CAS NE101 EXAM #1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CAS NE101 EXAM #1
1. Researchers have noted that young rodents develop a capacity to learn before they develop a capacity to form long-term memories. This implies that:
a. rodents have poorer memory systems than other mammals.
b. rodents are not appropriate models for studying the fundamentals of memory processes.
c. learning and memory involve different processes.
d. learning does not require functional neural circuits.
2. Which question does the mechanisms perspective in biological psychology address?
a. How do learning and memory performance change over the life span?
b. What physiological changes in the brain encode memories?
c. What are the prospects for a “smart pill” to improve memory performance?
d. What pattern of movements must an animal make in order to learn a maze?
3. Which question is an example of the comparative/evolutionary perspective in behavioral neuroscience?
a. To what extent can different species see color?
b. What environmental experiences in early life are required for vision to develop normally?
c. What kind of treatments can correct faulty vision?
d. How are the visual areas of the brain organized?
4. Which question derives from thefunctional description of behavior?
a. How does mating depend on hormones in different species?
b. How are the sounds of speech patterned?
c. How do specialized patterns of behavior contribute to mating and to care of offspring?
d. How do reproductive behaviors develop over the life span?
5. Which statement represents a structural description of behavior?
a. Different species of mammals produce similar types of hormones.
b. The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are related to depletion of a specific neurotransmitter.
c. When an animal learns, the number and morphology of neuron connections change in specific brain regions.
d. The amount of aggressive behavior between male rodents changes after puberty.
6. Which of the following is an example of a somatic intervention study?
a. Measurements of the extent of brain abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia
b. Observations of patterns of brain activity in animals trained in a maze
c. Measurements of hormones in male rats exposed to female rats
d. Observations of the effects of giving a drug to some rats but not to others
7. Which of the following is an example of a behavioral intervention study?
a. Measurements of the extent of brain abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia
b. Observations of patterns of brain activity in animals trained in a maze
c. Measurements of hormones in male rats exposed to female rats
d. Observations of the effects of giving a drug to some rats but not to others
8. Refer to the figure.
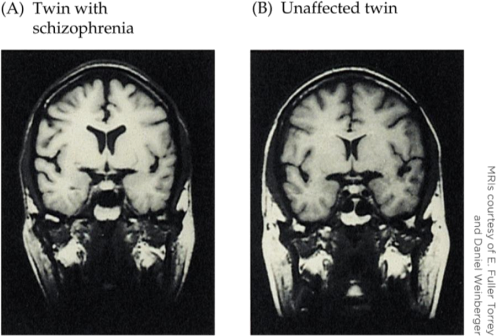
A researcher who is studying schizophrenia examines the images above. What sort of study is this researcher conducting?
a. A study to determine causality
b. A somatic intervention
c. A behavioral intervention
d. A correlational study
9. Which statement represents the most reductionist explanation of an observed phenomenon?
a. A group of fish form a school to avoid predation.
b. Muscle contractions are caused by spinal cord neurons.
c. Each neurotransmitter released by neurons must bind to a specific receptor protein.
d. The eyes send light information to the visual cortex at the back of the brain.
10. Refer to the figure.
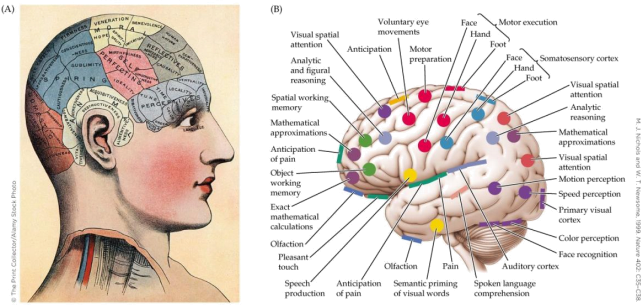
Which statement accurately describes the information represented by the figure?
a. There is evidence that the brain functions as a whole.
b. Phrenology localizes areas of peak activation in the brain.
c. It is possible to determine a person’s strengths from the shape of their head.
d. There is localization in the brain, but it does not reliably correspond to bumps on the head.
11. Which statement is supported by phrenology?
a. The brain functions as a whole.
b. There is some localization of function in the brain.
c. Visual processing occurs in several lobes of the brain.
d. There is more than one brain area that is responsible for aggression.
12. Which statement about dendrites isfalse?
a. A single cell’s dendrites form a dendritic tree.
b. The diversity of neuronal shapes is caused primarily by variation in the form and shape of dendrites.
c. Dendrites may be several meters in length in giraffes.
d. Dendritic spines appear to be subject to modification as a result of experience.
13. Refer to the figure.
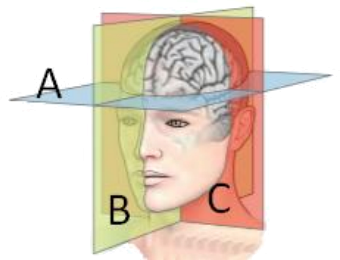
The plane labeled A is called the _______ plane, the plane labeled B is the _______, and the plane marked C is the _______.
a. dorsal; sagittal; posterior
b. sagittal; ipsilateral; coronal
c. horizontal; sagittal; coronal
d. coronal; horizontal; sagittal
14. In which plane of section would it be easiest to see the corpus callosum?
a. Sagittal cut directly down the midline
b. Horizontal cut at the level of the brainstem
c. Coronal cut at the level of the cerebellum
d. Sagittal cut at the level of the temporal lobe
15. Refer to the figure.
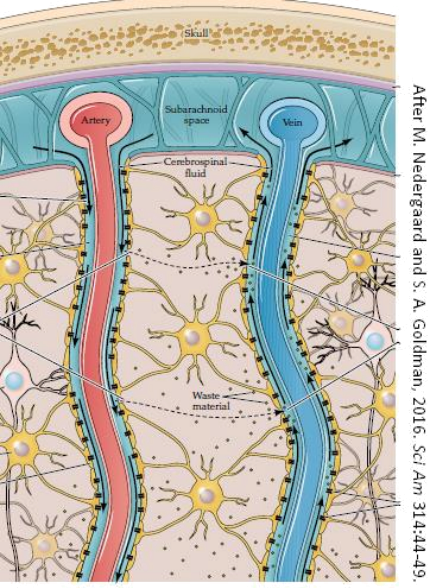
The dashed arrows in this figure represent what key process?
a. The vascular circulation of blood that maintains blood pressure
b. The glymphatic flow that provides protection from harmful substances in the brain
c. The regeneration of the choroid plexus.
d. The opening and closing of the aquaporins to waste material.
16. A person suffers a stroke that affects the base of the anterior cerebral artery. This will likely result in reduced blood flow to the:
a. medial frontal and parietal lobes.
b. occipital lobe.
c. lateral temporal lobe.
d. lateral frontal and parietal lobes.
17. Which arteries provide blood to the brain?
a. Basilar artery and carotid artery only
b. Carotid artery and vertebral artery only
c. Basilar artery, carotid artery, and vertebral artery
d. Carotid artery, choroid plexus, and vertebral artery
18. Which imaging technique is not used for studies of the structural details of the brain?
a. CT scan
b. fMRI scan
c. MRI scan
d. Angiography
19. Which imaging technology could provide a physician with a very high-resolution image of the thalamus?
a. MRI
b. CT
c. PET
d. DTI
20. Which statement about conventional fMRI is true?
a. Subjects must fast before testing.
b. Subjects must lie completely motionless.
c. It involves the use of X-rays.
d. Subjects must perform specific cognitive tasks.
21. A dyadic fMRI could be used to:
a. test a person’s response to two voices coming through headphones.
b. sequentially examine the brain responses of identical twins.
c. simultaneously examine how two people respond to the same stimulus .
d. stimulate movement of two people simultaneously.
22. Refer to the figure, which shows two voltage-gated Na+ channels (in blue) in the center.
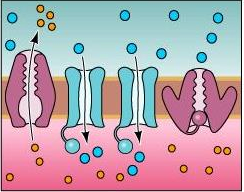
What is taking place in this figure?
a. A depolarizing force is bringing the membrane closer to threshold.
b. The voltage-gated Na+ channels have opened, and action potential is triggered.
c. The open Na+ channels have created the resting potential.
d. The open Na+ channels have produced afterpotential.
23. The sodium-potassium pump is responsible for
a. pushing three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions pumped in.
b. initiating the action potential.
c. pumping potassium and sodium into the cell.
d. creating a positive net charge inside the cell.
24. Action potentials generally are not transmitted along dendrites because they have:
a. sodium channels.
b. few voltage-gated Na+ channels.
c. no myelin.
d. mitochondria.
25. When applying hyperpolarizing or depolarizing stimulus to the membrane of a neuron, the beginning and end of the neuron’s response become distorted. This is due to:
a. conductance of the membrane.
b. the insulating properties of myelin.
c. capacitance of the membrane.
d. gated ion channels.
26. Whether a synapse is excitatory or inhibitory is determined by the:
a. number of action potentials arriving at the presynaptic axon terminal.
b. size of the calcium current flowing into the presynaptic axon terminal.
c. type of transmitter released by the presynaptic neuron and the receptor to which that transmitter binds on the postsynaptic neuron.
d. sensitivity of the postsynaptic membrane.
27. At chemical synapses, most of the synaptic delay (the time between the arrival of a presynaptic action potential and the appearance of a postsynaptic EPSP or IPSP) is attributable to the:
a. the time needed for Ca2+ to enter the terminal and the vesicles to fuse.
b. rate of diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules across the synapse.
c. rate at which vesicles move to the presynaptic membrane and rupture.
d. interaction of the transmitter with its receptors.
28. Which process is not involved in chemical synaptic transmission?
a. Electrical conduction across the synaptic cleft
b. Binding to autoreceptors
c. Influx of calcium at the presynaptic membrane
d. Reuptake
29. Muscarine and nicotine mimic the action of:
a. G proteins.
b. calcium.
c. acetylcholine.
d. GABA.
30. Curare and bungarotoxin are similar in that they both:
a. act on the GABA receptor.
b. act as acetylcholine receptor agonists.
c. come from animals.
d. act as acetylcholine receptor antagonists.
31. The poison extracted from the mushroom Amanita muscaria is a(n):
a. GABA receptor agonist.
b. GABA receptor antagonist.
c. acetylcholine receptor antagonist.
d. acetylcholine receptor agonist.
32. Which compound would prevent the release of neurotransmitters from stimulated neurons?
a. Bungarotoxin because it disables t-SNAREs.
b. Tetanus toxin because it cuts up SNARE proteins.
c. Synaptotagmin because it senses Ca2+ .
d. Tetrodotoxin because it blocks exocytosis.
33. Which statement about retrograde synapses is false?
a. The postsynaptic cell releases a gas neurotransmitter.
b. Transmission starts with classic axo-dendritic activity.
c. The presynaptic cell is signaled to release more transmitter.
d. They typically involve dendro-dendritic activity.
34. In an animal research study, channelrhodopsin is inserted into neurons that make GABA (which inhibits neurons), and halorhodopsin is inserted into neurons that make glutamate (which excites neurons). Both sets of neurons make connections with a set of neurons responsible for eye blinking. If the eye-blink neurons are stimulated by blue light, the animal will _______ because the _______ neurons will be _______.
a. blink; glutamate; depolarized
b. not blink; GABA; depolarized
c. not blink; glutamate; hyperpolarized
d. blink; GABA; hyperpolarized
35. Which of the following is not a specific criterion for classifying a substance as a neurotransmitter?
a. Existence of the substance in the presynaptic terminal
b. Release of the substance when nerve impulses reach the terminal ending
c. Existence of specific receptors for the substance on the postsynaptic membrane
d. Ability of the substance to travel long distances between the site of origin and target area
36. Which substance is not a catecholamine neurotransmitter?
a. Dopamine
b. Serotonin
c. Epinephrine
d. Norepinephrine
37. Which substance is a monoamine neurotransmitter?
a. Dopamine
b. Glutamate
c. GABA
d. Glycine
38. Muscarine is a hallucinogen that is an agonist at muscarinic receptors. Which of the following neurotransmitters is also an agonist at muscarinic receptors?
a. Dopamine
b. Serotonin
c. GABA
d. Acetylcholine
39. The effects of the drug scopolamine suggest that _______ plays an important role in _______.
a. dopamine; schizophrenia
b. serotonin; depression
c. acetylcholine; learning and memory
d. GABA; seizures
40. Drugs such as alprazolam (Xanax) work at _______ receptors which are _______.
a. GABAa; metabotropic
b. GABAa; ionotropic
c. D1; ionotropic
d. D1; metabotropic
41. If drug A is found to bind to a certain type of receptor for a longer time period than drug B does, then drug A is said to have greater:
a. affinity.
b. selectivity.
c. potency.
d. specificity.
42. What is the process that is being depicted in this figure?
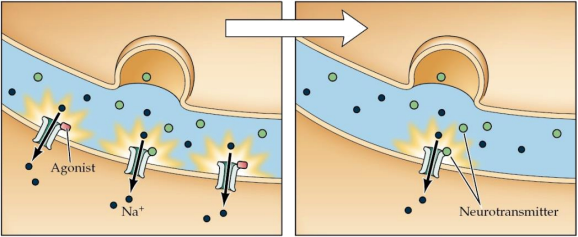
a. Up regulation
b. Cross tolerance
c. Down regulation
d. Metabolic tolerance
43. A person who develops involuntary contractions of some muscles after walking barefoot in the woods may have been exposed to:
a. botulinum toxin.
b. black widow venom.
c. tetanospasmin.
d. psilocybin.
44. You discover a compound that has a similar molecular structure to amphetamine. This compound will probably affect _______ receptors.
a. catecholamine
b. acetylcholine
c. endogenous opiate
d. GABA
45. Which substance competes with the neuromodulator adenosine? And where on this figure would it act?

a. Caffeine; B
b. Caffeine; A
c. Colchicine; B
d. Colchicine; A
46. What is the difference between first-generation antipsychotics and second-generation antipsychotics?
a. First-generation antipsychotics only treat the negative symptoms of schizophrenia
b. Second-generation antipsychotics only function at D2 receptors; whereas first-generation antipsychotics function at both D2 receptors and serotonergic receptors.
c. Second-generation antipsychotics can treat both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia; whereas first-generation antipsychotics only treat positive symptoms
d. Second-generation antipsychotics can treat only negative symptoms of schizophrenia; whereas first-generation antipsychotics only treat positive symptoms and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
47. Alcohol’s calming influence may be attributable to its ability to _______ secretion.
a. decrease norepinephrine
b. increase anandamide
c. decrease opiate
d. increase allopregnanolone
48. You discover a protein that has a binding site for benzodiazepines, steroids, and barbiturates. This protein probably binds:
a. dopamine.
b. serotonin.
c. GABA.
d. acetylcholine.
49. Which of the following is a possible consequence of long-term, chronic amphetamine use?
a. Compulsive behavior and depression
b. Psychosis and somnolence
c. Anxiety and cognitive impairment
d. Compulsive behavior, cognitive impairment, and psychosis
50. Which of the following has not been shown to be an effect of the drug MDMA (“Ecstasy”) in humans?
a. Memory disturbances
b. Alteration of serotonergic neurons
c. PTSD
d. Depression
51. Stimulation of serotonergic receptors in the visual cortex by which drug causes hallucinations?
a. THC
b. Ketamine
c. LSD
d. Cannabidiol
52. Ketamine is a hallucinogen which functions by blocking NMDA receptors. Which neurotransmitter typically activates NMDA receptors?
a. Glutamate
b. GABA
c. Norepinephrine
d. Nitric Oxide
53. As a psychologist treating a client with recalcitrant depression and a client with obsessive– compulsive disorder, you recommend _______ and _______, respectively.
a. LSD; ketamine
b. psilocybin; ketamine
c. ketamine; psilocybin
d. ketamine; MDMA
54. Which statement about substance abuse treatments is true?
a. Behavioral methods do not require much time.
b. Pharmacological treatments can only treat the discomfort of withdrawal.
c. We may be able to disrupt the connection between drug cues and the rewards of a drug.
d. Vaccination studies have not produced promising results.
55. An effective anti-cocaine vaccine would:
a. cause absolute aversion to cocaine.
b. increase the effort required to obtain and use cocaine.
c. decrease the pleasure provided by any drug.
d. decrease the pleasure provided by cocaine.
56. Neuronal and hormonal communication both involve:
a. all-or-none impulses.
b. specialized receptor molecules.
c. movement of materials through the bloodstream.
d. voluntary control.
57. Which substance is not a peptide hormone?
a. LH
b. oxytocin
c. aldosterone
d. GH
58. Which of the following is not a steroid hormone?
a. Growth hormone
b. Cortisol
c. Androstenedione
d. Estrogen
59. A newly developed drug that blocks cell membrane receptors would likely have the greatest effect on:
a. aldosterone.
b. testosterone.
c. cortisol.
d. vasopressin.
60. When _______ is released from the cells of the pancreas, blood levels of glucose _______.
a. glucagon; stay level
b. insulin; rise
c. glucagon; fall
d. insulin; fall
61. Which technique could be used to determine whether the receptors of a particular hormone are located in a specific type of cell?
a. Immunocytochemistry
b. Radioimmunoassay
c. Autoradiography
d. Both a and c
62. If a person does not release sufficient amounts of oxytocin and vasopressin, the sources of the problem are likely to be found in the _______ or the _______.
a. hypothalamus; posterior pituitary
b. hypothalamus; anterior pituitary
c. posterior pituitary; median eminence
d. anterior pituitary; median eminence
63. Oxytocin and vasopressin are:
a. both secreted in response to suckling in postpartum female mammals as part of a milk production and release process.
b. both amine hormones transported along the hypophyseal portal system to the posterior pituitary.
c. anterior pituitary hormones controlled by hypothalamic releasing hormones.
d. synthesized in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus and transported along axon terminals to the posterior pituitary.
64. Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei are important for the:
a. production of releasing hormones.
b. production of oxytocin and vasopressin.
c. release of ACTH.
d. production of melatonin.
65. Normal levels of blood plasma TSH, LH, FSH, ACTH, prolactin, and growth hormone are maintained by the:
a. posterior pituitary.
b. anterior pituitary.
c. adrenal gland.
d. GnRH-secreting cells.
66. The steroid hormones cortisol and corticosterone are released by the _______ in response to the hormone _______ from the ______.
a. kidney; ACTH; posterior pituitary
b. kidney; AVP; anterior pituitary
c. adrenal cortex; ACTH; anterior pituitary
d. adrenal medulla; AVP; posterior pituitary
67. Sympathetic nervous system activation leads to the release of _______ from the adrenal medulla.
a. glucocorticoids
b. mineralocorticoids
c. epinephrine and norepinephrine
d. androstenedione
68. The symptoms of “jet lag” experienced following a few hours of eastward travel is caused by a(n):
a. excessive secretion of melatonin.
b. under-secretion of melatonin.
c. exposure to sunlight at the end of one’s melatonin secretion phase.
d. disruption of one’s activity routine.
69. The principal hormones of the adrenal medulla are _______ and _______, which are secreted in response to signals from the _______.
a. cortisol; hydrocortisone; pituitary
b. epinephrine; norepinephrine; parasympathetic nervous system
c. epinephrine; norepinephrine; sympathetic nervous system
d. cortisol; hydrocortisone; sympathetic nervous system
70. Cortisol is classified as a _______; it is secreted by the _______ in response to ______ from the _______.
a. glucocorticoid; adrenal cortex; ACTH; anterior pituitary
b. mineralocorticoid; adrenal medulla; TSH; posterior pituitary
c. glucocorticoid; adrenal cortex; TSH; anterior pituitary
d. glucocorticoid; adrenal cortex; ACTH; posterior pituitary
71. Without gonadal hormone negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, which of the following would be disrupted?
a. Regulation of GnRH release
b. Follicle development and spermatogenesis
c. Postpartum maternal milk production
d. All of the above
72. A male ringdove that is castrated in adulthood would have trouble with:
a. neural‒neural transmission when first seeing a female.
b. endocrine‒endocrine transmission involving the anterior pituitary.
c. endocrine‒neural transmission for initiating courtship behavior.
d. making sperm, although courtship behavior would be normal.
73. Which of the following lists is arranged from most inclusive to most specific?
a. Phylum, class, family, genus
b. Family, phylum, class, genus
c. Phylum, family, order, genus
d. Class, order, genus, family
74. A population subject to natural selection exhibits a decrease in variation in hair color. What kind of selection did the population experience?
a. Constructive selection
b. Directional selection
c. Disruptive selection
d. Stabilizing selection
75. Why is it believed that the storage of food for later use is an example of convergent evolution across species of birds?
a. The hippocampus is enlarged in food-storing birds.
b. Families of birds that store food are no more closely related to other food-storing families than they are to families of birds that do not store food.
c. Some species that store food do not have enlarged hippocampi.
d. Spatial memory is not important to species that do not store food.
76. In a series of mammalian brains arranged by encephalization factor from small to large, the region that increases most is the:
a. hippocampus.
b. medulla.
c. neocortex.
d. cerebellum.
77. Which class displays the most similarity to the ancestral vertebrates?
a. Amphibians
b. Birds
c. Lampreys
d. Reptiles
78. Refer to the figure.

Which statement regarding comparisons among brains can be concluded from the figure?
a. Ancestral vertebrates did not have cerebral hemispheres.
b. The evolution of larger brains in sharks is linked to the development of larger brains in mammals.
c. Both birds and teleost fishes have relatively small olfactory bulbs because they evolved from a common ancestor.
d. The relatively large cerebellum of birds and mammals evolved independently.
79. Refer to the figure.

Which location on the graph is most likely to represent orangutans?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
80. Refer to the table.

Based on the data in the table, which species has the greatest encephalization factor?
a. Rhesus monkey
b. Baboon
c. Chimpanzee
d. Gorilla
81. Which statement has been proposed as the reason the human brain, in terms of its size, has likely reached a plateau?
a. If the brain were larger, an adult head would be too heavy for the body to carry.
b. The size of a baby’s head already puts significant strain on the mother in terms of the difficulties of childbirth.
c. Evolutionary pressures on humans have been removed because humans have already attained control over the environment.
d. None of the above
82. Which of the following supports the idea that sexual selection for creativity may be connected to selection for larger brain size?
a. Bowerbird species that build the most elaborately decorated bowers have the largest brains.
b. Women choose men with large muscles over men who paint beautiful art.
c. Elephants have preferences for the color of paint they use when paints are provided.
d. Creativity in men is independent of brain size.
83. Which scenario would not contribute to the ongoing process of natural selection in humans?
a. Women choosing mates who earn large salaries
b. A person inheriting malaria-fighting sickle-celled red blood cells
c. The development of new drugs to treat cancer
d. A mutated virus that selectively kills people with blue eyes
84. Trauma that affects the central nervous system of a human embryo between 22 and 24 days after fertilization would not affect:
a. neural crest formation.
b. brain formation.
c. neurogenesis in the forebrain.
d. Both b and c
85. Based on what you know about phenylketonuria, which meal would be contraindicated for an 18-month-old child who has PKU?
a. Low-protein rice, carrots, and cantaloupe
b. Pepper, special formula, and apple
c. Tomato, grilled cheese sandwich on low-protein bread, and special formula
d. Spinach, special formula, and banana
86. Lead poisoning in an infant, which destroys newly forming myelin, would mostly affect the
a. forebrain.
b. cranial nerves.
c. hindbrain.
d. spinal cord.
87. A person over 55 years of age shows problems with delayed memory, and MRI images show a decrease in normal volume of the hippocampal formation. PET scans show no decrease in cerebral metabolism. This person most likely has:
a. senile dementia.
b. Alzheimer’s disease.
c. age-related memory loss.
d. Parkinson’s disease.
88. A vertebrate born with damage to the rhombencephalon is also likely to have damage to the:
a. metencephalon.
b. mesencephalon.
c. telencephalon.
d. diencephalon.
89. Which statement regarding gene expression is true?
a. Gene expression in vertebrates is a predetermined result of mitotic lineages.
b. Environmental factors, including experience, affect gene expression and thus cell differentiation.
c. In vertebrates, gene expression in neural cells is independent of signals from the external environment.
d. Gene expression and cell differentiation in C. elegans is regulated by cell-cell interactions.
90. Which of the following plays little role in the development of the nervous system of C. elegans, given that cell fate is closely regulated by the mitotic lineage in this species?
a. Cell–cell interaction
b. Induction
c. Regulation
d. All of the above
91. Which process occurs to only a limited extent after birth?
a. Synaptogenesis
b. Glial cell formation
c. Neurogenesis
d. Myelination
2023-06-03