MCD4160: Physics for Engineering Test 2- Oscillations & Waves Practice Test 1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MCD4160: Physics for Engineering
Test 2- Oscillations & Waves
Practice Test 1
QUESTION 1 (2 + 3 = 5 marks)
A block with mass M1 = 5.00 kg is sliding to the right with a speed of 15.0 ms- 1 when it hits and sticks to a block of mass M2 = 3.00 kg, attached to a spring of spring constant k = 3000 Nm- 1 . The second block was at the equilibrium position and the spring uncompressed at the time of the collision. The horizontal surface
is frictionless.

(a) Determine the angular frequency of vibration for the system.
(b) Calculate the maximum compression of the spring.
QUESTION 2 (2 + 3 = 5 marks)
A block with mass m kilogram is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 0.9 Nm- 1 . A damping force which is proportional to velocity (Fd = -b v ) is also acting on the block and the equation of motion of the system is given by:

where

(a) Find the mass m of the block. Give an appropriate reason to support your answer.
(b) Determine the damping constant b.
QUESTION 3 (2 + 2 + 2 = 6 marks)
A string of length 3 m and total mass of 12 g is under a tension of 160 N. A transverse harmonic wave with wavelength λ = 25.0 cm and amplitude A = 2.0 cm travels to the right along the string. It is observed that the displacement at x = 0 and t = 0 is 0.87 cm.
(a) Determine the speed of the wave.
(b) Calculate the angular frequency ω of the wave.
(c) Calculate the phase constant φ0 of the wave.
QUESTION 4 (2 + 2 = 4 marks)
A moving source of sound at frequency f0 is moving toward you at half the speed of sound v. You and the air are stationary.
(a) What is the frequency you hear? Express your answer in terms off0 .
You are now moving toward a stationary source of sound at frequencyf0 at half the speed of sound.
(b) What is the frequency you hear? Express your answer in terms off0 .
QUESTION 5 (1 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 6 marks)
A composite cord (shown below) has uniform linear mass density of 16 gm- 1 (gram per metre) in section A and 4 gm- 1 in section B. One end of the cord is tied to a wall, the other to a vibrating source, which vibrates with a frequency of 100 Hz. Both sections are under the same tension.

(a) Find the ratio of the frequency of the waves travelling in sections B and A, i.e., fB / fA .
The vibrating source delivers an incident pulse as shown below.
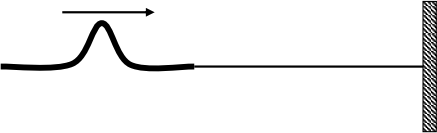
(b) In the space provided below draw the pulse(s) shortly after the tail of the initial pulse reaches the
boundary between sections A and B. Indicate the direction of propagation of the pulse(s).
(c) Sound waves may be described in terms of displacement. Another quantity is also used, instead of displacement, to describe the wave properties of sound. What is this alternative quantity?
(d) A sound wave can transmit acoustic power. If the frequency of a sound wave is doubled (with all other parameters kept constant) how will the transmitted power change?
QUESTION 6 (2 + 2 = 4 marks)
Light of wavelength λ travels left to right through two narrow slits and is incident on a screen as shown below.

(a) The slits are initially very narrow. Sketch, a graph of intensity versus position on the screen. Use
the axes provided on the right above (in the diagram above).
(b) The slits are now each made wider (e.g., about one-quarter of the separation between the slits).
Sketch the new intensity distribution to show the new feature, which results from the slits being wider. No calculation is required.

QUESTION 7 (2 + 2 = 4 marks)
Unpolarised light with intensity 400 W/m2 passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical, then through a second polarizing filter, which has its axis at an angle of θ = 30º with respect to the vertical.
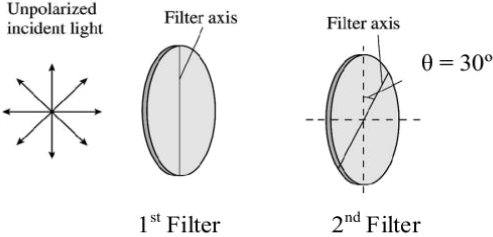
(a) On the diagram above draw the orientation of the polarized light emerging from the 1st and 2nd
filters. Use a double-headed arrow to indicate the polarization orientation.
(b) Determine the intensity of light emerging from the 2nd filter?
2023-05-25