INFO90002 Database Systems and Information Modelling Practice Exam 1 Semester 1 2022
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
INFO90002
Database Systems and Information Modelling
Practice Exam 1
Semester 1 2022
Q1. ER Modelling (20 marks)
Q1. Criterion Classics is an on-demand streaming service that streams old television shows (e.g. ‘Skippy’) and movies (‘Lawrence of Arabia’), including black-and-white movies (‘Casablanca’) and television shows ("I dream of Lucy"). Currently the company offers 3 subscriptions plans. Each plan has a code (B, S or P), name (Basic, Standard, Premium) and monthly price. Each Criterion Classics account can have multiple profiles associated with it – for example, a family account could have one profile for the parents and one profile for each child. Profiles of type ‘Child’ can only view titles classified as ‘U’ (Universal) and ‘G’ (General).
Each profile is stored with an avatar or digital image. About each account we store a name ('Mary Lawson'), the number of concurrent screens allowed, the day of the month (18th ) the account is charged and the subscription plan. Each movie is an individual title. TV shows can have one or more seasons and up to 24 episodes in a season. Each title of a TV show (e.g. “Breaking Bad”) will also have episodes title (e.g. “Ozymandias”) as well as season number (5) and episode number (14) as well as its running time 47:35 (minutes and seconds) and classification ('MA').
Criterion Classics stores the length of each title/episode in minutes and seconds, as well as the elapsed time a particular profile stopped watching the title/episode. This is so users can 'continue watching' where they left off if they have to stop watching for any reason. If a user watches the title to the end, the abandon time is equal to the title/episode length time.
By collecting and storing this information, Criterion Classics can make recommendations to other users based on profile data analysis. Criterion Classics makes recommendations about rating appropriate titles to all profiles. Criterion needs to store the name of the title, the date it was suggested to a profile and the number of times (total count) a particular title has been recommended to a user. Using this information and the viewing information of a profile it can determine if its suggested viewing algorithm is working.
Q1. You are asked to model a physical Model of the Criterion Classics case study in Crows Foot notation. State any assumptions you have made.
Q2. SQL (20 marks)
This case study is for the SQL model to help contextualise the Physical ER model
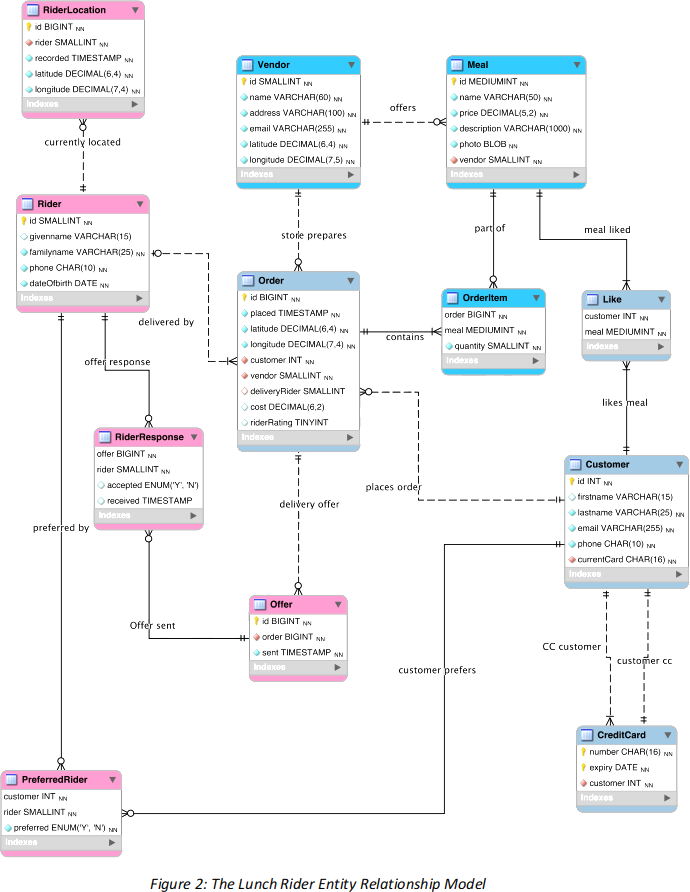
Lunch Rider
LunchRider is a new startup in the food delivery business. LunchRider allows people to order lunches from local food vendors and have them delivered by a delivery rider on a bike. When a customer opens the LunchRider app, it first presents a list of local vendors such as cafes, restaurants and snack bars. The customer clicks on a vendor. Then the app shows the meals available from that vendor.
The customer chooses which meals they want from that vendor: for example “2 chili burgers meals" and "1 mango smoothie” . The phone sends this order to the LunchRider server, along with the customer's phone GPS coordinates - the meals will be delivered to this location. Customers can click to “like” a meal and the total number of likes (across all customers) is displayed beside each meal. When a customer’s order is received, LunchRider broadcasts a work offer to riders who are near the customer. Riders see the offer pop up on their app and can press “accept” or “no thanks” .
The chosen rider goes to the vendor, picks up the meals, and delivers them to the customer’s location. We record at what time the rider delivers the order. Payment is automatically deducted from the customer’s credit card and bank transactions are handled by the bank. LunchRiders provide their name, mobile phone number, and date of birth. Whenever a rider is on duty, the rider’s app sends the GPS coordinates about once per minute, allowing us to keep track of each rider’s location.
If someone wants to order a meal, they need to first register as a customer, giving their name, email address, mobile phone number and current credit card. Over time a customer may register more than one credit card. Vendors must register the name and address of their business, including GPS coordinates and a contact email address, and provide the name, price, description (max 1,000 characters) and photo of each meal that they want to sell.
After delivery, the app allows the customer to rate the rider’s service, choosing from 1 star (worst), 2, 3, 4 or 5 stars (best). The app also allows the customer to add the rider to their “favourite” list. LunchRider uses this information to help choose riders for future work offers.
All locations are recorded as a pair of numbers representing latitude and longitude. Latitudes are between -90 and 90 degrees (south pole to north pole) while longitudes are between -180 and 180 degrees (west or east of the prime meridian). LunchRider uses a precision of 4 decimal places, which is about 11 metres at the equator (smaller in Melbourne). For example, the Doug McDonell building at The University of Melbourne is at latitude -37.7989, longitude 144.9627.
Questions 2A-2G require you to write one single SQL statement per question. Do not use views, temporary tables or inline views. Format code for ease of reading. Ensure user-friendly output by renaming columns where appropriate. Values of column fields are in italics e.g. Tom Hardy.
For Example:
Q. List the name and salary of Jane Grey
SELECT firstname, lastname, salary
FROM employee
WHERE firstname = 'Jane' and lastname = 'Grey';
Q2A. Write the SQL for the following query:
List all Vendor names who offer a meal where the price is more than $60.00 and below $80.00. (1 marks)
Q2B. List the names of riders born in 1997 have accepted an offer in August 2020? (3 marks)
Q2C. How many customers have ordered and liked the 'Betty Deluxe Burger Meal' meal ordered from the Melbourne store with coordinates latitude -37.8156 and longitude 144.9636 ? (4 marks)
Q2D. List the names of riders who are also customers of the Lunch Rider app (assume the rider uses the same phone number as they would as a customer). (4 marks)
Q2E. List the vendor names who have at least one ordered meal never liked by any customer. (3 marks)
Q2F. List the vendor names who have never had any ordered meal liked by a customer. (3 marks)
Q2G.Name the riders who have received a rating of 4 or above from more than 500 different customers. (5 marks)
Note marks are just indication of difficulty, e.g. 1 mark question is considered easy .
Q3. Normalisation (20 marks)
The table below is part of the medical records for a Veterinarian Clinic
PRACTICE (Animal_ID, Animal, Animal type, OWNER_ID, Owner, Phone, Consult, PROC_ID, PROC_DESC)
|
Animal ID |
Animal |
Animal Type |
Owner_ID |
Owner |
Phone |
Consult |
ProcID |
Description |
|
317 |
Ralph |
Dog |
10 |
Julie Sumner |
0409 673-888 |
13-Oct-13 |
101 |
Annual Checkup |
|
317 |
Ralph |
Dog |
10 |
Julie Sumner |
0409 673-888 |
27-Apr-13 |
115 |
Teeth Clean |
|
317 |
Ralph |
Dog |
10 |
Julie Sumner |
0409 673-888 |
14-Oct-14 |
119 |
3 month Checkup |
|
398 |
Zeno |
Canary |
23 |
Tony Rijks |
0408 322-444 |
21-Jul-14 |
105 |
Parasite treatment |
|
398 |
Zeno |
Canary |
23 |
Tony Rijks |
0408 322-444 |
14-Oct-13 |
119 |
3 month Checkup |
|
441 |
Panda |
Short haired cat |
47 |
Helene Hanff |
0419 121-212 |
24-Apr-14 |
715 |
Initial Consultation |
|
441 |
Panda |
Short haired cat |
47 |
Helene Hanff |
0419 121-212 |
27-Apr-13 |
115 |
Teeth Clean |
|
518 |
Zeno |
Canary |
23 |
Tony Rijks |
0408 322-444 |
1-Mar- 15 |
001 |
6 month Checkup |
The combination of ANIMAL_ID and PROC_ID is the candidate key for the relation. The following functional dependencies hold:
• Animal_ID → ANIMAL, ANIMAL Type, OWNER_ID
• OWNER_ID → OWNER, PHONE
• PROCID → DESCRIPTION
• ANIMAL_ID, PROC_ID → Consult
Q3. Please normalise the data to third normal form (3NF). At each stage give an example of an anomaly. Show each stage of normalisation (i.e. 1NF, 2NF, 3NF).
Key: BOLD primary key ITALIC foreign key BOLD + ITALIC primary foreign key
Q4. NoSQL (4 marks)
Q4. There are trade-offs between the principles of ACID and BASE. Discuss the trade-off between availability and consistency for relational and NoSQL databases. Illustrate your answer using either the example of Facebook or the example of Twitter. (4 marks)
Q5. Applications (4 marks)
Q5. There are problems with giving end users an SQL interface to access a database. Describe two (2) distinct problems, and for each, how providing application software to users solves the problem. (2+2=4 marks)
Q6. Distributed Databases (4 marks)
Q6. Describe how synchronous updates work and the advantages and disadvantages of this approach. (4 marks)
Q7. Data Warehouses (14 Marks)
Sennheiser Australia wants to track information about the selling of audio equipment (microphones, headphones, turntables) via physical retail stores located throughout Australia. You need to design a data warehouse to report information about sales of audio equipment over time. You need to store the retail store (store ID, Manager’s first name, Manager’s last name, phone number, address, state), and product (product-id, name, description, category, retail price, wholesale price). The sales managers want to find the number of items sold (e.g. turntables), the revenue and profit. The information needs to be accessible by the retail store, its state, product name (e.g. “Sen-300-II”) and for different times (week, month, quarter, half year and year).
Q7A. Draw a star schema to support the design of this data warehouse, showing the attributes in each table. Be sure to denote PK, FK and PFK. (8 marks)
Q7B. Briefly explain what OLTP and OLAP databases are and demonstrate the difference between these two types of databases. (6 marks)
Q8. Security and Backups (4 marks)
Q8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a logical backup when compared with a physical backup of a database? (4 marks)
2023-06-02