BIO 183 – Exam 2 – Spring 2018
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BIO 183 – Exam 2 – Spring 2018
1. Which of the following best describes an endergonic reaction?
A. ΔG < 0, and free energy is released during the reaction
B. ΔG > 0, and free energy is released during the reaction
C. ΔG < 0, and the reaction requires the addition of free energy
D. ΔG > 0, and the reaction requires the addition of free energy
E. In the presence of enzymes, both B and D could be endergonic
2. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by
A. Converting substrates into products in their allosteric site
B. Lowering the activation energy necessary to start the reaction
C. Converting endergonic reactions into exergonic ones
D. Both B and C are correct
3. The scenario below describes which type of enzyme inhibition?
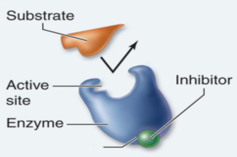
A. Non-competitive inhibition
B. Allosteric inhibition
C. Positive feedback inhibition
D. Competitive inhibition
E. Both A and B are correct (the are virtually the same thing)
4. Which of the following factors would have the ability to denature a protease commonly found in your stomach (at a
pH of approximately 2.0)?
A. Placing the enzyme in the fridge (around 4 degrees C)
B. Placing the enzyme in a neutral pH environment (pH = 7.0)
C. Placing the enzyme in an environment containing the wrong salt concentration
D. Placing the enzyme in the oven (around 350 degrees C)
E. B, C and D could potentially denature this enzyme
5. Which of the following molecules most closely resembles ATP?
A. A protein
B. A nucleotide
C. A carbohydrate
D. A triglyceride
E. Water
6. The main products of the citric acid cycle (also called Krebs cycle) are
A. ATP and citric acid
B. Citric acid that is used in oxidative phosphorylation.
C. ATP, NADH, and FADH2
D. Citric acid and NADPH
E. Krebs protein and ATP
7. In cellular respiration, which of the following are products of glycolysis?
A. Acetyl CoA and ATP
B. Acetyl CoA and citric acid
C. Pyruvate, ATP, and Acetyl CoA
D. Pyruvate, ATP, and NADH
E. NADPH, FADH2, and ATP
8. During cellular respiration, glycolysis takes place in which of the following?
A. The mitochondrial matrix
B. The inter-membrane space in mitochondria
C. The cytoplasm
D. The inner mitochondrial membrane
E. In the extracellular environment
9. When anaerobic metabolism (fermentation) takes place in mammalian muscle cells, which of the
following are produced?
A. 36-38 ATPs and lactic acid
B. 2 ATPs and lactic acid
C. 36 -38 ATPs and ethanol
D. 2 ATPs and citric acid
E. 36 ATPs and lactic acid
10. The fermentation process that leads to the production of ethanol is most likely to takes place in
A. Bacteria
B. C3 plant cells
C. Animal muscle cells
D. Yeast
E. B, C, and D are correct
11. What is the purpose of stomata on the underside of leaves, in green plants?
A. They allow the passage of electrons required for photosynthesis
B. They allow the movement of water into the leaves when it rains
C. They are mainly empty spaces between grana, in chloroplasts
D. They allow the movement of CO2 in and O2 out of leaves
E. They allow the filtration of the air we breathe
12. The proton-motive force generated during oxidative phosphorylation is used to drive the activation
of which of the following?
A. ATP synthase
B. Ubiquinone
C. Cytochromes
D. NADH dehydrogenase
E. Low-energy electrons
13. Organisms that generate their own food by converting inorganic molecules into organic ones are
called:
A. Heterotrophs
B. Organotrophs
C. Autotrophs
D. Chemiotrophs
E. Prototrophs
14. The 2 main stages of photosynthesis, in chloroplasts are
A. Photosynthesis and gluconeogenesis
B. Oxidative phosphorylation and Citric acid cycle
C. Light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle
D. Light and heavy reactions
E. Carbon-fixing and Calvin cycles
15. Which of the following justifies the need for a cyclic electron flow in the thylakoid membrane
A. The Calvin cycle uses more NADPH than ATP
B. When oxygen is not available, chloroplasts switch to cyclic electron flow
C. When CO2 is not available, chloroplasts make glucose in a cyclic fashion
D. The Calvin cycle uses more ATP than NADPH
E. When oxygen is not available, the Calvin cycle has to stop
16. Photorespiration can best be explained by which of the following?
A. Photorespiration happens when plants use oxygen in chloroplasts instead mitochondria
B. During periods of drought, plants open their stomata to better absorb water through their leaves
C. At night or in the dark, C3 plants store CO2 in the form of organic molecules such as malate
D. Some plants utilize light energy to pump oxygen in their leaves
E. When temperatures get high, plants close their stomata, and the increased level of O2 in the mesophyll causes rubisco to work as an oxygenase instead of a carboxylase
17. The answer to this question is
A. Not this one
B. Not this one either
C. That’s it! The answer is C!
D. Oooops, you’ve gone too far. Please go back to C
Fill in the blanks (2 points/sentence):
1. When carbohydrates and lipids are not available for cellular respiration, cells can still obtain energy from lipids through a process known as ___________________________.
2. In the following reaction, circle the molecule that is in its reduced form: Mg + O ---> Mg2+ + O2-
3. Sea water would be said to be hypertonic/hypotonic/isotonic (circle the correct answer) to one of your muscle cells. If left in sea water for an extended period of time, your muscle cell would ________ _________________
Short answers:
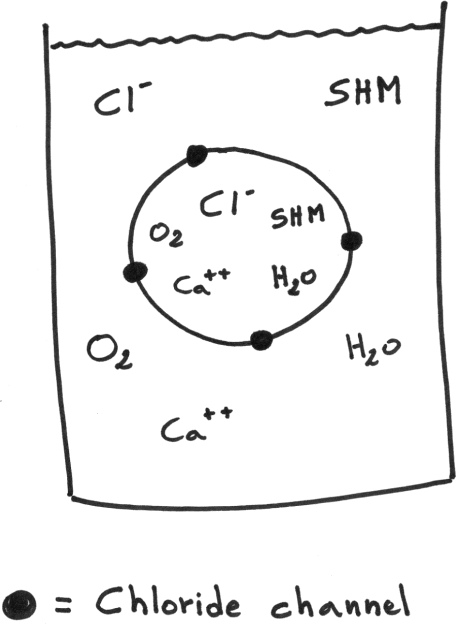
S.A. Question 1 (10 points)
The hypothetical cell represented below has a plasma membrane made of phospholipids in which are embedded a few leak channels only – nothing else. When the cell is immersed in the following environment, some molecules will be able to cross the cell membrane while others won’t. On the following sketch, draw arrows that represent the net movement of the various molecules involved, as the system is moving toward equilibrium. If there is no net movement, do not draw any arrow. (10 points)
|
Concentration in intracellular environment |
Concentration in beaker |
|
Ca+ = 10mM Cl- = 50mM Small hydrophobic molecule (SHM) = 30mM Oxygen = 20% |
Ca+ = 100mM Cl- = 25mM Small hydrophobic molecule (SHM) = 10mM Oxygen = 10% |
|
|
S.A. Question 2: Sodium fluoroacetate is a colourless salt similar to sodium chloride (table salt) that occurs naturally as an anti-herbivore metabolite in various plants of Brazil, Africa, and Australia. The mechanism by which sodium fluoroacetate kills herbivores is by combining with coenzyme A to form fluoroacetyl CoA, which reacts with citrate synthase to produce fluorocitrate which binds very tightly to aconitase, thereby halting the Kreb’s cycle. This inhibition results in an accumulation of citrate in the blood. Citrate and fluorocitrate are allosteric inhibitors of phosphofructokinase-1, a key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis.
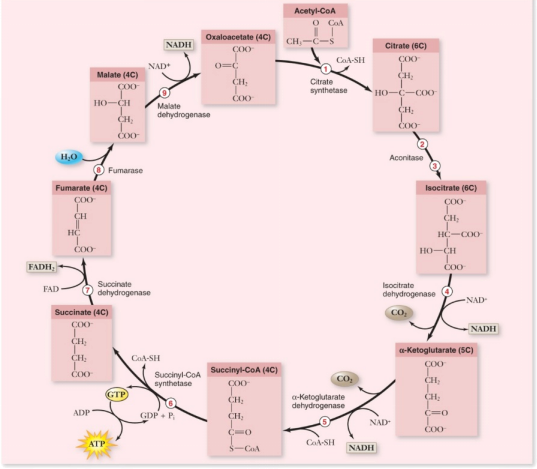
Here is a representation of the Kreb’s cycle to help you understand the statement above:
On the next (blank) page, draw the complete pathway of aerobic cellular respiration as it normally happens in a healthy cell. For each step, make sure that you indicate what molecules go in and what molecules come out. Your sketch should hopefully be very similar to the summary that you submitted on Moodle. Additionally, clearly indicate the sites of action of sodium fluoroacetate.
For the few molecules described below, what kind of change (if any) would you expect to observe in a herbivore that ingested a plant containing sodium fluoroacetate (2 points each)
O2 consumption: increase / decrease / stay the same (circle the correct answer)
NADH production: increase / decrease / stay the same (circle the correct answer)
Glucose intake in cells: increase / decrease / stay the same (circle the correct answer)
CO2 production: increase / decrease / stay the same (circle the correct answer)
Pyruvate production: increase / decrease / stay the same (circle the correct answer)
Approximately how many ATPs would you expect this herbivore to produce per molecule of glucose after ingestion of this plant? __________
Draw your aerobic respiration sketch here. Don’t forget to indicate the sites of action of sodium fluoroacetate (18 points)
S.A. question 3: In the space below, CLEARLY draw a cross section of a thylakoid membrane to illustrate the process of cyclic photosynthesis that you would observe in a C3 plant. Make sure to indicate what goes in and what comes out in term of energy, electrons, protons and indicate their direction of movement. Be as thorough as possible. (18 points)
What is/are the products of cyclic photosynthesis, and where do they go?
2023-06-06