Assignment 2 for Stat3021
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Assignment 2 for Stat3021
1. Suppose that electronic parts arrive at a processing plant in accordance with a Poisson process with rate λ(> 0). At a fixed terminal time T > 0, all parts are dispatched from the system. Now, in addition to the terminal dispatch time T, we wish to choose an intermediate time t e (0, T), at which all parts in the system are dispatched, so as to minimize the total expected waiting time of all parts until their dispatch.
(a) Describe, in detail, the distribution of the number of arrivals by the interme- diate time t, along with step-by-step justification.
(b) Given that n parts arrive during the first interval (0, t), how are those n arrival times distributed on the interval (0, t)?
(c) Again, given that n parts arrive during the first interval (0, t), what is the ex- pected total waiting time of the n parts until their dispatch at the intermediate time t?
(d) What is the unconditional expected total waiting time of parts (which arrived before the intermediate time t) until those are dispatched at the intermediate time t?
(e) Describe, in detail, the distribution of the number of arrivals in the second interval (t, T), along with step-by-step justification.
(f) What is the unconditional expected total waiting time of all parts (which have arrived in the whole interval (0, T))?
(g) What is the optimal intermediate dispatch time so as to minimize the total expected waiting time of all parts?
2. In an insurance company, the number of claims from 8am to 5pm is a nonhomoge- neous Poisson process with intensity function:

Suppose that the amount of each claim is uniformly distributed on [$200, $800], the amounts of claims are independent and are also independent of the number of claims.
(a) Find the average amount of the total claims received in t hours from 8am.
(b) Let N be the number of claims with claim amount less than $500 by 11am. Find the distribution of N
(c) Let ![]() be the number of claims with claim amount greater than $500 by time 2pm. Given
be the number of claims with claim amount greater than $500 by time 2pm. Given ![]() = 4, find the expected value of N .
= 4, find the expected value of N .
3. Consider a continuous MC {Xt }t.0 with the following generator matrix:
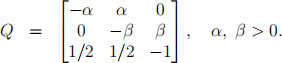
(a) Find the corresponding jump matrix P and the average holding time for each state.
(b) Find the stationary distribution of {Xt }t.0 .
(c) Find the limit distribution of {Xt }t.0 .
(d) Find limt≥→ P (t), where P (t) is the transition matrix.
4. A rent- a- car maintenance facility has capabilities for routine maintenance for only one car at a time. Cars arrive for this routine maintenance according to the Pois- son process at the mean rate of 3 per day, and the service time to perform this maintenance has the exponential distribution with the mean of 7/24 days.
(a) Explain why the stationary dist. of the system exists and provide the stationary distribution.
(b) It costs the company a fixed $150 a day to operate the facility and the company estimates a loss $10 per day in profit for each car that is tied up in the shop. The company, by changing certain procedures and hiring faster mechanics, can decrease the mean service time to 1/4 day. This also increase their operating costs. Find the operating cost before it is no longer economically attractive to make the change.
5. Calls arrive at a 2-line switchboard in a Poisson stream at rate α . Call times are exponential with mean 1/β . Callers finding 2 lines engaged do not wait but go elsewhere. Find the maximum ratio of α/β so that the proportion of lost calls should be not greater than 0.04 in the long run.
2023-07-03