the floor distance of 16 mm before it stops.
What is the coefficient of kinetic friction uk between the floor and the box? Use g = 10 m/S 2 but neglect the effect of gravity on the velocity of the ball and recall that 1000 mm = 1 m .
a. uk = 0.78
b. uk = 0.205
c. uk = 0.5
d. uk = 0.32
e. uk = 0. 15
f. uk = 0. 11
2023-07-11