MATHS 361: Partial Differential Equation Tutorial 11: Green’s function
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATHS 361: Partial Differential Equation
Tutorial 11: Green’s function
1. Suppose I have the equation:
uxx + ux = ex
with the boundary conditions ux(0) = 0 and u(1) = 0.
How would I solve this using Green’s functions?
2. Suppose I have the equation:
uxx + u2 = sin(x)
with the boundary conditions ux(0) = 0 and u(1) = 0.
How would I solve this using Green’s functions?
3. Suppose I have the equation:
uxx + u = x
with the boundary conditions ux(0) = 4 and u(π) = − 1.
How would I solve this using Green’s functions?
4. Suppose I have boundary conditions ux(0) = 0 and u(1) = 0.
Can you construct an Linear operator L[u] such that these boundary conditions are forbidden.
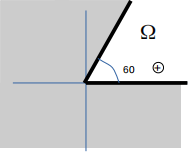
5. I am in domain depicted above: my function is in 2D, and I seek solutions to the equation ∆u = δ(x − 1,y − 0.2) within a wedge shaped domain (the angle of the wedge is 60 degrees, a.k.a. π/3 radians). For this question, please give your answers as diagrams, rather than explicit calculations.
(a) Assuming I have reflecting boundary conditions on both my edges, is it possible to solve via
reflections? If it is possible, where would I place my δ spikes on the plane, and what sign would they be? If it is not possible, what goes wrong?
(b) Assuming I have absorbing boundary conditions on both my edges is it possible to solve via
reflections? If it is possible, where would I place my δ spikes on the plane, and what sign would they be? If it is not possible, what goes wrong?
(c) Assuming I have one absorbing and one reflecting boundary condition is it possible to solve via reflections? If it is possible, where would I place my δ spikes on the plane, and what sign would they be? If it is not possible, what goes wrong?
2023-06-28