BUS1 170 Fundamentals of Finance Midterm #1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BUS1 170 Fundamentals of Finance
Midterm #1
List of topics and problems that may appear on the Midterm Exam #1
Disclaimer: This study guide contains problems that you may use to practice for the midterm exam #1. This is not an exhaustive list by any means. Additional problems will also be included in the exam, as well as modifications to the problems’
structure/content/question may be introduced. In addition, the midterm exam #1 will include many conceptual questions, that are not listed in this guide. To prepare for them, students need to read respective textbook chapters and review lecture slides and notes. In addition, I highly recommend students to review problems covered in class and in homework assignments. Cengage Adaptive Test Preparation is available for each Chapter in MindTap and is highly recommended for practice.
1. Chapter #1
a. Organizational forms of business, their main characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
b. Available forms of funding
c. Intra-company conflicts:
i. Stockholders – managers conflict
ii. Stockholders – bondholders conflict
d. Main definitions from the chapter
2. Chapter #2
a. Capital allocation process
i. Classes of securities
ii. Market participants
iii. Types of capital transfer
iv. Types of financial markets
v. Financial institutions and intermediaries
vi. IPO process
vii. Stock markets and their transactions
b. Know and understand main definitions from the chapter
c. Be able to apply principals discussed in a chapter to a real world questions
3. Chapter #3
a. Main financial statements: their construction and structure, information they contain
b. Calculations related to main financial statements covered in class and the textbook
4. Chapter #4
a. Ratio analysis: main types of financial ratios and their interpretation
b. ROE decomposition (Dupont equation)
c.
Practice problems
Chapter #3
Problem #1
Brown Office Supplies recently reported $155,500 of sales, $89,250 of operating costs other than depreciation, and $10,750 of depreciation. It had $150,000 of bonds outstanding that carry a 5.0% interest rate, and its federal-plus-state income tax rate was 26%. How much was the firm's earnings before taxes (EBT)?
Solution:
Simple Income Statement
Sales
-Cost of Goods Sold
=Gross Profit
-Operating Costs
-Depreciation & Amortization
=Operating Profit or Income (EBIT)
-Interest Expenses
=Earnings before taxes (EBT)
-Taxes
=Net Income
EBT=Sales – Cost of Goods Sold – Operating Costs – Depreciation & Amortization – Interest Expenses
It looks like in this problem cost of goods sold is included in operating costs, then EBT = $155,500 - $89,250 - $10,750 - $150,000*5%= $48,000
Answer: $48,000
Problem #2
AB Airlines began operating in 2018. The company’s taxable income (EBT) for its first five years is listed below. Each year the company’s corporate tax rate has been 26%. Assume that the company has taken full advantage of the Tax Code’s carry-back, carry-forward provisions and that the current provisions were applicable in 2018. How much did the company pay in taxes in 2021?
|
Year
|
Taxable Income
|
|
2018 |
-$5,000,000 |
|
2019 |
$1,000,000 |
|
2020 |
$2,000,000 |
|
2021 |
$3,000,000 |
|
2022 |
$5,000,000 |
Solution:
|
Year
|
Taxable Income
|
|
|
2018 |
-$5,000,000 |
-$5,000,000 |
|
2019 |
$1,000,000 |
-$5,000,000+$1,000,000= -$4,000,000 |
|
2020 |
$2,000,000 |
-$4,000,000 + $2,000,000= -$2,000,000 |
|
2021 |
$3,000,000 |
-$2,000,000+$3,000,000= $1,000,000 |
|
2022 |
$5,000,000 |
|
Every year company will use a portion of it’s loss of $5,000,000 from 2018. In 2021, the company completely exhausts carry-forward losses and have to pay taxes on $1,000,000 over it’s unused carry-forward losses.
Taxes in 2021 = $1,000,000 * 26% = $260,000
Answer: $260,000
Problem #3
The PROBiz INC reported the following information:
Net Income: $600,000
Tax Rate = 27%
Interest Expense = $150,000
What is the company’s EBT?
What is the company’s operating income (EBIT)?
What is the company’s after-tax operating income (NOPAT)?
Solution:
In this problem we will have to reverse our calculations and start not from Sales, but from Net income and consecutively add all line items to it.
Simple Income Statement
Sales
-Cost of Goods Sold
=Gross Profit
-Operating Expenses
-Depreciation & Amortization
=Operating Profit or Income (EBIT)
-Interest Expenses
=Earnings before taxes (EBT)
-Taxes
=Net Income
Net Income = EBT – Taxes = EBT – EBT * Tax rate = EBT (1- Tax rate) EBT = Net Income / (1 – Tax rate) = $600,000 / (1 – 0.27) = $821,917.81
EBT = EBIT – Interest Expenses
EBIT = EBT + Interest Expenses = $821,917.81 + $150,000 = $971,917.81 NOPAT=EBIT(1-T) = $971,917.81(1-0.27)=$709,500
Problem #4
AutoMotors recently reported the following information:
Net income = $730,000.
Tax rate = 27%.
Interest expense = $200,000.
Total invested capital employed = $9 million.
After-tax cost of capital = 8%.
What is the company’s EVA?
Solution:
EVA = NOPAT – (Total invested capital * WACC)
NOPAT = EBIT (1-Tax Rate)
As in previous problem:
EBT = Net Income / (1 – Tax rate) = $730,000 / (1 - 0.27) = $1,000,000
EBIT = EBT + Interest Expenses = $1,000,000 + $200,000 = $1,200,000
EVA = $1,200,000*(1 - 0.27) - $9,000,000 * 8% = $876,000 - $720,000 = $156,000
Answer: $156,000
Problem #5
Bauer Software's current balance sheet shows total common equity of $10,550,000. The company has 780,000 shares of stock outstanding, and they sell at a price of $12.50 per share. What is company’s MVA? By how much do the firm's market and book values per share differ? (Round your intermediate and final answer to two decimal places.)
Solution:
MVA = (P0 x Number of shares) – Book value = ($12.50 * 780,000 ) - $10,550,000= -$800,000
Answer: -$800,000
Problem #6
Lovell Co. purchased preferred stock in another company. The preferred stock’s before-tax yield was 7.50%. The corporate tax rate is 27%. What is the after-tax return on the preferred stock, assuming a 50% dividend exclusion? (Round your final answer to two decimal places.)
Solution:
BT Yield = 7.50%
50% of 7.50% is excluded from taxation dur to the dividend exclusion rule. Thus, 50% of 7.50% = 3.75% is excluded
Therefore, the company will have to pay taxes only on 7.50%-3.75%=3.75%
After-tax Yield = 3.75% (which are excluded from taxation) + 3.75% * (1- 0.27) = 6.4875%
Answer: AT Yield = 6.4875%
Problem #7
During 2022, Bascom Bakery paid out $55,000 of common dividends. It ended the year with $110,000 of retained earnings versus the prior year’s retained earnings of $86,600. How much net income did the firm earn during the year?
Solution:
Change in Retained Earnings = $110,000 - $86,600 = $23,400 – this means that in 2022 the Bascom Bakery retained $23,400. Since company paid $55,000 in dividends, then Net Income = $23,400 + $55,000 = $78,400
Answer: $78,400
Problem #8
Vasudevan Inc. recently reported operating income of $6.12 million, depreciation of $1.35 million, and had a tax rate of 27%. The firm's expenditures on fixed assets and net operating working capital totaled $0.95 million. How much was its free cash flow, in millions?
Solution:
FCF = [NOPAT + Depreciation & amortization] – [Capital expenditures + DNOWC] FCF = $6.12M*(1 - 0.27) + $1.35M – $0.95M = $4.8676M
Answer: $4,867,600
Problem #9
Assume that the corporate tax rate is 27% and the personal tax rate is 25%. The founders of a newly formed business are debating between setting up the firm as a partnership versus a corporation. The firm will not need to retain any earnings, so all of its after-tax income will be paid out to its investors, who will have to pay personal taxes on whatever they receive. What is the difference in the percentage of the firm's pre-tax income that investors actually receive and can spend under the corporate and partnership forms of organization ?
Solution:
Let firm’s pre-tax income = X.
If founders organize the firm as a corporation:
1) They corporation will have to pay income tax of 27% AT corporate income = X minus 27% = 0.73X
2) When founders receive dividends from a corporation, they will also have to pay personal income tax of 25% on dividends. Thus
AT personal income = 0.73X minus 25% = 0.73X(1-0.25)=0.5475X
This means that founders will receive 54.75% of the pretax corporate income
If founders organize the firm as a partnership, then the partnership does not have to pay any corporate income tax, so the entire pre-tax income (X) will be transferred to founders. Founders will only have to pay their personal income tax of 25% on X. Thus,
AT personal income = X minus 25% = 0.75X
This means that founders will receive 75% of the pretax corporate income if they organize as a partnership.
The difference in founders’ income between corporation and partnership will be:
Difference = 0.75X – 0.5475X = 0.2025 or 20.25%.
If founders organize firm as a partnership, they will receive 20.25% more of a pre-tax firm’s income.
Chapter #4
Problem #1
Riverlands Corp's total assets at the end of last year were $330,000 and its net income was $32,750. What was its return on total assets?
Solution:
ROA = NI / TA = $32,750 / $330,000 = 0.0992 or 9.92%
Answer: 9.92%
Problem #2
IMAG Corporation has operating income of $355,000 and a 25% tax rate. The firm has short-term debt of $145,000, long-term debt of $211,000, and common equity of $506,000. What is its return on invested capital?
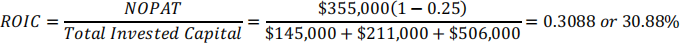
Answer: 30.88%
Some of the problems will require a few more steps to solve.
Problem #3
Find by how many days customers of Mills Corp are paying early or late given the following information. Mills Corp credit policy allows customers 45 days to pay for merchandise. Its sales last year were $315,000, and its year-end receivables were $60,000. If its DSO is less than the 45-day credit period, then customers are paying on time or even early. Otherwise, they are paying late. Base your answer on this equation: DSO – Credit Period = Days early or late. A positive answer indicates late payments, while a negative answer indicates early payments. Assume all sales to be on credit. Do not round your intermediate calculations.
Solution:
Credit period = 45 days
Sales = $315,000
AR = $60,000
DSO = AR / Sales per day
Sales per day = Sales / 365 = $315,000 / 365 = $863.01
DSO = $60,000 / $863.01 = 69.52 days
Company DSO – Credit period = 69.52 – 45 = 24.52 days (late)
Answer: 24.52 days
Problem #4
Franco Inc. has sales of $200,000 and accounts receivable of $18,500, and it gives its customers 25 days to pay. The industry average DSO is 27 days, based on a 365-day year. If the company changes its credit and collection policy sufficiently to cause its DSO to fall to the industry average, and if it earns 8.0% on any cash freed up by this change, how would that affect its net income, assuming other things are held constant? Assume all sales to be on credit. Do not round your intermediate calculations.
Solution:
Current AR = $18,500
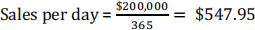
Industry DSO = 27.0
New AR = Sales per day * Industry DSO = $14,794.65
Cash freed from AR = $18,500 - $14,794.65 = $3,705.35
Return on freed cash = $3,705.35 * 8% = $296.43
Answer: $296.43
Problem #5
Last year Baltimore Corp had $275,000 of assets (which equals total invested capital), $305,000 of sales, $20,000 of net income, and a debt-to-total-capital ratio of 37.5%. The new CFO believes that a new computer program will enable the company to reduce costs and, thus, raise net income to $33,000. The firm finances using only debt and common equity. Assets, total invested capital, sales, and the debt to capital ratio would not be affected. By how much would the cost reduction improve the ROE? Do not round your intermediate calculations.
Solution:
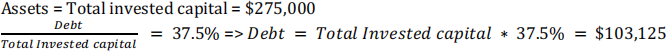
Equity = Total assets – Debt = $275,000 - $103,125 = $171,875
ROEOLD = NI/Equity = $20,000 /$171,875 = 0.1164 or 11.64%
ROENEW = $33,000 / $171,875 = 0.192 or 19.2%
Increase in ROE = ROENEW - ROEOLD = 19.2% - 11.64% = 7.56%
Answer: 7.56%
If you need more problems to practice before the exam, look at the Adaptive Test Preps in MindTap.
2023-07-01