BIO 183 – Exam 1A – Fall 2016
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BIO 183 – Exam 1A – Fall 2016
Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer for each. Write your answers on the provided Scantron sheet. (2 points each)
1. Proteins are broken down into individual amino acids during a process known as
A. Denaturation
B. Anabolism
C. Dehydration
D. Hydrolysis
E. Condensation
2. The molecules represented below may be described as
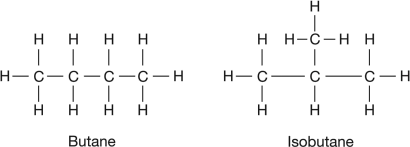
A. Stereoisomers
B. Enantiomers
C. Structural isomers
D. Dimers
E. None of the above
3. Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide composed of
A. Starch and glycogen
B. Glycogen and glucose
C. Lactose and fructose
D. Glucose and fructose
E. Maltose and glucose
4. Which of the following polysaccharides are likely to be used for structural purposed (instead of energy storage)?
A. Glycogen
B. Chitin
C. Starch
D. Cellulose
E. Both B and D
5. What is/are the main differences between DNA and RNA?
A. DNA is double-stranded while RNA is single-stranded
B. RNA uses Uracil instead of guanosine
C. RNA contains only 3 nucleotides, whereas DNA contains 4
C. DNA is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, while RNA is not
D. Both A and C are correct
6. What is the macromolecule illustrated below?
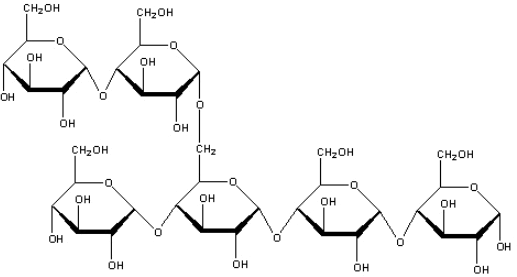
A. A protein
B. A polysaccharide
C. A nucleic acid
D. A monosaccharide
E. A lipid
7. Match the level of protein structure on the left with the appropriate description on the right.
i. Primary w. 3-dimensional shape of polypeptide chain
ii. Secondary x. linear sequence of amino acids
iii. Tertiary y. assembly of subunits into functional protein
iv. Quaternary z. hydrogen bonding within peptide backbone (ex: α-helix)
A. i=x, ii=w, iii=z, iv=y
B. i=z, ii=x, iii=y, iv=w
C. i=x, ii=z, iii=w, iv=y
D. i=y, ii=w, iii=x, iv=z
E. i.=x, ii=y, iii=z, iv=w
8. Which of the following structures would least likely be found as part of a bacterium?
A. A lysosome
B. A cell membrane
C. A Golgi apparatus
D. Ribosomes
E. Neither A nor C are found in prokaryotes
9. Which of the following structures allows cells to “read” the extracellular matrix and be influenced by it?
A. Desmosomes
B. Gap junctions
C. Tight junctions
D. Collagen fibers
E. Integrins
10. In plant cells, most of the ATP to be used by the cell is produced by which of the following?
A. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum
B. Chloroplasts
C. The rough endoplasmic reticulum
D. Mitochondria
E. None of the above
11. The cytoskeleton is composed of which of the following (in order, from small to large size):
A. Proteins, small bones, and cartilage
B. Actin filaments, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
C. Microtubules, intermediate filaments, and actin filaments
D. Actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
E. Flagella, microtubules, and actin filaments
12. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved primarily in which of the following?
A. Calcium storage, detoxification, and steroid synthesis
B. Protein packaging
C. Lysosome synthesis
D. Energy production
E. Macromolecules hydrolysis
13. The hydrolysis of macromolecules and organelles that are no longer needed in the cells is most likely to take place in which of the following?
A. Microbodies (peroxisomes)
B. Lysosomes
C. Endoplasmic reticulum
D. Golgi apparatus
E. Both A and B are involved in macromolecule and organelle degradation
14. Mitochondria contain DNA
A. True
B. False
15. Which of the following cell connections allows the movement of small ions such as calcium from one cell to another?
A. Desmosomes
B. Tight junctions
C. Gap junctions
D. Integrins
E. Claudins
16. The plasma membrane is best described as:
A. A double layer of proteins that is impermeable to water, but allows free movement of ions
B. A double membrane of phospholipids arranged in a fluid-mosaic of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates
C. A stiff double membrane composed of phospholipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
D. A double layer made entirely of glycoproteins, glycolipids, and cholesterol
E. None of the above
17. In fishes, O2 and CO2 move freely across the cell membrane of gill cells, down their concentration gradients, and
without the requirement of any carrier protein or any input of external energy. This is an example of
A. Active transport
B. Osmosis
C. Passive diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion
E. pumping action
18. The average intracellular voltage of most cells in the human body varies between which two values?
A. -500 to -1000 volts
B. -5 to -100 millivolts
C. 5 to 100 megavolts
D. -5 to -100 volts
E. -70 to +90 millivolts
19. The main difference between active and passive transport across a cell membrane is
A. Active transport requires channels while passive transport does not
B. Active transport requires transport proteins while passive transport does not
C. Active transport requires energy while passive transport does not
D. Active transport involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient
E. Both C and D are correct
20. All of the following plasma membrane activities require energy from ATP hydrolysis, except
A. The activation of the Na+ /K+ pump
B. Osmosis
C. Active transport
D. Activation of a flagellum
E. Neither B nor D requires ATP hydrolysis
Fill in the blanks. Please, write legibly.
1. Proportionally to the animal’s volume, the surface area of a bear is smaller/larger (circle the correct answer) than that of a mouse. (2 points)
2. All proteins are made of chains of amino acids. There are __________ (give a number) standard amino acids found in
eukaryotes. (2 points)
3. Draw the basic backbone of an amino acid. Circle and label the various functional groups. (6 points)
4. Cells in our salivary glands secrete the enzyme amylase. Amylase is a protein that allows us to hydrolyze starches into smaller subunits of mono- and oligosaccharides (= small chains). In the space below, draw a salivary gland cell, and explain how it produces and secretes amylase. Make sure that you draw all the macromolecules and organelles involved in this process, and give a short but precise explanation of each step. Make sure to use the precise terminology that we learned in class. (12 points)
5. On a hot spring day, you collect some skin cells from a black bear that you captured in southern Florida. Meanwhile, a friend of yours who is doing research in northern Alaska also collects skin cells from a polar bear that just woke up from hibernation. You and your friend decide to compare the cell membranes of the skin cells that you collected. With the help of a little cartoon/drawing, explain how you would expect the 2 cell membranes to differ. Make sure that you focus your attention mainly on phospholipids. (8 points)
6. The cell below was just placed in a container filled with water and some dissolved CO2. Over time, some molecules are going to cross the cell membrane while others might not be able to. On the following cartoon, draw arrows to represent the net movement of the various molecules involved in this system. (10 points)
This cell was placed in an environment that is hypotonic – isotonic – hypertonic (circle the correct answer)
Over time, you would expect this cell to crenate – stay the same – lyse (circle the correct answer)

Extra credit (2 points)
Tell me either a joke, the title of your favorite movie, or draw a little something nice J
2023-06-25