BUS1 170 Fundamentals of Finance Final Exam
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BUS1 170 Fundamentals of Finance
List of topics and problems that may appear on the final exam
Disclaimer: This study guide contains problems that you may use to practice for the final exam. This is not an exhausting list of problems by any means. Additional problems will also be included in the exam, as well as modifications to the problems’
structure/content/question may be introduced. In addition, the final exam will contain conceptual questions, that are not listed in this guide. To prepare for them, students need to read respective textbook chapters and to review lecture slides. In addition, I highly recommend students to review problems covered in class, in homework assignments and study guide for midterm exam #2.
Chapter #1
1) Forms of business organization and their advantages and disadvantages (liability, taxation and etc.)
2) Conflicts between company’s stakeholders
a. Stockholder-Manager conflicts
b. Stockholder-Debtholder conflicts
Chapter #2
1) Financial markets and their participants
2) Types and functions of financial institutions
3) Market efficiency
Chapter #3
1) Financial statements and related calculations:
a. Balance Sheet
b. Income statement
c. Statement of Cash flows
2) Free cash flows
Chapter #4
1) Financial ratios: liquidity ratios, asset management ratios, debt management ratios, profitability ratios, market value ratios
2) DuPont analysis
Chapter #5
1) Calculation of PV, FV, PMT, I, N
2) Uneven cash flows calculations
3) Amortized loans and related calculations
Chapter #6
1) Cost of money and factors that affect it
2) Determinants of Interest Rates for corporate and treasury securities
3) Term structure of interest rates and yield curve
4) Pure expectation theory and its application
Chapter #7
1) Types of bonds, bond’s key features and cash flows; premium and discount bonds
2) Valuation of a bond (with all kinds of payments) and all related computations:
a. Coupon payments
b. value of a bond
c. yield to maturity
d. yield to call
e. current yield and capital gains yield
3) Bond’s relationships: coupon rate and YTM
4) Bond’s risk: price and reinvestment risks
Chapter #8
1) Expected vs realized return
2) Scenario analysis and calculation of expected return and stand-alone risk (variance and standard deviation of returns)
3) Coefficient of variation
4) Portfolio construction and related calculations: weights, expected return and risk
5) Correlation
6) Market risk and diversifiable risk
7) CAPM and related calculations: beta, portfolio beta, required rate of return
8) Security market line and factors that affect it
Chapter #9
1) Dividend discount model and constant growth DDM
2) Corporate valuation model (discounted cash flows model)
3) Comparables approach (P/E ratio)
Chapter #10
1) Calculation of components of WACC
2) Calculation of WACC
Chapter #11
1) Net Present value
2) Internal rate of return
3) Modified Internal rate of Return
4) Payback and discounted payback
Chapter #9
Problem #1
The most recent dividend paid by MMM Inc. was $0.50 per share. The dividend is expected to grow by 7% forever. Find the MMM’s stock intrinsic value per share if the required rate of return is 12%.
Solution:
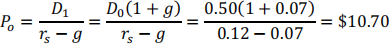
Answer: $10.70
Problem #2
The most recent dividend paid by MMM Inc. was $1.20 per share. The firm reinvests 45% of its earnings and generates ROE of 20%. The dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate forever since the company plans to keep current reinvestment ratio for a foreseeable future. Find the MMM’s stock intrinsic value per share if the required rate of return is 14%.
Solution:

Answer: $26.16
Problem #3
Sorenson Corp.’s expected year-end dividend is D1 = $1.90, its required return is rS = 11.00%, its dividend yield is 6.00%, and its growth rate is expected to be constant in the future. What is Sorenson's expected stock price in 7 years? Do not round intermediate calculations.
Solution:
Assuming constant growth DDM,
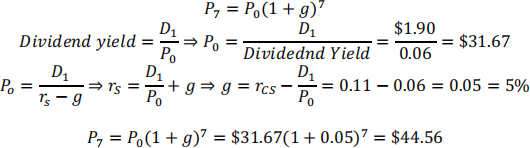
Problem #4
Huang Company's last dividend was $1.25. The dividend growth rate is expected to be constant at 15.0% for 3 years, after which dividends are expected to grow at a rate of 6% forever. If the firm's required return (rs) is 11%, what is its current stock price? Do not round intermediate calculations.
Solution:
D$ = $1.25
D" = D$ (1 + g)" = 1.25 ∗ 1.15 = 1.4375
D2 = D$ (1 + g)2 = 1.25 ∗ 1.152 = 1.653125
D3 = D$ (1 + g)3 = 1.25 ∗ 1.153 = 1.901093
After year 3, growth rate become stable g=6%, so D4 = D3 (1 + 0.06) = 2.0152 We find horizon value in year 3:
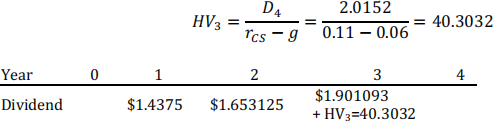
Using CF register of your calculator find present value of those cash flows:
CF0=0
CF1=1.4375
F01=1
CF2=1.653125
F02=1
CF3=$1.901093+ $40.3032 = $42.2043
F03=1
I=11
Compute NPV=33.50
Answer: $33.50
Problem #6
UComp forecasts that it will have the free cash flows (in millions) shown below. Assume the firm has zero non-operating assets. If the weighted average cost of capital is 15% and the free cash flows are expected to continue growing at the same rate after Year 3 as from Year 2 to Year 3, what is the firm’s total corporate value, in millions?
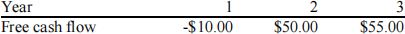
Solution:
1) Find growth rate of free cash flows from year 2 to year 3

2) Compute HV in year 3 because after year 3 growth rate becomes constant

3) To find corporate value, compute present value of all future FCF (including Horizon value in year 3)
Input in CF register of your calculator:
CF0=0
CF1=-10
F01=1
CF2=50
F02=1
CF3=55+1210=1265
F03=1
I=15
Compute NPV=860.87
Answer: Corporate value = 860.87
Chapter #10
Problem #7
The Firm that has a target capital structure of $5 million of debt, $1 million of preferred stock, and $4 million of common equity with respective before tax cost of 8%, 6% and 15%. Ifthe firm has marginal 26% tax rate:
1) Calculate weight of each component of the cost of capital
2) Calculate WACC
Solution:
1) Total amount of invested capital = $5M+$1M+$4M=$10M Weight of debt = $5M/$10M=0.50
Weight of preferred equity= $1M/$10M=0.10
Weight of common equity= $4M/$10M=0.40
2) ![]() ACC = wd rd (1 − T) + wp rp + wc rs
ACC = wd rd (1 − T) + wp rp + wc rs
![]() ACC = 0.50 × 8% × (1 − 0.26) + 0.10 × 6% + 0.40 × 15% = 9.56%
ACC = 0.50 × 8% × (1 − 0.26) + 0.10 × 6% + 0.40 × 15% = 9.56%
Problem #8
At the present time, ProperComp has 10-year noncallable bonds with a face value of $1,000 that are outstanding. These bonds have a current market price of $1,100 per bond, carry a coupon rate of 12%, and distribute annual coupon payments. The company incurs a federal-plus-state tax rate of 25%. If PC wants to issue new debt, what would be a reasonable estimate for its after-tax cost of debt?
Solution:
Find YTM of the bond
PV=-1100
PMT=120
N=10
FV=1000
Compute I=10.3481%
Chapter #11
Problem #9
Fernando Designs is considering a project that has the following cash flow and WACC data. What is the project's ordinary payback and discounted payback?
|
WACC: |
10.00% |
|
|
|
|
Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Cash flows |
-$750 |
$500 |
$500 |
$500 |
Solution:
a) Payback period:
|
WACC: |
10.00% |
|
|
|
|
Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Cash flows |
-$750 |
$500 |
$500 |
$500 |
|
Cumulative |
-750 |
-750+500=-250 |
250/500 |
|
Payback period = 1 + 250/500=1.5 years
b) Discounted payback period:
|
WACC: |
10.00% |
|
|
|
|
Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Cash flows |
-$750 |
$500 |
$500 |
$500 |
|
PV(CF) |
-750 |
PV(500)=454.545 |
PV(500)=413.22 |
|
|
Cumulative |
-750 |
-750+454.545=-295.55 |
295.55/413.23 |
|
Discounted payback period = 1 + 295.55/413.23=1.71 years
Problem #10
Hindelang Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow and WACC data. What is the project's NPV, IRR, MIRR?

Solution:
a) Net Present Value (NPV)
To solve for NPV put cash flows in CF register of your financial calculator:
CF0=-1000
CF1=500
F01=1
CF2=600
F02=1
CF3=700
F03=1
CF4=800
F04=1
I=13
Compute NPV=$888.15598
b) Internal rate of Return (IRR)
To solve for IRR put cash flows in CF register of your financial calculator:
CF0=-1000
CF1=500
F01=1
CF2=600
F02=1
CF3=700
F03=1
CF4=800
F04=1
Compute IRR=47.6272%
c) Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR)
To find MIRR we need to find present value of cash outflow and future value of cash inflows.
Step 1. Find PV(Cash outflows)=-1000 since there is only 1 cash outflow in time=0 Step 2. Find FV of cash inflows.
1) Find Present value of all inflows
Using CF register input only positive cash flows (cash inflows) in your calculator preserving their timing
CF0=0
CF1=500
F01=1
CF2=600
F02=1
CF3=700
F03=1
CF4=800
F04=1
I=13
Compute NPV=$1,888.15598
2) After that, you need to find future value of the present value of all cash inflows from previous calculation.
Use 5 TVM variable in your calculator:
PV=-$1,888.15598
N=4
PMT=0
I=13
Compute FV=$3078.5885
Step 3. Using 5 TVM variable of your calculator calculate MIRR by using PV of outflows and FV of inflows computed in previous steps
PV=-1000
N=4
PMT=0
FV=3078.5885
Compute I=32.46096%
MIRR=32.46096%
Problem #11
Calculate the crossover for the following projects A and B.
|
Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Project A CFs |
-5,000,000 |
2,000,000 |
2,500,000 |
500,000 |
|
Project B CFs |
-5,000,000 |
500,000 |
1,500,000 |
4,000,000 |
Solution:
Compute differential cash flows:
|
Project\Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Project A CFs |
-5,000,000 |
2,000,000 |
2,500,000 |
500,000 |
|
Project B CFs |
-5,000,000 |
500,000 |
1,500,000 |
4,000,000 |
|
Difference (A-B) |
0 |
1,500,000 |
1,000,000 |
-3,500,000 |
Input differential cash flows in the CF register of your financial calculator
CF0=0
CF1=1,500,000
F01=1
CF2=1,000,000
F02=1
CF3=-3,500,000
F03=1
Compute IRR=23.0139%
Answer: Crossover rate =23.0139%
2023-07-01