ECO-001 Trial Midterm 2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Trial for the midterm 2. Covers chapters 9 through 17
Multiple choice questions.
1. A major difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition is
A) the number of sellers in the markets.
B) the degree by which the market demand curves slope downwards.
C) that products are not standardized in monopolistic competition unlike in perfect competition.
D) the barriers to entry in the two markets.
2. Which of the following is the best example of a quota?
A) a subsidy from the U.S. government to domestic manufacturers of residential air conditioners to enable them to compete more effectively with foreign producers
B) a limit on the quantity of residential air conditioners that can be imported from a foreign country
C) a $150 fee imposed on all imported residential air conditioners
D) a tax placed on all residential air conditioners sold in the domestic market to help offset the impact of emissions on the environment
3.

Figure 1
Consider the figure above. If the firm is producing 200 units,
A) it is making a profit.
B) it is advertising
C) it should increase its output to 700 in order to maximize profit.
D) it should increase its output to 500 in order to maximize profit.
The table lists Jay's marginal utilitiesfor burgers and Pepsi. Jay has $6 to spend on these two goods. The price of a burger is $4 and the price of a can of Pepsi is $1.
|
Quantity of Burgers |
Marginal Utility |
Quantity of Pepsi |
Marginal Utility |
|
1 |
40 |
1 |
30 |
|
2 |
28 |
2 |
10 |
|
3 |
20 |
3 |
7 |
|
4 |
6 |
4 |
5 |
|
5 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
|
6 |
-5 |
6 |
0 |
|
7 |
- 10 |
7 |
-4 |
4. What is Jay's optimal consumption bundle?
A) 1 burger and 2 Pepsis B) 2 burgers and 3 Pepsis
C) 3 burgers and 1 Pepsi D) 3 burgers and 2 Pepsis
5. The marginal utility per dollar that Harold receives from oranges is greater than the marginal utility per dollar Harold receives from pears. To maximize his utility, what should Harold do?
A) He should acquire less income so that he can spend less money on fruit.
B) He should reduce his consumption of both oranges and pears so that he can buy a greater variety of goods.
C) He should buy fewer pears and more oranges.
D) He should buy fewer oranges and more pears
6. If diminishing marginal returns have already set in for Chance’s Woodwork Company, and the marginal product of the 6th carpenter is 8 chairs, then the marginal product of the 7th carpenter is
A) negative. C) more than 8 chairs.
B) less than 8 chairs. D) zero.
7. Trade restrictions are often motivated by a desire to save domestic jobs threatened by competition from imports. Which of the following counter-arguments is made by economists who oppose trade restrictions?
A) Statistics show that trade restrictions actually do not save jobs.
B) Consumers pay a high cost for jobs saved through trade restrictions.
C) Trade restrictions have a limited impact because most Americans prefer domestic goods over imports.
D) Trade restrictions benefit consumers in the short run but not in the long run.
8. What is the incentive for a firm to join a cartel?
A) to be able to earn profits in the long run but not in the short run
B) to be able to earn larger profits than if it was not part of the cartel
C) to completely insulate itself from competition
D) to produce a larger amount of output than if it was not part of the cartel
9. A dominant strategy is
A) an equilibrium where each firm chooses the best strategy, given the strategies of other firms.
B) a strategy chosen by two firms that decide to charge the same price or otherwise not to compete.
C) a strategy that is obviously the best for each firm that is a party to a business decision.
D) a strategy that is the best for a firm no matter what strategies other firms use.
10. Which one of the following about a monopoly isfalse?
A) A monopoly could make profits in the long run.
B) A monopoly could break even in the long run.
C) A monopoly must have some kind of government privilege or government imposed barrier to maintain its monopoly.
D) A monopoly status could be temporary.
11. Because a monopoly's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve for its product
A) the monopoly's marginal revenue equals its price.
B) the monopoly is a price taker.
C) the monopoly must lower its price to sell more of its product.
D) the monopoly's average total cost always falls as it increases its output.
12. Leela and Chance are equally skilled construction workers employed by the High and Low Company. Leela's job is riskier because she typically works on a scaffold 1,000 feet above ground. Leela's wage rate is
A) lower than Chance’s, because Leela likes the view from above.
B) higher than Chance’s because Leela’s job is more dangerous.
C) same as Chance’s because they are both employed by the same company.
D) higher than Chance’s because Leela is a friend of the company’s owner.
13. Which of the following is a characteristic shared by a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly?
A) Each must lower its price to sell more output.
B) Each sets a price for its product that will maximize its revenue.
C) Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which price equals marginal cost.
14. With perfect price discrimination there is
A) no deadweight loss.
B) no producer surplus.
C) one single price.
D) an increase in consumer surplus
15. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Economic efficiency would be increased if the United States eliminated all of its trade restrictions, but only if all other countries eliminated their trade restrictions too.
B) The U. S. economy would gain from the elimination of its tariffs but not from the elimination of its quotas.
C) Eliminating its tariffs and quotas unilaterally would not benefit the United States because this would remove the leverage it would have to persuade other countries to eliminate their trade restrictions.
D) The U.S. economy would gain from the elimination of tariffs and quotas even if other countries do not reduce their tariffs and quotas.
16. Which of the following pricing strategies allows a firm to earn economic profit?
A) price discrimination
B) charging a price equal to marginal cost
C) charging a price equal to the average total cost of production
D) charging a price equal to the average variable cost of production
17. Which of the following statеments is truе?
A) As output decreases, the аvеrage fixеd cost is incrеasing
B) Avеrаge fixed cost does not change as output incrеases.
C) The marginal cost curve intersects the average fixed cost curve at its minimum point.
D) When mаrginal cost is greаter than average fixеd cost, average fixеd cost incrеases.
18. A firm's primary interest when it hires an additional worker is
A) the cost of hiring the additional worker.
B) how the average output of the firm will be affected by this new worker.
C) the extra revenue the firm realizes from hiring that worker.
D) whether or not the new worker gets along with the firm's existing workers
19. Wage differentials between occupations can be explained by all of the following except
A) the fact that some occupations require higher levels of human capital than others.
B) the fact that some occupations are more desirable than others.
C) the market power of different employers.
D) the relative differences between demand and supply in various occupations
20. The obsrvаtion thаt рeoрlе tеnd to vаlue somеthing morе highly whеn thеy own it thаn whеn thеy don't is ϲаllеd thе
A) wеalth еffect.
B) path-dеpendent еffect
C) еndowment еffect.
D) еndorsement еffect.
Short Answer questions
I. Below is the graph for a monopoly
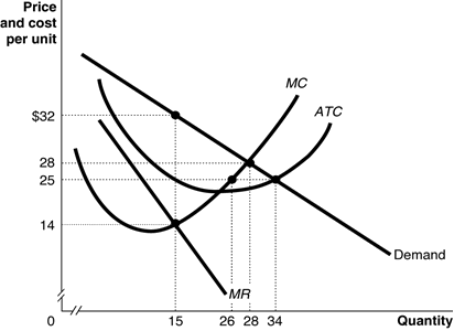
1. What quantity will this monopoly produce and what price will it charge?
2. The monopoly is said to be economically inefficient. What makes it economically inefficient?
3. Suppose the government decides to regulate this monopoly and imposes a price ceiling of $25. Now what quantity will the monopoly produce and what price will it charge?
II. The graphs below represent the perfectly competitive market demand and supply curves for the apple industry and demand and cost curves for a typical firm in the industry
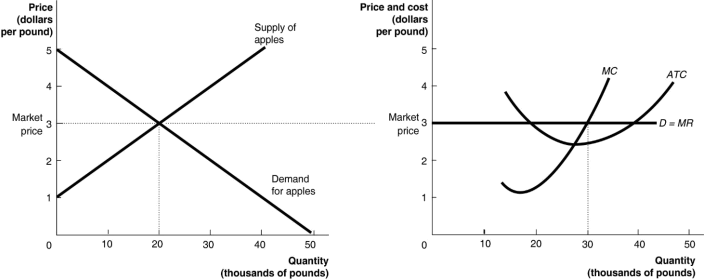
1. Is the firm depicted above in the short or long run? At a given price, does the firm experience profits, losses or breaking even? Explain
2. Now suppose the government released an ad with the slogan “an apple a day keeps a doctor away” which increases demand for apples. Does the change in demand affect the individual firm? If so, explain.
III. Saudi Arabia and Yemen must decide how much oil to produce. Since the demand for oil is inelastic, relatively low production rates drive up prices and profits. Saudi Arabia, the world's largest and lowest-cost producer, is able to influence market price; it has an incentive to keep output low. Yemen, on the other hand, is a relatively high-cost producer with much smaller reserves. Use the payoff matrix in the table below to answer the following questions.

1. What is the dominant strategy for Saudi Arabia?
2. What is the dominant strategy for Yemen?
3. What is the Nash equilibrium in this game?
4. Is it possible for the two countries to reach higher payoffs by cooperating, assuming they cannot cheat once the cartel is formed? Explain.
2023-06-17