BIO 183 – Exam 3 – Fall 2018
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BIO 183 – Exam 3 – Fall 2018
Please, read the instructions below carefully, then fill out the Scantron sheet as requested. You may write on the examination, but only the scantron will be used to determine your grade for the multiple choice questions. When you are finished with the exam, hand in both the scantron and the written exam to your instructor/proctor.
For the Scantron part of the exam, mark answers in the appropriate bubbles. Please, follow the instructions for use of the scantron sheet exactly.
Failure to follow these instructions carefully will result in a penalty of 1 point on the exam:
You should begin by filling in only the following information on the Scantron sheet (items must be both written in the spaces available, and marked in the appropriate bubbles).
Your name (last name, followed by one space, followed by your first name)
Your student ID#, if available
You may not use any supporting material (calculators/phones/computers…) on the written part of the exam, you must answer the questions in the space provided. Only questions answered in non-erasable pen will be eligible for a re-grade.
Honor code
I, ___________________________________________________ (PRINT), sign my name to this Honor Code to declare my intentions of upholding the ideals of academic honesty as a student at North Carolina State University. I understand that plagiarism and other forms of cheating, specified in Student Law, are unconscionable misconduct subject to review by campus courts. I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid in completing this examination.
Signature:_____________________________________________
My lab section is: Day: Time:
Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer for each. Write your answers on the provided Scantron sheet. (2 points each)
1. Sister chromatids move toward the opposite poles of a dividing cell during
a. Telophase of mitosis
b. Anaphase of meiosis I
c. Prophase of mitosis
d. Prophase of meiosis I and II
e. Anaphase of meiosis II
2. In what phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell?
a. Metaphase I
b. Anaphase I
c. Prophase I&II
d. Anaphase II
e. Metaphase II
3. The membrane that forms at the end of telophase to separate daughter cells at the end of mitosis in plants
is known as
a. Cleavage furrow
b. A septum
c. Cytokinetic constriction
d. A cell plate
e. Mitotic split
4. Which of the following is NOT a reason for mitotic cell division?
a. Pollen production in flowers
b. Fetal growth
c. Tissue repair after injury
d. Tumor formation
e. All of the above are reasons for mitotic cell division
5. Which of the following is/are true about nucleosomes?
a. Nucleosomes are arranged in a zig-zag pattern to make a 30nm DNA fiber
b. Nucleosomes contribute greatly to DNA compaction
c. Nucleosomes may be found in euchromatin or heterochromatin
d. Nucleosomes are found in eukaryotes
e. All the above are true
6. Nucleosomes are composed of DNA and proteins known as
a. SNPs
b. Kinetochores
c. Centrioles
d. Histones
7. DNA follows a pattern of replication known as
a. Conservative
b. Conservative, Semi-conservative, or dispersive (depending on the type of cell)
c. Liberal
d. Dispersive
e. Semi-conservative
8. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are required for which of the following processes?
a. DNA replication (during S-phase)
b. DNA transcription
c. Cell cycle regulation (check point regulation)
d. Sister chromatids separation (during mitosis)
e. Cellular communication
9. In the karyotype of a carrot cell, you would expect to see
a. More chromosomes than in a human karyotype
b. Fewer chromosomes than in a human karyotype
c. The same number of chromosomes as in a human karyotype, since carrots are diploid too
d. It depends on the stage of the cell cycle during which the comparison is made
e. There is no way to predict an organism’s chromosome count just by looking at its phenotype
10. The protein complexes that hold sister chromatids at their center are known as
a. Centrioles
b. Cohesins
c. Kinetochores
d. Spliceosomes
e. Centromeres
11. Typically, in a healthy cell, the longest phase of the cell cycle is the
a. M phase
b. G1 phase
c. G2 phase
d. S phase
e. Cytokinesis
12. Which of the following proteins acts as an important tumor suppressor?
a. SNP
b. Ras
c. P53
d. MPF
e. Gyrase
13. What type of enzyme is usually associated with the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-
donating molecules to specific substrates (i.e. associated with the phosphorylation of substrates)?
A. Phosphatase
B. Catalase
C. Hydroxylase
D. Kinase
E. Phosphate dehydrogenase
14. The advantage of using Ca2+, cAMP, or a pyramid-shaped cascade of events downstream of
membrane-bound receptors is
A. ATP conservation
B. Conservation of energy
C. Signal amplification and speed
D. Signal redundancy
E. Enzyme recycling
Short Anwers:
1. Epinephrine is a ligand that binds to ß-adrenergic receptors on cardiac muscle cells. ß-adrenergic receptors are a type of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). In the space below, CLEARLY draw a cell membrane with an embedded ß-adrenergic receptors, and label the various components of your drawing. In a few words, explain the steps that follow the activation of this receptor by epinephrine. Be as thorough and specific as possible. I do not want you to draw the entire mechanism. Just draw and explain the first few steps leading to phospholipase C or adenylyl cyclase activation. (10 points)
Molecules that bind to GPCRs would most likely be large and hydrophilic/small and hydrophobic (circle the correct answer)
The cellular response to this type of stimulus would most likely happen in 1 second / 1 day (circle the correct answer)
2. The structure of a DNA (or RNA) nucleotide may be simplified as follows:
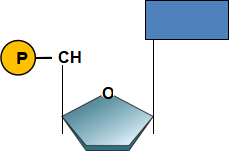
In the space provided below, link 2 of these nucleotides as if they were part of the same DNA strand. Then, clearly indicate the 3’ and the 5’ ends of your strand.
The bond formed between nucleotides in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and mRNA is called a ____________________________ bond, while the bonds that link the 2 strands to each other (between purines and pyrimidines) are called __________________________________ bonds (8 points)
3. In mammals, females are born with all the primary oocytes (= gametes – located in ovaries) that they will ever release. At birth, the primary oocytes are arrested in prophase I, and during each round of the estrous (or menstrual) cycle, a few primary oocytes proceed to develop into secondary oocytes that are arrested in metaphase II until fertilization takes place.
In the space below, draw a primary oocyte for a diploid mammal that has a 2N=4, as it develops into a secondary oocyte (i.e. as it goes from prophase I to Metaphase II).
Your drawing should at least include the chromosomes / chromatids / centrosomes / centromeres / membranes / etc. Clearly label the various phases, and for each phase, indicate whether the cell is haploid (N) or diploid (2N). You do NOT need to explain anything, but your drawings must be clear! (18 points)
4. Fern gametophytes are haploid. In the space below, draw a fern gametophyte (N=4) in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, in metaphase, and after cytokinesis (i.e. draw the 2 daughter cells). (6 points)
G1 phase:
Metaphase:
Daughter cells in G1 phase:
5. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a paracrine molecule that stimulates cell proliferation by binding to a tyrosine kinase receptor (RTK) known as EGFR. In the space below and with the help of a sketch, explain how EGF stimulates cells to proliferate. (10 points total)
In your explanation, make sure that you include a an explanation of the sequence of events that follow the binding of EGF to EGFR, as well as a description of the cell cycle with its regulation points (check points) and explain how it gets affected by EGF.
The protein Ras (the effector protein directly downstream of RTKs) is known to be a proto-oncogene.
What does this mean? What is a proto oncogene? (2 points)
How can a mutation in Ras lead to cancer? (2 points)
6. On the drawing below, clearly label all 3’ and 5’ ends, label the leading and lagging strands, and draw the primers and newly polymerized DNA. (22 points)
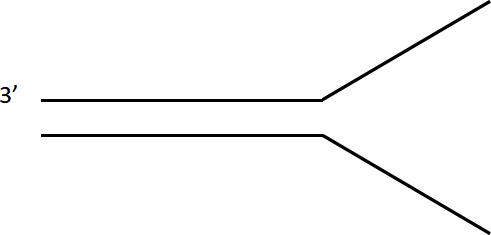
This drawing represents the process of (finish the sentence) _______________________________ that takes place during the _______________________ phase of the cell cycle.
In the space below, write a short but precise description of 6 enzymes that we discussed in class and that are directly involved in the mechanism drawn above.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
2023-06-13